Demodicosis in humans is caused by iron mites, which belong to the Demodex species. These are opportunistic microorganisms. They are part of the natural microflora of humans, under normal conditions they live with him in symbiosis, destroying other pathogenic microorganisms. With normal health and lifestyle, there is a small amount of them on human skin. They do not manifest themselves in any way and do not cause irritation or inflammation. But when unfavorable conditions occur, their number increases sharply, which leads to pain and skin rashes. Of course, the question arises: is it possible to become infected with demodicosis? Is it transmitted from person to person? To answer these questions, you need to understand what this disease is and how it develops.
Subcutaneous mites in cats (demodex): what is it?
In domestic animals, askariasis is caused by different types of parasites. But the most commonly diagnosed is demodicosis - a chronic disease caused by Demodex cati and Demodex gatoi.
The arthropod is localized in the hair follicle, sweat (epocrine) and salivary glands. Larvae hatch from oocytes laid by females on days 4-6. After 7-10 days, individuals ready for reproduction grow. Pathogenic microorganisms live in colonies, forming painful nodules on the body of predators. Enlarged colonies cause atrophy of the sebaceous glands and disruption of skin functions.
There are two types of demodicosis: generalized and localized. The latter is characterized by damage to certain areas of the body: ears, eyes, chin and neck. Generalized spreads throughout the skin. This form is common in purebred Siamese and Burmese breeds.
Do cats get encephalitis?
Cats, just like dogs, suffer from encephalitis. The disease can appear in absolutely any pet, regardless of gender and age, so the owner must not only know the answer to the question of whether cats get encephalitis from a tick bite, but also immediately begin treatment for the pet as soon as he notices the first signs of pathology.
The carriers of the encephalitis virus are ixodid ticks. Most often, insects attack stray animals and those with access to the street, but a domestic cat can also be bitten by a tick, which can become ill if the owner brings the insect on clothes or shoes.
Typically, tick-borne encephalitis in cats is detected in pets between May and October. During this time period, ticks are most active. However, not only an insect bite can provoke the development of pathology. Encephalitis can be caused by:
- infection with infectious listeriosis. This disease is also called pseudorabies. It is caused by pathogenic microorganisms that enter the brain tissue through lymph and blood;
- toxoplasmosis. Toxoplasma living in the body of cats can sometimes affect the lining of the brain, causing an inflammatory process;
- otitis. Chronic inflammation of the inner ear can cause your cat to develop a severe form of encephalitis;
- head injuries. Brain edema, characteristic of head injuries, leads to compression and damage to blood vessels, provoking an inflammatory process.
"Important information! If the owner does not begin timely treatment of the animal, encephalitis can lead to the death of the pet.”
Causes of subcutaneous mites in cats
Ticks are part of animal life. Some live in hair follicles for years, feeding on dead epithelial cells. The predator's immune system controls the parasite population. If the pet is weakened, the body's protective functions reduce the ability to regulate the number of arachnids. Arthropods multiply rapidly, attacking healthy cells.
Factors influencing weakened immunity:
- helminthic infestations;
- hereditary or chronic diseases;
- unbalanced diet, lack of vitamins and minerals;
- improper maintenance and care (dirty litter);
- rare or lack of water procedures using antiparasitic agents.
Stress also reduces the body's protective functions.
How does demodicosis develop?
The causes of the development of the disease can be considered:
- prolonged exposure to the sun, solarium, bathhouse, sauna;
- errors in nutrition, abuse of sweet, salty, fatty foods, foods with a high content of dyes;
- alcohol and smoking abuse;
- neglect of personal hygiene rules;
- incorrect selection or excessive use of cosmetics;
- long-term use of antibiotics or hormonal drugs;
- hormonal imbalance and other endocrine diseases.
Infection with demodicosis does not mean that ticks get on people's skin from another person. This suggests that the skin of a sick person turned out to be suitable for the active reproduction of parasites.
