Corneal ulcers in cats are a dangerous disease that can lead to serious consequences if the owner does not contact a veterinarian in time. Ulceration affects the animal's eye gradually, starting from the surface epithelium and moving towards the base of the cornea. The larger the area of the cornea is populated with ulcers, the more complex and expensive the treatment will be prescribed for your pet. Moreover, in a number of advanced cases of corneal ulceration, doctors are powerless. We discuss below the causes of such ulcers and methods of their treatment.
Corneal ulcer in a cat
General information about the disease
The cornea performs protective functions. It does not allow the external environment to influence the eyeball. The structure of this organ has three layers:
- thin epithelium;
- stroma, which is the core;
- Descemet's membrane.
At the initial stage, the epithelial layer is damaged. Access is opened for microbes and bacteria to the stroma. If the disease is detected at the stage of destruction of the epithelium, you can get rid of it in a conservative way. When the lesion spreads to the stroma, surgical intervention is usually used.
Corneal ulcer in dogs symptoms
There are 2 forms of the disease:
- Superficial. Characterized by damage to the epithelial layer and stroma.
- Deep. The process extends to the entire thickness of the stroma. Over time, discemet's membrane may become damaged, leading to perforation of the anterior membranes of the eye.
The acute stage (onset of the disease) is characterized by increased lacrimation and photophobia. The animal constantly tries to rub its eye with its paw, which aggravates the disease due to additional trauma and secondary infection. Redness of the conjunctiva appears, the eyelids spasm.
As the disease progresses, ulcers may form. If the process is left untreated, a perforated ulcer will develop, leading to panophthalmitis or loss of the internal structures of the eye.
In addition to perforation, other complications may develop. Over time, the cornea becomes overgrown with blood vessels, which leads to clouding, the appearance of pigmentation, and decreased visual acuity.
Blood vessels on the cornea
In healthy eyes, blood vessels are not visible. When an ulcer forms, elements of the blood flow network become noticeable. This symptom indicates that the ulcerative lesion has invaded the deep layers of the organ.
Blood vessels originating in the sclera rush to the site of ulcer formation. This reduces visual acuity. Even after successful treatment, this symptom persists for a certain time.
Corneal ulcer in dogs treatment
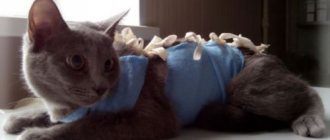
A plastic collar is used to prevent further damage. First of all, drops and ointments containing antibiotics are prescribed, even if pathogenic microflora has not joined. This will prevent future infection.
Mild superficial forms usually do not require hospitalization and are treated with local drugs. To treat corneal ulcers in dogs, antibiotics and anti-inflammatory films are prescribed, and medications that improve tissue regeneration are prescribed. Surgical treatment involves closing the defect with a conjunctival flap. After plastic surgery, improvement occurs within a week.
Types of disease
Veterinarians define three types of corneal ulcers:
- average,
- deep,
- perforative.
In the middle stage, the affected area covers the stroma. A large volume of intercellular fluid penetrates into its tissues. The cornea becomes cloudy, and partial loss of vision is observed. In the deep stage, Descemet's membrane is damaged. At this stage, the eyeball is filled with intercellular fluid. A perforated ulcer is diagnosed very rarely. If the disease is detected at this stage, the visual organ must be removed.
Diagnostic methods
As mentioned earlier, it is completely impossible to recognize corneal ulceration with the naked eye, so veterinarians resort to special techniques to obtain an unambiguous result.
Superficial ulcers
In most cases, doctors prefer to instill a special fluorescent solution into the eyes of cats, which colors the eyeball. After staining, an ultraviolet lamp is placed on the animal’s eye, which allows the injected liquid to be illuminated and any defects on the cornea to be recognized. This method is effective when working with large ulcers, and if the presence of small ulcers is suspected, the veterinarian additionally uses magnifying devices and special filters.
Eye dripped with fluorescent solution
Deep ulcers
If we are talking about deep ulcers, whose course is chronic, then specialists first take material for microscopic examination in order to analyze the characteristics of the ulcer and select a suitable treatment regimen.
Causes of the disease
Disease of the corneal tissue can occur for various reasons. Knowing the provoking factors will help prevent the appearance of ulcers and take timely measures.
Eye injuries
The cause of the ulcer can be injury received during a fight, falling, or causing microscopic scratches on the protective layer. With strong immunity, such wounds heal in cats without any consequences. But if they are received during a weakening of the body, pathogenic bacteria can actively multiply and create an infectious focus.
The most common causes of injuries include:
- injury to the cornea with a claw while washing;
- getting hit by a foreign object while walking;
- chemical burns from household chemicals and fertilizers.
At the first stage of the appearance of an infectious focus, serous conjunctivitis and keratitis develop. Lack of treatment causes the development of ulcers.
Penetration of infection
The cause of a corneal ulcer may be an infection that has penetrated the tissue due to damage to the epithelium and lack of protection. Infection with pathogenic microorganisms in the absence of vaccination is possible.
Corneal ulcers are rarely diagnosed as an independent disease. For the most part, it is a complication of existing inflammation in the body.
Genetic predisposition
There are cat breeds whose representatives have a hereditary predisposition to this ophthalmological pathology. Breeds at risk include:
- British,
- Himalayan,
- exotic,
- Persian,
- Scottish.
Predisposition to the disease is due to the specificity of incomplete closure of the eyes due to the structural features of the skull. It should also be taken into account that this disease is diagnosed more often in older animals than in young pets.
