Paratyphoid fever or salmonellosis in cats is an infectious disease caused by enterobacteria. The disease causes severe intoxication of the pet’s body and, if not properly treated, can even lead to death. Therefore, it is important for the owner to notice any changes in the cat’s condition, and if it worsens, immediately contact a veterinary clinic.
What symptoms indicate pathology?
The average incubation period is 10 days. The course of the pathology is directly related to the degree of virulence of the pathogen and the resistance of the cat’s body to it. Salmonellosis, which affects pets, has three forms:
- chronic;
- acute;
- subacute
The main symptom of this disease is diarrhea. In addition, the pet is experiencing dehydration, and an increase in the number of leukocytes can be seen in the analysis of its blood.
Proceeds in the acute stage
With this course of the disease, the animal suffers from hyperthermia.
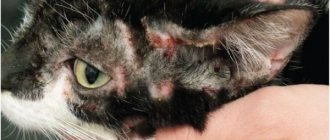
The acute form is observed when a large amount of doses of the pathogen enters the cat's body. This stage is characterized by a rapid progression. The pet refuses to eat, its body temperature increases, the animal visits the toilet many times, and the stool is loose. The cat weakens, becomes apathetic, and vomits. The animal's feces are predominantly green in color, and blood may be seen in it.
When palpating the abdomen, the pet experiences pain and begins to meow and hiss. The visual organs become watery, purulent discharge is sometimes noticeable, and the mucous membranes turn pale. Since the pathology provokes serious intoxication of the body, which is accompanied by dehydration, death on the 2-3rd day of this condition is not excluded. The pathology sometimes provokes lung damage, which can be determined by difficulty breathing and coughing.
Chronic and subacute
The subacute form is characterized by an increase in temperature up to 40 degrees, loss of appetite and diarrhea. Dehydration is not as critical as during the acute stage, but death is also possible. It may come in a week. The chronic course of the pathology has the same symptoms, but sometimes salmonellosis provokes the development of anemia and purulent conjunctivitis. Death may occur after 14 days due to severe exhaustion.
All about the pathogen and the disease
The causative agent of paratyphoid fever is the rod-shaped bacteria Salmonella. They are highly resistant to adverse environmental factors.
Depending on temperature conditions, bacteria found outside a living organism retain their pathogenicity and viability from 4 months to 1 year. To destroy them, heat above 75°C, ultraviolet rays and disinfectants are used.
After entering the body, salmonella begins to actively multiply. In the process of their life, they release a large amount of toxins that inhibit the functioning of internal organs. Over time this leads to:
- degenerative and necrotic changes in the liver, spleen, kidneys, intestines, lungs and joints;
- internal hemorrhages;
- the development of sepsis, that is, blood poisoning.
The main damage occurs in the gastrointestinal tract. Because of this, the first symptoms are often mistaken for poisoning or feline distemper.
How dangerous is the disease?
A person can easily adopt this disease from his furry pet.
The main danger lies in the fact that salmonellosis in a cat can be transmitted to humans. The infection is insidious, since in pets that have strong immunity, signs of pathology sometimes do not make themselves felt for a long period. However, when the immune system deteriorates, symptoms are noticeable almost immediately. Salmonellosis is most dangerous for adult cats, in which it causes serious complications. First of all, it should be noted the development of infectious-toxic shock due to severe intoxication and damage to the adrenal glands.
The consequences of salmonellosis include dehydration, which develops against the background of diarrhea and vomiting. The possibility of pancreatitis, which is inflammation of the pancreas, cannot be ruled out. Sometimes kidney failure develops, to which young pets are most susceptible. Due to infection, the organ stops purifying the blood.
Laboratory diagnostic methods
To make a diagnosis, it is necessary to conduct a bacteriological examination of stool for the presence of salmonella. In dead animals, secretions from parenchymal organs are examined.
Since the pathogen is not always detected in feces, additional methods are used to confirm or refute the diagnosis - microscopic, serological, biochemical blood and urine tests.