Subcutaneous mites in cats: routes of infection
Infection of a healthy predator occurs through direct or indirect contact with a sick one. Parasites are spread by using a shared brush to comb out wool and bedding. Microorganisms enter the apartment with clothing when a person comes into contact with an animal affected by arthropods.
Be sure to read:
Pyrantel for cats: dosage, instructions for use for different forms, indications and contraindications
Routes of infection:
- direct contact with a sick predator;
- contact with the fur of a predator affected by demodicosis;
- intrauterine.
If a breeder has several pets, therapeutic measures are applied to all of them without exception.
Is demodicosis contagious?
Demodicosis is a disease caused by the active reproduction and activity of ticks. It is individual. That is, whether a person gets demodicosis or not depends solely on the state of his body, lifestyle and predisposition. It is possible that general and local immunity will be so strong that an increase in the number of parasites will not have a negative effect on the skin. That is, the disease is not contagious.
But you can catch ticks from another person. They are transmitted through direct contact, when using someone else's cosmetics, combs, towels, bedding and accessories. Most likely, people living together and using the same household items will become infected with ticks from each other. But this does not mean that after mites pass from one person to another, they will immediately cause skin problems.
Almost all people have Demodex mites. It is believed that up to 80 percent of the population are carriers of ticks, and the vast majority are not even aware of their existence. The child is born without these mites, but during the first week of life he receives all the skin microflora from the mother through close contact. It is very difficult to avoid such close contact, so ticks are easily transmitted. But children, especially under the age of one year, do not suffer from demodicosis, because the activity of the sebaceous glands is minimal, which means the number of mites is small.
Animal risk group
Parasitic arachnids affect all predators, regardless of breed, sex, or age. A healthy pet with a strong immune system is not in danger. Under such conditions, the animal and arthropods are in an antagonistic relationship, where the cat’s body slows down the growth of parasitic microorganisms.
The following groups are susceptible to demodicosis:
- young individuals, especially those separated from their mother early;
- affected by leukemia and immunodeficiency viruses;
- with diagnosed immunosuppressive diseases (diabetes mellitus, toxoplasmosis);
- animals in the postoperative period;
- young offspring during the period of change of milk teeth to molars (4-6 months);
- exhausted after fasting;
- patients with rickets.
Stress caused by moving and frequent visits to the groomer negatively affects the health of the pet. The risk of ascariasis increases.
Vaccination
Unfortunately, not a single vaccination against tick-borne encephalitis can protect a cat 100%. However, in combination with sprays or anti-tick collars, it gives a very good result.
Even if a tick attacks an animal, after it attaches itself to the skin, it will simply fall off and die without causing any harm to the cat.
From the beginning of spring to mid-summer, when ticks are especially active, it is better to try not to let the animal go outside, and if that fails, then try to carefully examine it after each walk.
"Important information! During the examination, the ears, armpits, groin and abdomen should be checked most carefully. These areas are least covered with fur, so ticks try to attach themselves to these areas.”
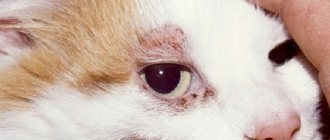
Subcutaneous mite symptoms in cats
The clinical picture is specific. An increased number of parasitic microorganisms causes itching. First, there is increased hair loss, as if molting. Patchy bald patches of regular oval shape appear. In areas of alopecia, the skin is intensely red and covered with ulcers. Secondary staphylococcal infectious pathologies are added. The area around the eyes, under the neck, and front paws is most often affected.
Summary symptoms:
- hair loss;
- “demodectic glasses” - lack of hair around the eyes;
- inflammation, redness of the skin, swelling;
- skin pustules, ulcers;
- unkemptness, foul odor;
- the bites cause itching, the predator scratches the ear area until it bleeds;
- lack of appetite;
- weight loss.
In the generalized form, sepsis develops. Sometimes pets recover without treatment, but only with a localized form.
Signs and symptoms
If subcutaneous mites are suspected in cats, symptoms and treatment depend on the form of the disease. There are 3 of them in total.
