Among various health problems, scabies in cats occupies a special place. The complex of dermatological pathologies is characterized by increased contagiousness. The causative agents of the disease are parasitic insects. They not only cause cats anxiety and itchy skin, but also threaten more serious consequences, including sepsis and death. A pet owner should know how to recognize pathology, treatment options and prevention methods that can protect both the cat and themselves.
Do cats and kittens get mange?
Not every cat is infected and suffers from scabies. There are direct and indirect reasons for this. Pathology develops faster in unsanitary conditions, with reduced immunity of animals. It is characterized by skin inflammation, itching, and baldness in the affected area. The pathogen cannot be seen with the naked eye, but a veterinarian can make an accurate diagnosis after a visual examination and tests (skin scrapings) taken from a cat. During the study, the type of scabies mite is determined. If the pathology is not diagnosed in time and treatment is not started, the process of skin damage becomes so severe that necrosis occurs, abscesses and ulcers appear.
The disease is easily transmitted from a cat to other animals and humans and can occur in three forms:
- scaly;
- generalized;
- juvenile
The scaly form is the lightest. Occurs in cats and kittens under two years of age. The skin is itchy, there are patches of lesions on it, but no more than five. There are scales on the ears, neck and eyelids. There are no signs on the back or paws.
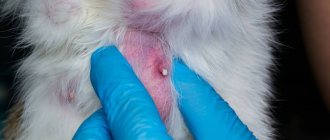
With the generalized form of scabies in cats, there is a massive subcutaneous lesion with the formation of pustules, bleeding wounds, erythema, scratching and scabs. At the location of the scabies mite, you can see a raised area with a crater, from which, when pressed, a white mass is released. This form develops quickly, affecting the cat's head, neck, muzzle, nose, eyelids and tips of the ears.
The juvenile form differs from the generalized form only in that the disease is hereditary and is transmitted to the kitten in the womb.
Causes
Scabies is caused by itch mites - Demodex, Sarcoptes, Notoedrus and Otodectes. The disease is promoted by unsatisfactory housing and feeding conditions, as well as infectious or invasive pathologies that weaken the immune system. Sarcoptes poses a danger to humans, so further we will talk about it.
Sarcoptes under a microscope
Routes of infection
The causative agent of scabies in cats is the scabies mite. Parasites feed on blood and lymph, living on the surface of the skin. In its upper layers, tiny insects dig tunnels, and their females lay eggs. Cats with scabies feel unbearable itching.
The main route of tick transmission is contact. Infection occurs not only from another cat, but also from dogs and birds. Insects especially often settle on the body of pigeons. If an adult kitty is sick, her offspring will most likely become infected from the mother during the feeding period.
When several cats live in a house, they can become infected without even going outside. To do this, it is enough for the owners to bring a scabies mite on their clothes or shoes, and for the kisul to walk along the rug in the hallway or rub against the owner’s feet. A tick can live in the environment for a whole week and remain dangerous to animals and humans.
Infection often occurs through care and maintenance items - leashes, beds, toys. For this reason, if scabies is detected in one cat or male cat living in the house, all of them must be treated at the same time.
It should be noted that due to their strong immunity, street cats rarely suffer from scabies, but they are carriers of parasites. For this reason, it is worth limiting contact between domestic kisuls and homeless people.
How is scabies transmitted to humans?
For infection from a sick animal, ordinary contact is sufficient. For example, a child who pets a stray animal on the street becomes a carrier of scabies mites. Infection can also occur if a free-ranging pet brings parasites home. However, not all types of cat scabies are dangerous to humans, among them:
- Hair mites are able to survive exclusively in animal fur; human skin is not suitable for their life and reproduction.
- Parasites that can live on the human body for no more than two days - in this way, insects only move long distances and, not finding a more suitable host, die.
- Small mites that appear during the period when the cat’s immune system is weakened are relatively harmless to a healthy person.
In medical circles, there is a special term that characterizes infection from a cat to a person - “pseudo scabies.” The fact is that ticks that carry invasive diseases can only comfortably exist on a cat’s body. Parasites can only stay on human skin for a short time, causing discomfort. Despite their apparent harmlessness, scabies mites can cause a lot of trouble, for example:
- feeling of discomfort;
- dryness and severe peeling of the skin;
- pimples and ulcers;
- cortical formations.
Pseudo scabies is not transmitted between people and goes away on its own, without medical intervention. If the above symptoms cause severe concern, you should consult a dermatologist.