When making a diagnosis, an important task for the veterinarian is to exclude viral and bacterial infectious diseases that cause fever, diarrhea and vomiting in animals. Such diseases include:
- Plague of carnivores.
- Viral gastroenteritis.
- Flu.
- Helminthiasis.
- Poisoning with chemicals, poisons.
First aid
Using an enema
It is important for cat owners to remember that therapy for salmonellosis must be carried out by a veterinarian. The owner has the right to exclusively provide first aid in order to alleviate the cat’s condition and reduce intoxication syndrome. An enema can be used to flush out the intestines. For these purposes, you will need to use a pear, the volume of which is 100 milliliters. Lavage is carried out until clean intestinal waters appear. For an enema, take boiled water at room temperature.
Gastric lavage
In this situation, a manganese solution will do more harm to the fluffy than help it recover.
With this manipulation it will be possible to remove undigested contaminated food. To carry out the procedure, you need to arm yourself with a syringe. Using it, you will need to introduce about 30 ml of boiled water into the cat’s oral cavity and induce vomiting in the cat by pouring a little salt on the root of the tongue. We should not forget that the use of potassium permanganate to lavage a cat’s stomach is strictly prohibited. This is due to the fact that the substance can cause a burn to the digestive tract, which will further aggravate the situation.
The use of sorbents and drinking plenty of fluids
These medications are able to absorb toxic compounds and eliminate them naturally through the digestive tract. Veterinarians recommend giving cats activated charcoal. You will need to crush half a tablet of the medicine, add 5 ml of boiled water and pour it into the cat’s mouth using a syringe. If we talk about the drinking regime, then your pet will need to be given water often, but little by little. It is also recommended to use a syringe. About once every 15 minutes you need to pour 10 ml of boiled water into the cat’s mouth.
Salmonellosis: what you need to know about insidious salmonella!?
Salmonellosis is an acute intestinal anthropozoonotic infection caused by microorganisms of the genus Salmonella, characterized by predominant damage to the gastrointestinal tract and occurring in the form of gastrointestinal, less often generalized forms.
The causative agent is the bacterial bacillus Salmonella, 0.0003 cm long, highly mobile, without the ability to form spores and capsules. The pathogen affects the gastrointestinal tract, causing intoxication and dehydration of the body.
The resistance of saplmonella is extremely high; they remain viable when smoked and salted, however, they die when boiled and when directly exposed to ultraviolet radiation.
Salmonellosis disease is most often observed in the warm season, when favorable conditions are created for the proliferation of microorganisms in food products.
The relevance of the problem of salmonellosis is that salmonella are relatively stable in the environment.
They can remain viable in water for up to 5 months, in soil for up to one and a half years, in meat for up to six months, in poultry carcasses for up to a year or more. When chicken eggs are stored in the refrigerator for more than 30 days, the bacterium is able to penetrate through the whole shell into the egg and actively multiply inside the yolk.
They last for about 20 days in milk, a month in kefir and four in butter. Salmonella can remain alive in cheese for up to a year, 3-9 months in powdered eggs and 17-24 days on egg shells.
Salmonella die after 5-10 minutes at a temperature of 70°C; they can withstand boiling for some time if they are found in the thickness of a large piece of meat. When boiled, eggs die within 4 minutes. In milk and meat products, salmonella not only persists, but also actively multiplies, without affecting the organoleptic properties of the products. Microorganisms are quite resistant to salting and smoking, and when frozen, their lifespan increases. Currently, Salmonella strains have been isolated that have a high degree of resistance to antibiotic therapy and disinfectants.
The insidiousness of salmonella is that while living and reproducing on products, they do not in any way affect their appearance or taste.
Sources of infection.
Salmonella is widespread in domestic and wild animals, primarily in food animals such as poultry, pigs and cattle; and among domestic animals, including cats and dogs, birds and reptiles such as turtles. Birds with salmonellosis can contaminate their surroundings and food with droppings.