Pathologies of the eyelids and eyes
Provoking factors include various pathologies of the visual organs:
- blepharitis;
- inversion of the eyelids;
- entropy;
- trichiasis;
- ectopia.
Treatment of corneal ulcer in cats
The general principles of treatment of the disease do not differ from those listed above. Due to the frequent development of herpesvirus keratitis, careful sanitation of chronic foci of infection is necessary. For this purpose, antiviral drugs are prescribed, mainly after relief of the symptoms of inflammation.
Cats often undergo tarsorrhaphy, in which the eye is “covered” by the third eyelid. This creates additional protection for the healing cornea.
To prevent pathology, it is necessary to monitor the animal’s behavior, get vaccinations in a timely manner, and if there is a suspicion of damage to the cornea, consult a veterinarian as soon as possible.
Main symptoms of the disease
The symptoms of corneal ulcers are poorly identified; it is difficult even for an experienced specialist to recognize the disease at an early stage. Obvious signs appear only during periods of exacerbation; an accurate diagnosis can be established by an ophthalmological examination. The most typical symptoms include:
- increased tearfulness, moisture, shine in the eyes;
- clouding of the cornea, redness of the proteins;
- inappropriate behavior, squinting of eyes, rubbing with paws.
Symptoms of a corneal ulcer are similar to those of conjunctivitis. But this disease usually affects one eye.
Corneal ulcer in cats symptoms
Manifestations of ulcerative keratitis in cats are similar to those in dogs. More often, purulent complications caused by the addition of an infection come to the fore, especially in pathologies caused by a foreign body entering the eye. In this case, the basement membrane of the epithelium is affected, the regenerative process is disrupted, as a result of which the corneal ulcer in cats takes longer to heal or does not heal at all.
There are general symptoms with redness, swelling, and lacrimation. Additionally, purulent discharge may appear, which indicates infection. A common cause of ulcerative keratitis in cats is herpesvirus, as evidenced by the appearance of symptoms after a respiratory illness.
Therapeutic treatment
The conservative complex includes:
- eye drops with antibacterial properties;
- antibacterial ointments;
- painkillers, sedatives;
- wearing a protective collar.
Drops of a range of antibiotics are instilled every 4 hours. You can replace them with ointments that retain the effect longer. The treatment complex includes Atropine, which relieves spasms and pain symptoms. It should be taken into account that this drug dilates the pupils and cats under its influence will experience discomfort from bright light.
Forecast
Timely treatment allows you to preserve vision and prevent complications. During treatment, fluorescein tests are carried out, the results of which determine the degree of healing. Superficial forms epithelialize within 4-5 days. The healing time for deep defects varies from person to person (usually 3-4 weeks). The main factor influencing the recovery period is the treatment of the underlying disease that caused ulcerative keratitis. When it is eliminated, regenerative processes are accelerated.
In our clinic, a doctor is an ophthalmologist, a doctor of the highest category, A. E. Kopenkin .
Diagnosis and treatment of keratitis
The diagnosis of the disease is established on the basis of characteristic clinical symptoms.
In order to clarify the etiological factor, it is necessary to conduct various general and laboratory studies, as well as a thorough analysis of anamnestic data, since most keratitis are always symptoms of a general disease. Biomicroscopy using a slit lamp helps establish the diagnosis. Defects in the corneal epithelium are easily detected after instillation of a 1% fluorescein solution.
Treatment of keratitis in dogs and cats
Treatment depends on the cause of keratitis, the depth of damage to the cornea, and the severity of the disease, which is determined by a veterinary ophthalmologist. For keratitis, medications are used in the form of eye drops, ointments, some drugs are administered as injections under the conjunctiva, into the postorbital space. Tablet forms, intramuscular, subcutaneous and intravenous injections are recommended.
In the treatment of viral keratitis, antiviral therapy is used: drugs containing interferon and interferon stimulators. For herpetic keratitis - drops, ointments, tablets containing acyclovir.
For bacterial keratitis, antibiotics and broad-spectrum sulfonamide drugs are prescribed, and upon receipt of the results of a bacteriological study, taking into account the sensitivity of the pathogen to the antibiotic.
The treatment of allergic keratitis requires the use of antiallergic drugs, both local and general. Products are used to promote corneal epithelization, usually in the form of gels and ointments.
If there is a threat of corneal perforation, a pronounced decrease in vision as a result of cicatricial changes, a cosmetic defect, etc., corneal plastic surgery is performed in varying volumes.
Prevention of keratitis consists of timely and adequate treatment of blepharitis, conjunctivitis and dacryocystitis, general diseases of the body that contribute to corneal disease, and the prevention of eye injuries.
Preventive measures
It is better to prevent any disease than to treat it. Keratitis in cats is no exception. To prevent illness in pets:
— Keep the house clean, wipe off the dust. — The animal’s diet must be balanced. The best choice is professional super-premium and holistic-class food. — “Murkoshi” volunteers recommend getting vaccinated in a timely manner. Vaccinations will help protect your pet's body from infection. - Brush the cat. Lost hair can get into the eye, rub the cornea and conjunctiva, leading to inflammation. — Do not keep open chemicals within the cat’s reach to avoid burns. — Strengthen your animal’s immunity with vitamins. Remember to deworm.
Read more about deworming: Preparations for deworming cats
— Examine your pet’s eyes, especially if there is watery eyes. Mechanical irritation of the cornea is possible. — If the animal has a predisposition to keratitis, eye examinations should be performed more often.
The danger of keratitis for a kitten or cat cannot be underestimated. But, at the same time, it is possible to cure the disease by noticing deviations in the animal’s well-being and unhealthy eye conditions in time and contacting a veterinarian.