Risk factors
The stronger the cat’s immunity, the greater the likelihood that he will cope with the parasite on his own, because not all animals that come into contact with scabies mites get sick. There are several factors that can increase your risk of infection. These include:
- damage to the skin (wounds, scratches, ulcers);
- close contact with sick cats, cats and other animals;
- weakened immunity due to recent surgery, treatment with antibiotics or hormonal drugs;
- the presence of helminths or external parasites (fleas, ticks, lice);
- unbalanced, insufficient calorie diet;
- age younger than two years or older than eight.
It should be noted that British and Siamese cats and male cats are slightly more likely to develop mange than other breeds. This is explained by the individual characteristics of their body.
Forms of scabies in cats
Depending on what type of mite a kitten or an adult cat is infected with, scabies has different names: demodicosis, otodecosis, sarcoptic mange, notoedrosis.
The causative agent of demodicosis can be two types of mites - Demodex cati and Demodex gatoi. The first can be found in most cats. It gets onto the skin of kittens in the first days of life from the mother. Clinical signs appear when parasites multiply strongly. And this happens only with a sharp drop in immunity or after using drugs that suppress it.
The second type of Demodex gatoi cannot be found on the skin of healthy cats or cats. With this type of scabies, the clinical manifestations are striking. If the disease occurs in a localized (scaly) form, the affected areas are small and difficult to notice. The generalized form of feline mange is aggressive, spreads over most of the body, and combines the presence of scales, ulcers, ulcers and severe itching.
Otodecosis is an infection of the skin of the external auditory canal of the pussy by the mite Otodectes cynotis. It occurs frequently and is transmitted between pets very quickly. The size of the insect is up to 0.5 mm. During bites, it injures and irritates the skin, causing burning and itching.
Sarcoptic mange is a type of scabies caused by Sarcoptes scabiei. Parasites most often settle on the cat’s face, and then spread throughout the body. A distinctive feature of sarcoptic mange is red spots with gray lines and nodules at the end. The symptoms of this type resemble kitty allergy, but it is dangerous for the development of sepsis.
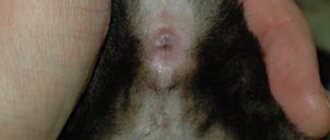
Notoedrosis, or pruritic scabies, is caused by the scabies mite Notoedres. The parasite has a round shape and gray color. Affects the outer side of the pussy ear. A gray, unpleasant-smelling liquid accumulates there. Because of this, the fur sticks together, later falls out and the cat's head goes bald. Gradually, scales accumulate on exposed areas and scabs form.
Types of ticks
The following types of ticks can parasitize an animal’s body:
- Ear. Parasites cause the disease otodectosis.
- Scabies pliers. Rarely found insects. They are carriers of sarcoptic mange.
- Cheyletiella mites. Another rare variety. An animal attacked by these parasites becomes infected with chylitis.
- Demodex cati mites provoke the development of demodicosis.
- Notoedres cati mites cause a disease called notoedrosis.
Diagnosis of the disease
The speed of recovery depends on how quickly the diagnosis is made and how soon treatment is started. To do this, you need to go to a veterinary clinic, where they will conduct an external examination of the cat or cat, and take a skin scraping for microscopic analysis. To confirm the diagnosis, it is repeated several times. Based on the results of the study, we can draw a conclusion about the cause of the problem. A laboratory test is mandatory, since scabies mites can easily be confused with an allergic reaction, dermatitis, eczema and lichen.
The duration and intensity of treatment depends on the severity of the disease, the degree of damage and the condition of the cat at the time of examination. On average, therapy lasts from one to four weeks.
Symptoms of scabies in cats and cats
After the scabies mite gets on the skin of a cat, it begins to gnaw through the epidermis and make moves at a speed of up to 3 mm per day. Females succeed in this especially quickly, since they need to lay eggs. The larvae into which the eggs turn also begin to make passages in the skin and move closer to its surface. Having turned into adults, scabies mites begin to mate and the process repeats. All movements of parasites in the thickness of the skin are accompanied by irritation and itching. The cat itches around the clock, is in a stressful state, and cannot eat or drink. From the moment insects hit the animal’s skin until symptoms appear, it takes from several days to a month. It all depends on the degree of damage and the immune response of the cat’s body.
The main signs of scabies include:
- skin redness;
- bald spots on the neck, paws, muzzle, body;
- baldness of the ears;
- severe itching, scratching on the body;
- small and large scratches that may fester or bleed;
- the fur becomes matted, dull, dirty;
- the cat and cat have apathy;
- loss of appetite;
- poor sleep;
- disruption of the functioning of internal organs and systems.
As the disease progresses, additional symptoms may appear:
- A cat is looking for a cool place to relieve itching and cool inflamed skin.
- The animal meows pitifully, does not respond to its name, and does not play.