Humans usually become infected with salmonellosis through consumption of contaminated animal foods (primarily eggs, meat, poultry, and milk), although other foods, especially vegetables contaminated with manure, may also be involved in transmission.
In recent years, cases of salmonellosis infection due to contact with aquatic turtles have become more frequent. Small turtles are often purchased as pets or as inhabitants of living corners in schools. You should be aware that salmonella is part of the normal intestinal flora of turtles, and there is no way to distinguish a healthy turtle from an infected one. These bacteria are present in their droppings and in the water of the aquarium where the turtles live. After any contact with a turtle or its habitat, you must wash your hands thoroughly, otherwise infection cannot be avoided.
In some cases, the source of infection may be a person. If animals are infectious for several months, then a person can transmit the infection for a period of several days to three weeks, sometimes carriage can persist for years.
Humans are highly susceptible to salmonellosis. The severity of the infection depends on a complex of factors, both external (the number of pathogens entering the body, their antigenic composition and biological characteristics) and internal (the state of the human body’s defense systems, concomitant pathology, especially the digestive system). The infection is most severe in infants and the elderly.
How does infection occur?
The transmission mechanism of salmonellosis is fecal-oral, bacteria are released by a sick person or animal with feces, salmonella enters the human body through the mouth, and into the mouth through dirty hands or contaminated products.
Food route of transmission of infection to humans. Infection occurs during consumption of food prepared without following the rules of heat treatment.
Water transmission is most often carried out in poultry and livestock farms. A person can become infected by drinking raw water.
Contact with sick animals or carrier animals. A person becomes infected while caring for them, while working in meat processing plants, or eating infected (during life or after slaughter) meat or dairy products. Birds are the most active carriers of salmonella; humans can become infected by eating contaminated meat, eggs, or foods contaminated with the droppings of sick birds.
Contact and household route of infection. There is a high probability of becoming infected from a person (both a patient and a carrier of salmonella); this route of transmission is more often realized in organized groups, kindergartens, schools, and hospitals. Infection through contact and household means occurs through: household items, pots, linen, towels, toys, unwashed hands of a sick person, including medical staff or family members, medical instruments and equipment (probes, catheters) that have not been processed according to all sterilization rules.
Airborne dust path. Relevant in urban environments, the main factor is the pollution of streets and public places with bird droppings (sick or carriers of salmonellosis).
After an illness, immunity is formed, which lasts up to six months; after which there is a possibility of re-infection, however, the disease will proceed in a milder form.
After an infection, unstable immunity remains, lasting no more than one year.
____________
The most susceptible to infection with salmonellosis are: young children, elderly people, people who, for one reason or another, have a reduced immune system, workers in poultry and livestock farms, people who are fond of a raw food diet, people who neglect the rules of personal hygiene and heat treatment of food.
Clinic.
From the moment of infection to the appearance of the first signs of the disease, it usually takes from several hours to 2-3 days.
The main clinical symptoms are: increased body temperature, nausea, vomiting, spastic abdominal pain and loose stools mixed with mucus, blood, often greenish in color with a foul odor. The disease can occur in both severe and mild forms.
In severe cases of the disease, seizures may develop, mainly in the lower extremities.
If signs of illness appear, you should definitely consult a doctor.
In some cases, the development of various kinds of complications is possible: pancreatitis, cholecystitis, cholangitis, chronic colitis, infectious-toxic shock, which is accompanied by pulmonary and cerebral edema, cardiovascular, renal and adrenal insufficiency. Generalized forms can lead to the development of purulent complications.
How does the disease progress?
Salmonellosis is characterized by a sharp increase in temperature, abdominal pain, diarrhea, nausea and sometimes vomiting. Symptoms of the disease appear 6-72 hours (usually 12-36 hours) after the bacterium enters the body. The illness lasts from 2 to 7 days.
The disease is usually relatively mild. In most cases, recovery occurs without special treatment.