Localized form
When the parasite penetrates the skin, inflammation occurs at the site of penetration. The skin swells and turns red. Small tubercles (3 mm in diameter) with blood or pus form. There are a lot of such elements, especially if timely treatment is not undertaken. The danger is that an infection occurs, causing the animal’s condition to worsen. Otitis media develops, focal baldness develops, the skin turns red, becomes covered with ulcers and scales. Therefore, this form is also called “scaly”.
With local demodicosis in cats, symptoms appear primarily in the area around the eyes, ears, head, and neck. There are no more than 5 lesions. The hair on them noticeably thins. The paws and back remain unaffected. D. cati does not cause concern to the animal, while D. gatoi causes severe itching. The localized form often goes away on its own in 1-1.5 months.
Generalized demodicosis
When the disease process spreads throughout the body, the following manifestations are observed:
- Areas of hair loss throughout the body.
- Redness, hyperpigmentation of the skin.
- Acne, pustular rashes.
- Inflammation of the outer ear.
- The skin peels severely, bleeds, and itches unbearably.
- Fungal and bacterial infections are added.
The head, muzzle, neck, lower and lateral sides of the torso, and limbs are most often affected. With D. gatoi, complete baldness of the affected part of the body occurs. The animal may look untidy. The wool is dull, as if sprinkled with flour, sticks together. Many owners mistakenly believe that it is dandruff. The skin becomes shiny, sticky, and an unpleasant odor begins to emanate from the cat.
The disease progresses quickly. Separate foci are connected. Most of the body is affected by Demodex. The skin becomes thicker and gathers into folds, making the head seem prohibitively large compared to the body. The eye shape narrows. Lymph nodes become inflamed - this symptom is characteristic of demodicosis.
The general condition is depressed. The cat may refuse food and not be active. Possible increase in body temperature. The disease spreads throughout the body, and signs of intoxication begin to appear.
Juvenile demodicosis
It differs from generalized only in that it is inherited. The kitten becomes infected while still in the womb. This is a very severe form, as the entire cat’s body is affected.
What does a subcutaneous mite look like in cats?
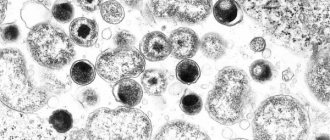
Demodexes are very small and can only be seen under a microscope. They are worm-shaped. An adult male is 182 microns long, 20 microns wide, a female is 220 microns long, about 30 microns wide. Arachnids are gray in color.
The cephalothorax and abdomen are fused. The prosoma has 4 pairs of short legs, each of which consists of three segments ending in claws. The proboscis is well developed.
Be sure to read:
When to worm kittens for the first time: for what, at what age is it better, how to do it correctly, the best drugs
How is tick-borne encephalitis transmitted to humans?
When a tick bites a person, the virus enters the bloodstream along with its saliva, but this does not always happen. If there was a small dose of the virus in the insect's saliva, or if the person has a strong immune system, then the disease will not develop.
In addition to a tick bite, encephalitis can also be contracted through the saliva of a sick cat, therefore, to avoid infection, you should maintain hygiene and regularly examine the animal.
If a person does become infected, he will exhibit the following symptoms, presented:
- fatigue;
- constant feeling of cold due to spasmodic blood vessels;
- increase in temperature indicators;
- nausea and headache;
- conjunctivitis;
- muscle hypotonicity of the face and neck;
- disorder of consciousness.
To avoid infection with this dangerous disease, it is enough to get vaccinated against encephalitis, which is included in the vaccination calendar.
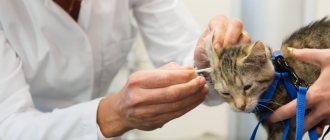
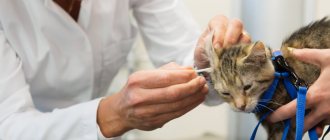
Treatment of subcutaneous mites in cats
At the first symptoms, your furry friend should be taken to the veterinary clinic. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis.