When the first signs of scabies appear in a cat and his restless behavior, you should seek help from a veterinary clinic.
Symptoms
Scabies in cats is manifested by severe itching, as a result of which the animal becomes restless.
The disease initially affects the head area, including around the ears and neck. Penetrating into the deep layers of the skin, the mite digs passages there in which females lay eggs. All this causes severe irritation and itching in the cat.
The animal shakes its head, constantly itches, scratches and scratches appear, and then the hair on the affected areas falls out and dark crusts (scabs) can be clearly seen.
Typically, hair loss begins at the edges of the ears and gradually moves to the forehead and neck. In advanced cases, the lesion spreads throughout the animal's body.
Treatment of cat mange
Depending on the severity of scabies, the intensity and duration of scabies treatment differ. Two methods are used - with the help of medications and folk remedies. At home, treatment can be carried out in different ways or a combination of them. The combined method and integrated approach are especially in demand in cases of extensive damage and severe forms of the disease. In any case, it is necessary to contact a veterinary clinic, establish a diagnosis and begin therapy in accordance with the doctor’s prescriptions. He can prescribe ointments and lotions based on sulfur, tar, and intramuscular injections of antibiotics. The course lasts from one to three weeks. Self-medication without consulting a specialist is unacceptable. It is possible to cure a kitten of scabies at home with the same drugs that are prescribed to an adult cat, but an overdose can be extremely dangerous for their life. The doctor often prescribes additional supportive therapy in the form of shampoos, vitamins and immunostimulants to strengthen the body's protective function. After eliminating the most acute and dangerous symptoms, the use of special drops against fleas and ticks and collars is recommended.
Pharmacy drugs
In the complex treatment of scabies, medications are used in different forms - drops, solutions, ointments, injections, shampoos. For mild lesions, external agents are used. The most popular and inexpensive drug that is most often used to treat scabies in cats is simple sulfur ointment. The active ingredient in it is sulfur, which destroys adult ticks and their larvae, but does not have a negative effect on the eggs. For this reason, the course of treatment with sulfur ointment is long - until all individuals hatch from the eggs and die.
Advocate - drops against scabies for adult cats and male cats weighing from 4 kg to 8 kg. This is a comprehensive remedy that can get rid of ticks, fleas and other parasites. It is applied to the neck of a cat or cat, where they cannot lick it off. Apply once a month.
Sanoderm is an inexpensive cream with a complex effect (against mites, fungal infections, bacteria). Apply once a day with a break of two days.
Dana-Spot-On is a liquid preparation for applying to the withers of cats and female dogs. The course consists of five treatments once a week.
Amidel is an anti-scabies gel that destroys parasites at any phase of their development. It is rubbed into the affected areas, including healthy skin. The product is used 2 to 5 times with a break of a week. For more severe forms of scabies, effective injections are used:
- Ivermek is a broad-spectrum drug that is absorbed by the body and does not cause side effects, suitable for kittens, adult cats and cats.
- Novomek is an injection solution that helps destroy parasites, the dosage for a specific cat is calculated by the doctor.
- Baymek - suitable for the treatment and prevention of scabies, it is administered subcutaneously under the supervision of a veterinarian.
When using medications, it is necessary to monitor the progress of treatment by obtaining intermediate test results.
Folk remedies
Folk remedies for scabies for cats are used at the initial stage of the disease or as a supplement to medications prescribed by a doctor. In other cases, alternative medicine methods do not give the desired result or lead to a deterioration in the cat’s condition.
Essential oils with extracts of tea tree, almond and lavender are used as medicines to treat scabies in cats. They can reduce inflammation, relieve itching and have an antiseptic effect. A few drops of the extract are rubbed into the skin of the pussy every day for two to three weeks. You can enhance the effect of essential oil with the help of vitamin E in liquid form.
One of the oldest remedies for scabies in cats and cats is tar soap, which contains sulfur. The affected areas are rubbed with a damp soap bar once every two days. It is permissible to bathe the kisul with soap before starting drug treatment. Sulfur and tar have a suppressive effect on parasites and are safe for your pet.
White vinegar essence is used to kill insects. It is diluted with water in a ratio of 1:2, the cat’s fur is sprayed or wiped twice a day for a week.
You can make an anti-scabies ointment using home remedies. The bay leaf is ground into powder with a blender and mixed with butter or lard. The resulting drug is used to treat the affected areas three times a day for 15-17 days.
To prevent a cat from licking off medicinal products, they are wearing a blanket or a medical collar.
How is sarcoptic mange treated?
This type of disease requires treatment of the cat's entire body, so treatment at home is a labor-intensive but necessary process. As in other cases, it is necessary to remove hair so that ointments and solutions are more effectively distributed over the skin. Next, the cat is washed with tar soap or shampoo (Nizoral, TM Doctor).