In more severe cases, symptomatic treatment is carried out, replenishment of electrolytes and lost fluid.
In mild or moderate cases of disease in healthy people, conventional antimicrobial therapy is not recommended. This is because such drugs may not completely kill the bacteria and may contribute to the development of resistant strains, which can render the drug ineffective. However, infants, the elderly, and immunocompromised patients may require antimicrobial therapy because disease-related dehydration can be life-threatening. Large outbreaks of salmonellosis attract media attention, but 60 to 80% of all salmonellosis cases occur outside of known outbreaks. Such cases are classified as sporadic cases of the disease or are not diagnosed as such at all.
How to avoid infection?
At the state level, preventive measures are carried out by veterinary and sanitary-epidemiological services. They exercise control over the meat processing industry (livestock slaughter and processing of raw materials), catering enterprises (preparation technology, storage and sale of finished products), and the organization of meals in kindergartens and schools. At the same time, sanitary services control the process of examining new employees at poultry farms, catering establishments, trade, child care institutions, and food service workers.
Effective prevention requires control of all links in the food chain - from agricultural production to processing, production and preparation of food both in public institutions and at home.
Rules for individual prevention of salmonellosis.
In order not to become infected or get sick from salmonellosis, everyone should remember and follow the following recommendations!
- Strictly observe the rules of personal hygiene. Instill hygiene skills in your children.
- Wash your hands thoroughly with soap (especially after visiting the restroom and before eating).
- Do not purchase meat, meat products, poultry, eggs, cottage cheese, milk, butter, cheese - in places of unauthorized trade.
- When purchasing eggs, strictly follow the sorting date (it is indicated both on the packaging and directly on the eggs). Acceptable period of implementation is 25 days.
- Observe the storage time and temperature of food products.
Important! The opinion has taken root that you can eat raw quail eggs without fear. Despite the fact that quails do not suffer from salmonellosis, they are carriers and distributors of salmonella, and can become a source of infection. Therefore, eating quail eggs without appropriate heat treatment is unacceptable.
- Follow the rules of food preparation (use cutting boards and knives separately for raw and finished products, treat raw eggs before cooking with a warm soap-soda solution for 5 minutes; boil eggs for 10 minutes from the moment of boiling; sufficient heat treatment of poultry meat and farm animals ).
- When purchasing products at the market or in a store, you should ensure that the product labels are respected. Raw and finished products must be located in separate display cases and sold by different people.
- At home, follow food storage rules (raw foods and prepared foods should be stored separately).
- Wash the refrigerator regularly and thoroughly clean the egg storage compartments.
- Thoroughly wash and scald kitchen utensils with boiling water.
- Boil eggs for at least 10 minutes from the moment they boil, poultry for 40 minutes, meat for at least 2 hours.
- Never sample raw ground meat.
- Don't drink raw milk.
- Rinse fruits, herbs and vegetables well under running and then boiled water. The best way is to scald with boiling water.
- When preparing food, wash your hands after cutting raw meat, fish, poultry, and contact with raw eggs.
If signs of illness appear (abdominal pain, loose stools, nausea, vomiting), you should seek medical help promptly!
Remember: there is no specific prevention of salmonellosis in humans.
Take care of your health, be careful about your diet and carefully monitor your hygiene!
How to check your pet?
If you suspect this disease, you cannot do without contacting a veterinary clinic.
If cat owners suspect that they have salmonellosis, it is important to contact a veterinary clinic as soon as possible, where feces and vomit will be analyzed for the presence of bacteria. Sometimes a bacteriological blood test is also required. In addition, it is recommended to check for the presence of bacteria in the suspected food, which could have caused the cat to become infected.
Causes
The main source of infection is raw poultry and farm animals that suffered from salmonellosis. You can become infected by consuming meat cat food, blood meat and bone meal, or cow's milk containing salmonella bacilli. Animals walking on the street or living in private homes are often infected by eating carrier mice.