Local therapy of uncomplicated forms:
- To eliminate exudate, dead epithelium, and dandruff, your furry friend is bathed with shampoos containing antiseptics (benzoyl peroxide).
- The area around the wounds is treated with Mitaban solution. For localized demodicosis, a 0.25% solution is used, for generalized demodicosis without complications - 0.5%. In generalized forms with pyodemodecosis and staphylocosis, 1% working concentration of the drug is used for treatment.
- The use of Advocate drops is indicated for therapeutic and preventive purposes. Using a pipette, the drug is applied to dry, intact skin in places inaccessible for licking (between the shoulder blades) at the rate of 0.1 ml per kg.
- Use topical medications containing pyrethrin or amitraz (Advantix, Prak-tik, Advantage). The regimen and dosage are calculated in accordance with the recommendations in the instructions or as prescribed by the veterinarian.
- To relieve inflammation, ointments (sulfur, Avexectin, Saproderm) and gels (Demox, Amidel, Ivermit) are prescribed.
During therapy at home, it is important to follow the dosage prescribed by your doctor. Exceeding concentrations can harm the health of your four-legged friend.
A person perceives the world using five senses: sight, hearing, taste, smell and touch. And although it is very difficult to single out one of the senses and call it the main one, vision is always named first on this list. And folk art testifies that the eyes have always been considered a very important human organ. “His eyes are behind him” people say about people who do not see obvious things; not only poets, but also psychologists call the eyes the mirror of the soul, and many such examples can be given. The world fades when something happens to the eyes. And there can be a lot of troubles here - from a speck that accidentally gets on the mucous membrane, to serious injuries and diseases.
Symptoms of the presence of demodex and demodicosis caused by it
If the eyelids begin to itch intensely and it is almost impossible to relieve this itching, if the eyelids swell and their edges turn red, if eyelashes fall out, and dry crusty scales form along the edges of the eyelids, then there is reason to suspect the presence of demodex.
What does a Demodex mite look like?
Often the disease also affects the mucous membrane of the eyes - the eyes become red, the mucous membrane becomes dry and irritated, and eye fatigue appears very quickly. In addition, mucous and sticky discharge appears, which accumulates along the edges of the eyelids, and yellowish crusts appear after sleep. Cream and any cosmetics, as well as ultraviolet rays (either in the sun or in a solarium) only aggravate and worsen the condition and increase both swelling and itching.
Symptoms that may lead one to suspect demodicosis include blurred vision, a feeling that the eyes are covered with sand, photophobia (the desire to hide from light sources or at least close the eyes), and the frequent formation of styes. Symptoms may appear at different times and with varying intensities.
Demodicosis of the eyes (and this is what we were talking about) can begin in any person (it is known that demodicosis has “blessed” 97% of people on the planet with its presence), but people with a weakened (for example, colds) immune system are at particular risk, with metabolic disorders, chronic diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, as well as pregnant women and elderly people whose immune status is reduced due to physiological reasons.
Factors that can provoke the disease can be the use of corticosteroids (especially in the form of ointments), climate change, and severe stress, that is, any life situation that in one way or another can affect the state of the immune system. Also, provoking factors include increased oily skin and seborrhea, many cosmetic procedures (including manual facial cleansing, solarium, and peeling), high temperatures (and it doesn’t matter at all whether it’s a hot shop or a sauna).
Among other things, it is necessary to note the importance of hygiene procedures, because insufficiently careful adherence to hygiene rules can also provoke this disease. As a rule, demodicosis becomes a chronic disease with periods of remission (when the condition becomes significantly better) and exacerbation (in most cases this is spring and autumn).
Causes of demodicosis
Demodicosis of the eyelids or eyes is a chronic eye disease that is caused by small parasites - Demodex eyelash mites (Demodex folliculorum or Demodex brevis). These mites are not just small, but literally microscopic (the largest specimens do not exceed 0.5 mm in size), and they can only be seen with sufficient magnification.
