Etiology
The causative agent of the pathology is a fungus of the genus Achorion, which has selectivity. In birds, symptoms are caused by A. gallinae, in rats and mice by A. quinckeanum, but cats, dogs, horses, and sheep can become infected. Favus in humans is caused by A. Schonleini, and it can sometimes cause pathology in primates, dogs, cats, calves, and mice.
The mycelium of the microorganism is thin. The cells are double-circuit, rectangular. The spores are round or multifaceted and are arranged in chains or groups. The optimal temperature for growth is 28-30 ᵒC. The fungus prefers wort agar and Sabouraud. Growth appears as white, smooth colonies. As it ages, the growth becomes wrinkled, mealy and changes color to all shades of pink, with a purple underside.
The bioassay is successful on white mice, guinea pigs, and rabbits.
Most often, the pathogen is recorded in young chickens, less often in turkeys, ducks and wild birds. The source of the disease is sick animals. Infection occurs through contact, through damage to the skin, through airborne droplets, through care items infected with the secretions of a sick bird. Carriers of fungal spores can be ticks, mice and rats. Soil is a natural reservoir of the favus pathogen.
The disease can be widespread or sporadic. When the disease occurs, the lesions become stationary.
The fungus begins its development in the peri-root zone of the feather and hair, forming a mycelial shield. The site of settling becomes inflamed, feathers become deformed, fall out, epidermal layers, sweat and sebaceous glands atrophy. If the fungus penetrates the blood, it can grow in parenchymal organs, where it forms favus nodules.
Animals that have recovered from the disease acquire lasting immunity.
Medicines prescribed for scabies
Today, veterinary pharmacies have a significant selection of drugs, but using them without a doctor’s recommendation and a preliminary examination of the animal is extremely irrational.
Drops "Bars".
Produced for cats and dogs to combat arachnoenthomosis. Active ingredients: fipronil, diflubenzuron and dicarboximide.
Drops "Bars Forte".
There are different packaging options for kittens and adult cats, puppies and adult dogs. "Bars Forte" for puppies and "Bars Forte" for kittens are convenient to use on animals with low weight.
Spray "Bars".
An insectoacaricide with fipronil is aimed at the larval and adult stages of parasites: fleas, lice, lice, microscopic and free-living mites.
Spray "Bars Forte".
Insectoacaricidal agent for treating animals (cats, dogs) and their habitats. The active ingredient is fipronil. The drug also helps to normalize metabolic processes in the skin and hair follicles of the animal.
Ear drops "Bars".
Used for the treatment and prevention of otodectosis in dogs and cats. The active substance, diazinon, acts against larvae and adults of scabies mites, including Otodectis.
"Dironet spot-on."
Drops on the withers (praziquantel and ivermectin) are prescribed to dogs and cats for arachnoenthomosis and helminthiasis.
"Amit forte"
Due to fipronil and diflubenzuron, the drug effectively affects ticks and is used to treat cats and dogs with tick-borne scabies.
Attention! Do not lick the drug! Before use, consult a specialist! The products are not intended for use in humans!
Symptoms
The incubation period is up to 4 months.
In dogs, cats and rabbits, the base of the claws, head, ears, and abdominal wall are affected. In sheep, the fungus most often localizes to the skin around the lips and nose, as well as the inside of the ears.
Rodents are very sensitive to the fungus. The scalp and body are initially affected, then the deeper layers, muscles and bones are affected, and the mice lose their vision.
The crusts (shields) that “grow” under the action of the fungus are easily removed in the initial stages, revealing underneath the wet surfaces with a depression in the center. Old processes do not allow the scutula to be removed and they continue to grow and occupy larger and larger spaces.
In birds, the incubation period is 3-4 months. The process begins with areas devoid of feathers (head, comb, earrings). These places are covered with white nodules, which, as they increase, merge, become dirty yellow, then gray. Within 2-3 months, the comb becomes completely covered with extensive crusts extending to the feather areas. During the process of generalization, feathers fall out and the skin becomes covered with scales.
With a protracted nature, the mucous membrane of the oral cavity, goiter, and intestines is affected. The bird refuses to eat food and develops diarrhea. Pathology can also affect the upper respiratory tract.
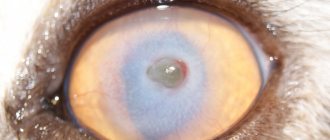
Scab in cats: description of the pathology
Scab or Favus is a fungal disease that affects the skin and coat. Reports that scab-causing fungi can attack internal organs are questionable. However, since Favus develops against the background of a weakened immune system, the development of septic processes under the influence of other microorganisms cannot be ruled out.
Infection occurs by contact or oral-fecal route. The reservoir of infection is rodents and stray cats. The incubation period depends on the condition of the pet at the time of infection. In weakened animals, pathological signs may appear after a few days, in stronger ones - after several months.
Treatment
Build-ups should be softened. To do this, use a soap-creolin emulsion or ointment. The affected areas are lubricated with a solution of formaldehyde 5-6%, potassium permanganate 1-2%, salicylic alcohol 4-5%. Treatments are carried out daily.
Small animals use zoomicol spray.
We will use a preparation prepared on the basis of a tincture of iodine 5% and a solution of salicylic acid 10%, or crystalline salicylic acid is added to the tincture of iodine to prepare a 10% concentration.