Cats can carry the disease but not show symptoms. By releasing pathogens into the environment along with excrement, the carrier cat becomes a source of infection for other animals, and sometimes even humans. Salmonellosis during pregnancy leads to intrauterine infection of kittens and miscarriage. There is a danger of stillbirth or litter death during the first 1-10 days of life.
Predisposing factors that increase the likelihood of infection are:
- Failure to comply with basic hygiene rules for keeping pets.
- Presence of colds.
- The presence of an inflammatory process in the gastrointestinal tract caused by improper feeding.
- Severe helminthic infestation.
- The period of teeth change in small kittens.
- The period of transition of a kitten from breast milk to independent food of unsatisfactory quality.
How is the treatment carried out?
Pets are prescribed antibacterial drugs from the sulfonamide group, for example, Biseptol. Activated charcoal is used to remove toxins, and glucocorticosteroids are used as maintenance treatment. If required, antiemetic medications are prescribed. In addition, treatment of salmonellosis in cats involves transferring the animal to dietary nutrition. The diet should be based on easily digestible food. You will need to exclude milk and raw meat from the menu. It is recommended to feed your pet boiled fish, lean meat and rice cereal. In order to prevent re-infection, the animal’s toilet and dishes will need to be treated.
Danger to others
Salmonellosis also poses a danger to pet owners. There is a risk of transmission of salmonella bacteria from an infected cat to humans. Therefore, after contact with a sick pet, you need to follow the rules of hygiene especially carefully:
- a sick cat should be isolated not only from other animals, but also from family members, especially children;
- disinfect those items that were used when caring for an infected cat;
- After handling a sick pet, hands should be washed twice with soap.
Even after treatment ends, the cat may remain contagious. Bacteria - pathogens - will be present in the feces. Her contact with other animals should be limited.
Prevention
To reduce the risk of salmonellosis in cats, you need to prevent them from coming into contact with stray animals. It is important to monitor your pet’s hygiene and avoid giving him raw meat and eggs. If your pet is fed industrial complementary foods that are sold in stores, you should choose high-quality representatives. Veterinarians recommend paying attention to premium and super-premium segment food. They contain the required amount of vitamins and microelements that are necessary for the normal functioning of the pet and strengthening the immune system.
About carriage in cats
By solving the problem of preventing salmonellosis, owners of pet purrs ensure the safety of not only their pets, but also themselves. According to the observations of researchers, more than a third of domestic cats and dogs with good immunity do not get sick themselves after direct contact with these microorganisms, but become carriers of salmonellosis. In other words, in order to get sick, sometimes it’s enough to pet a cat and not wash your hands after that.
If we are talking about animals with weak immunity (for example, kittens, elderly cats that have recently suffered from another disease), their body may not be able to cope with the infection, and then illness is possible.
Symptoms of the disease
In adult animals, the disease rarely develops acutely; most often the infection occurs latently or in the form of carriage. Salmonellosis is most severe in young cats and kittens.
Acute manifestations begin on the third day after infection; with large bacteremia, symptoms may appear on the first day. The cat becomes lethargic, refuses to eat, and sleeps almost constantly. At this time, body temperature reaches high numbers, up to 41 degrees. Against the background of prolonged low-grade fever, kittens may develop seizures.
The main manifestation of infection is diarrhea and repeated vomiting. This symptom is dangerous for the animal, as it leads to exhaustion and dehydration. Severe fluid loss can be suspected by your pet's sunken eyeballs.
You can also notice copious amounts of saliva and the appearance of purulent discharge from the nose and crusts. Feces are usually greenish in color, pungent-smelling, and watery. If proper treatment measures are not taken in time, young animals die quickly.
The infection can affect the respiratory tract, even leading to the development of pneumonia. Cats begin to breathe heavily and cough.
In the case of acute development of the disease, the death of the kitten occurs within a few days, in the subacute course - within a couple of weeks, most often from exhaustion of the body.