Demodex mites are opportunistic microorganisms, that is, for the time being they do not cause any concern or inconvenience to the person on whose skin they live. But when the immune system suffers (the reason does not matter), microscopic mites begin to actively reproduce, their population increases many times and this becomes a serious problem. Moreover, it should be understood that demodex mites (eyelash mites) feed on dead skin cells and therefore are completely harmless in themselves.
And all the inconveniences and problems are caused by the waste products of these microscopic parasites, because these are the strongest allergens that provoke the appearance of seborrhea, rosacea, blepharitis (demodex of the eyelids) and blepharoconjunctivitis (demodex of the eyes).
Attention! Demodicosis is a contagious disease that is transmitted through personal contact, including handshakes, and through cosmetics and care products.
Treatment of demodicosis
Treatment of demodicosis is a long and quite troublesome process, because it is not limited only to the use of medications.
Attention! The diagnosis must be made by a doctor after laboratory tests.
Since demodicosis is contagious, every effort must be made not to infect others and to prevent repeated self-infection. Thorough sanitization and disinfection of bed linen, towels, personal hygiene items and clothing is necessary. Naturally, it is not permissible to use shared towels - everything must be individual.
During treatment, it is recommended to change the pillowcase on the pillow daily, wash it and steam it with an iron.
All cosmetic products should have dispensers; it is better not to use mascara at all during this period, because changing the brush every day is very problematic. It is better to avoid contact lenses during treatment for demodicosis, and glasses must be disinfected daily (by the way, do not forget about the need to disinfect the glasses case). The same goes for shaving accessories. When washing, it is better to use only disposable wipes. And, unfortunately, you will have to limit close contact with your pets. Visits to the bathhouse, sauna, and swimming pool will also have to be postponed for now.
When treating demodicosis, nutrition is very important: spicy, salty, fatty, sweet and any irritating foods should be excluded from the menu. Alcohol is completely contraindicated.
It is very important to understand that demodicosis is a chronic disease with remissions and exacerbations, so it is very difficult to treat. It is almost impossible to cope with demodicosis on your own, so contacting an ophthalmologist will be the best solution in this situation.
Any medications are prescribed only after an accurate diagnosis has been established. In any case, cleansing of the eyelashes and eyelid skin with an alcohol-containing solution (for example, calendula tincture) will be prescribed, using only disposable cotton swabs or swabs. Some time after this procedure (about 15 minutes), it is necessary to apply a cream or ointment prescribed by the doctor to the edges of the eyelids.
The names of these medicines may be different, but only a doctor can determine which medicine should be used in a particular case. Using the “wrong” drug will only complicate further treatment and make it even longer.
The ointment or cream is applied to the eyelids twice a day after the skin of the eyelids has been thoroughly cleansed. It is likely that the treatment will not be limited to the use of ointment or cream, but eye instillation with antibacterial drops will be prescribed, which will be prescribed by the attending ophthalmologist. Self-prescription of any medications is unacceptable.
In addition to medications, physical therapy may be prescribed, possibly the use of drugs that can correct the functioning of the immune system and normalize metabolic processes in the body. It is possible to prescribe vitamin complexes. But any prescriptions for the treatment of demodicosis can only be made by the attending ophthalmologist.
It is very important not to postpone a visit to the doctor if alarming symptoms appear, because treatment of demodicosis in the early stages of the disease is disproportionately simpler and faster (but still long and difficult) than treatment of advanced forms.
Prevention of demodicosis of the eyelids (eyes)
- Firstly, you should not neglect the rules of hygiene and always use only individual hygiene items. Especially if any symptoms of the disease appear.
- Secondly, a healthy diet is very important, which will allow the body to maintain an excellent (or at least as good as possible) immune system.
- Thirdly, it is necessary to protect your eyes from sunlight and use sunglasses.
- Fourth, during periods of active sun exposure to the skin (especially in summer), you should use sunscreen with SPF of at least 15.