For injections, acaricidal agents Ivermectin, Doramectin, Aversect are prescribed. For the treatment of sarcoptic mange, Sayfli tablets and local ointments Aversectin, Novertin, and Sulfur are intended. Preparations in solutions are also suitable for external use: Stomazan, Amit Forte, Amitrazine Plus. A choice of drops of coffee is dropped onto the withers of a sick cat: Lawyer, Stronghold, Fighter, Frontline.
Most anti-scab drugs are strong poisons that place increased stress on the liver. To support it, the cat needs hepatoprotectors.
How long does it take to treat scabies in kittens and adult cats?
Scabies can only be treated comprehensively. Depending on the severity, the doctor may prescribe, in addition to special ointments and lotions, intramuscular administration of antibiotics and antiparasitic agents. The course of treatment lasts from one to three weeks.
Most often, sulfur ointment or amitrazine is used for external use, and injections for scabies are given subcutaneously with Ivermec. The medicine destroys adult ticks and tick larvae; it is recommended for both kittens and adult cats. The injection is given intramuscularly, in the back thigh. Insulin syringes are used for injections against scabies in cats. Experts recommend the minimum dosage of the drug – 0.2 ml per 10 kg of animal weight. If the pathology is mild, one injection is enough. For more severe damage, the injection is repeated after 10 days. Ivermek is also available in the form of a spray, which is safe and convenient to use:
- Damaged areas are cleaned of scales and crusts.
- Spray Ivermec onto the fur, covering diseased and healthy skin.
- Place a collar on the cat to prevent licking of the product.
As analogues, you can use the drugs Ivomec, Ivermin, Ivervexan, Ivermikol. Using them significantly reduces treatment time, but you need to remember the possible side effects:
- nausea;
- tearfulness;
- vomiting;
- increased salivation;
- muscle tremors.
Consequences of scabies in cats
Areas of skin affected by scabies mites are unbearably itchy. The cat itself scratches them with its claws until wounds and scratches form. Places where the integrity of the skin is damaged serve as a gateway for infections of a viral, bacterial and fungal nature. After pathogenic microorganisms enter open wounds, inflammation develops, and subsequently suppuration. In the absence of adequate treatment against the background of a secondary infection, sepsis and death of the cat are possible.
If scabies is left untreated, mites multiply rapidly. The lifespan of one individual is 30 days, during which time the female manages to lay about 100 eggs. Ticks lead an active lifestyle in the thickness of the skin, secrete toxins and gradually poison the kitty’s body. Toxic substances entering the blood cause disruptions in the functioning of the cardiovascular, bronchopulmonary and nervous systems. Under the influence of toxins, metabolic disorders and oxygen starvation occur at the cellular level.
The dangers of ignoring the disease
Without treatment, your cat will not get rid of mange. The disease can only be aggravated by the addition of a bacterial infection. Microorganisms enter through skin damaged by scratching, causing pustules and large wounds.
A mite that has settled in the ear can cause inflammation of the eardrum, middle and inner ear. As a result, the cat faces deafness, and in the most severe cases, death.
Disease prevention
Preventing scabies is easier than dealing with it and its consequences. The following actions are taken as preventive measures:
- regularly treat the fur of cats and cats against ticks, fleas and other parasites (once every six months);
- clean toys, wash bedding and bed covers;
- bathe the cat after a walk or wipe it with a damp cloth;
- before being released outside, put on an insecticidal collar;
- Periodically bring the cat to the veterinarian for examination.
If an animal becomes infected, it is isolated from other pets and family members. Household items that the sick cat has come into contact with are burned or frozen, and all surfaces are disinfected.
Preventive measures
To prevent infection with skin mites, it is necessary to remember and apply the rules of prevention. Firstly, if possible, it is advisable to protect your pet from contact with street animals. They often suffer from this contagious disease. Secondly, during routine insecticidal treatment it is periodically necessary to use selamectin-based products. It is enough to use such drugs once every six months. Thirdly, for hygiene procedures it is useful to use shampoos with insecticidal additives (for example, with tar).
At home, it is important to regularly carry out wet cleaning. A balanced cat diet also provides additional support. When you have enough minerals and vitamins in your diet, it is easier to keep your immune system healthy. It is also important to protect your pet from stress and hypothermia. A healthy, well-groomed cat is much less likely to be affected by subcutaneous mites and does not even pose a temporary threat to humans.
global $ads_google; //data-ad-slot=”2475549904″ $ads_google = empty($ads_google) ? false : true; ?> if ($ads_google == false) {?> $ads_google = true; ?> } ?>