In the period between treatments, it is recommended to use ASD-f3. The affected areas are repeatedly lubricated with a swab.
To quickly restore the functionality of the skin and hair growth, it is recommended to take vitamin preparations “Trivit” and “Tetravit”.
Pathogens
The causative agents of scabies in animals can be:
- sarcoptes (Sarcoptes);
- notoedris (Notoedres);
- Cheyletiella;
- demodex (Demodex);
- Otodectes.
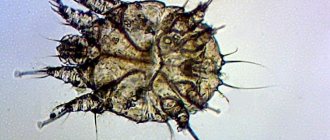
Scabies mites are microscopic arachnids. These are permanent parasites that settle on the skin or inside the skin, including in the deep layers. Dogs are most often affected by Sarcoptis and Demodex, and cats by Notoedris and Cheyletella. Otodectis, the causative agent of ear scabies, is dangerous for both species of animals.
By parasitizing a cat or dog, microscopic arachnids go through all stages of development from egg to adult.
Prevention
Preventive measures are based on the organization of balanced, nutritious feeding and compliance with veterinary and sanitary conditions for keeping animals and birds.
When a disease occurs, the farm is declared unsafe. It is necessary to provide mechanical cleaning of the places of detention and treatment with a solution of creolin, caustic soda, formaldehyde, and a sulfur-carbolic mixture every 10 days. The soil and walking yards are cleaned and irrigated with bleach with at least 5% active chlorine or a 4% formaldehyde solution.
Patients are isolated and subjected to therapeutic procedures. In the generalized form, slaughter is carried out with the disposal of carcasses in a biothermal pit. It is prohibited to regroup, change pastures, or remove animals from the farm territory.
Quarantine measures are lifted 21 days after the appearance of the last clinical case and final disinfection.
When forming a herd, quarantine measures should be carried out with mandatory examination of the skin and only from prosperous farms.
Share:
Skin tumors
Tumors that appear on a cat’s head differ in size, shape and origin:
- Lipoma. A fatty benign tumor can increase in size. There is no metastasis. It occurs in older cats on any part of the body.
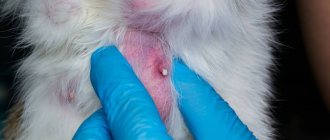
- Abscess. Appears under a cat's fur after an insect bite or an unsuccessful injection. Causes pain and fever.
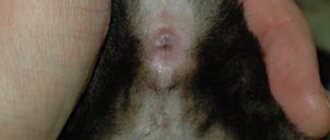
- Mite under the skin. Represented by a small tubercle. Does not cause pain or discomfort to the animal.
Important! Sometimes bumps in cats occur as a result of injury and go away on their own.
How to treat
For proper treatment, specific therapy must be carried out to confirm scabies. If the doctor was unable to identify the mite and scabies, a trial treatment will be prescribed. In addition, preventive treatment is prescribed to all family members and people in contact with the patient.
The doctor will prescribe medications that kill ticks. Most often they are:
- aerosols
- ointments
- creams
- suspensions
- emulsions
The prescribed drugs will be based on the following substances:
- benzyl benzoate
- permitrina
- sulfur
- piperonyl butoxide
- esbiola
Sometimes treatment includes washing with soap or treating the skin with emollient ointments before using the drug.
Only a doctor can prescribe a medicine and treatment method. It is based on the following criteria:
- clinical picture
- complications
- person's age
- pregnancy
Self-medication can cause complications, apathetic forms of infection or a protracted course of the disease.
Diagnostics
To determine the clinical picture, you need to do the following:
- Explain your symptoms to your doctor in detail. For example, itching only bothers you at certain times
- get tested
- examine the patient's body
- determine the source of infection
- find traces of the tick itself or its larvae
Typically, the disease is determined by the following criteria:
- purulent blisters
- dry crust
- redness on the buttocks
- scabies (the most important criterion)
To determine the itch, the lesion can be stained with iodine, oil containing minerals, or simply pressed on the epidermis with a glass slide. This will block blood from reaching the affected area and allow you to clearly see the affected area. It can also be detected using dermatoscopy (during the procedure the tick itself is detected).
Ticks can be detected using lactic acid. One drop (40%) should be applied to any lesion and wait 5 minutes. The loosened skin can then be scraped off with a sharp spoon until capillary bleeding appears. The resulting epidermis must be applied to a glass slide and looked at under a microscope. The method will allow you to identify most parasites and the products of their activity.
Reasons for appearance
The lesions are caused by the parasite Sarcoptes scabiei. Any living creature that has been infected can carry it. And the more lesions on the patient’s body, the higher the risk that he can infect someone.
what does a scabies mite look like?
Infection is carried out by females and larvae. The female lives in the skin. During the daytime it is inactive, but in the evening it actively gnaws through passages, reproduces, feeds and secretes waste products. Consequently, the greatest risk of infection appears precisely in the evening and night time, when the tick is more active.
Everyone who comes into contact with the infected person is at risk. For example:
- family member
- roommate
- roommate
However, you can also become infected through indirect contact. For example in the following places:
- bathhouse
- public shower
- crowded places
Interesting. Outside a living organism, the female can live up to 3 days.
The disease spreads quickly due to the fact that the female lays eggs from which larvae hatch. After maturation, the latter crawl out to mate. The male dies and the female burrows back into human skin to continue the cycle of reproduction and spread.