If demodicosis has been diagnosed at least once, the likelihood of its reappearance is very high, so you should constantly carefully monitor the condition of the eyelids and eyes.
It is necessary to understand, although you don’t want to believe it, that it is almost impossible to cure demodicosis without the help of a doctor. Therefore, only timely seeking qualified ophthalmological help can help, and such treatment is simply necessary.
Similar
Drugs and medications
Localized forms with complications and generalized forms are treated comprehensively. Medicines are selected individually, taking into account concomitant diseases and the condition of the predator.
In case of infection with D. cati and D. gatoi, use the following treatment regimen:
- Amitraz 0.25%. The oil solution is applied to the affected areas once a day every 3 days. Course 4-6 weeks.
- Invec spray is applied to the affected areas. Treat 2-4 times with an interval of 3-5 days.
- Doramectin orally once a day at a dosage of 40-60 mg per kg of body weight. Therapy is carried out for no more than a month.
- Antiparasitic drugs for parenteral administration (s.c.): Dectomax, Baymek, Cydectin.
- Antibacterial drugs Betamox (active ingredient amoxicillin), Kanamycin (amikacin), Ciprovet drops (ciprofloxacin).
Since the fundamental ethological factor is weakened immunity, biogenic stimulants are prescribed: Gamavit, Baksin.
Diagnostics
Identifying the causative agent of borreliosis in the body is not easy. Borrelia may be present in affected tissue (for example, at the edges of the erythema) or fluids, but they are very difficult to detect there. The most accurate and reliable method is serological testing for the presence of antibodies.
In the DILA portfolio, tests for Borreliosis, Borrelia, IgM antibodies and Borreliosis, Borrelia, IgG antibodies are available to identify antibodies. Class M antibodies (IgM) are the first to be produced (1-3 days after infection), so they are optimal for diagnosing recent infection. G family globulins (IgG) can only be detected several weeks after infection, making them a late diagnostic marker. If the test for antibodies gives questionable or positive results, it is recommended to undergo Borreliosis, IgM/IgG screening (immunoblot for doubtful/positive). To study the extracted tick, it is proposed to test the tick for borreliosis, Borrelia burgdorferi, PCR - quality, which is aimed at detecting DNA fragments of the causative agent of Lyme disease.
Folk remedies
In parallel with traditional ones, alternative methods of therapy are used. folk recipes against askariasis:
- Infusion of leather mackerel. 1 tablespoon of dry herb is poured into about 5 liters of boiling water and set aside until it cools completely. The strained solution is diluted with 0.5 liters of water and the pet is bathed. The plant has a bactericidal effect and promotes rapid healing of wounds.
- Wounds are treated with calendula tincture. To avoid side effects, it is better to buy the product at a pharmacy and use it according to the instructions.
- Treatment of wounds with concentrated chamomile infusion. To prepare it, 100 dry plants are poured with boiling water. The cooled infusion is filtered.
Be sure to read:
How to deworm a cat: when to do it, how often, the best drugs and folk remedies
It is forbidden to treat leather with kerosene. The substance causes severe intoxication.
It is possible to defeat parasites!
Antiparasitic Complex® - Reliable and safe removal of parasites in 21 days!
- The composition includes only natural ingredients;
- Does not cause side effects;
- Absolutely safe;
- Protects the liver, heart, lungs, stomach, skin from parasites;
- Removes waste products of parasites from the body.
- Effectively destroys most types of helminths in 21 days.
There is now a preferential program for free packaging. Read expert opinion.
Read further:
Are worms contagious to humans? Can a child get infected from a cat?
Ear scabies in cats: causative agent, symptoms and treatment methods
How to quickly get rid of worms in a cat using tablets or folk remedies
What worms can you get from a cat: a list of common cat worms
Long worms in cats: main types, description and methods of treating parasites in cats
Vetom 1 for cats: instructions on how to give the drug to a cat, reviews and description
Prevention of demodicosis in cats
The basis of prevention is strengthening the immune system and preventing diseases that contribute to the development of askariasis:
- Organization of adequate nutrition and proper care.
- Weekly treatment of the pet's bedding, tray, and bowls with disinfectants.
- Regular prevention of ectoparasites (fleas, lice eaters) and endoparasites (tapeworms, nematodes) using tablets and sprays.
- Wearing Multi-X anti-parasitic collars.
- It is recommended to sterilize a female who has suffered a generalized form.
If the animal has received therapy for demodicosis, the pet is taken to the clinic every 6 months for the first 3 years to monitor relapse.
Diagnosis of encephalitis
To make a diagnosis, the veterinarian needs to collect a complete history, examine the pet and take a blood and cerebrospinal fluid test. If pus is found in the cerebrospinal fluid, the doctor may suspect meningitis, and a large number of red blood cells and proteins indicates inflammation of the brain, more typical of encephalitis.
If the veterinarian suspects that encephalitis is caused by a virus, a serology blood test is performed. In case of inflammation of the meninges caused by otitis, an examination of the animal's inner ear is carried out.
When a tick is found on a cat’s body, the veterinarian removes it and performs an analysis to determine the causative agent of the disease. If the animal has been around for more than one day, then tick-borne encephalitis in a cat begins to show typical symptoms, from which one can understand that it was the insect that caused the development of the disease.
Pathogenesis
Anatomically, blepharitis is divided into anterior and posterior. Invasion of the eyelash follicles is referred to as anterior blepharitis. In case of damage to the meibomian glands - about the posterior one.
Factors determining the negative impact:
- Mechanical damage.
Eating epithelial cells by mites disrupts the direction of eyelash growth, increases their loss, and contributes to the development of trichiasis. The internal cavity of the hair follicles increases, hyperkeratosis and mild perifolliculitis occur. Mechanical blockage of the meibomian gland ducts by parasites causes their hypersecretion and inflammation - chalazion.
- Secondary infection.
Tick-borne blepharitis is often complicated by a secondary infection, staphylococcal or streptococcal, which can lead to the development of purulent conjunctivitis and ulcerative blepharitis.
- Allergic reaction.
Mite waste products and dead individuals have a toxic-allergic effect on the membranes of the eye, and eyelid dermatitis develops.
A tick may not show itself for a long time and remain unnoticed.
But with rapid growth and development, the fact of infection of the body becomes obvious due to the following symptoms. Severe irritation of the skin, some areas turn red. Visually there is a deterioration in the coat. Itching bothers the animal. Acne, bleeding wounds, pustules, nodular rashes and so-called demodicosis glasses appear (hair falls out near the eyes and the skin becomes very dry). The skin becomes pigmented and dandruff is present. The cat suffers from loss of appetite, is weakened, and growths with ichor may develop.
You can try to remove a single tick yourself. First, the visible skin with the parasite is treated with a product with a softening effect (kerosene, vegetable oil, petroleum jelly). Disinfect with alcohol or iodine and begin to pull out the parasite with tweezers, a tick-twister, or even a cut-off disposable syringe. The main thing is to pull it out entirely so that there are no parts left that provoke inflammatory processes.
After contacting a veterinarian and receiving the test results, you can begin treating the disease. After bathing your pet with shampoo, superficial ointments and creams are prescribed for non-advanced forms or injections for severe ones. The skin is treated with a soap solution, 1% coral solution or 1% solution of chlorophos and water. At the same time, the room is disinfected.
Small areas are cleaned of hair with a razor and covered with the following products: Vishnevsky ointment, iodine tincture (14%). Special feline acrodex, amatrazine, and epacid alfa are external preparations that have proven themselves in practice. Doctors recommend dosage and frequency; it is a good idea to read the instructions.
Consequences of the disease
If you contact the clinic in a timely manner, eye mites in cats respond well to treatment, responding to complex therapy. It is worth considering that “demodicosis glasses” are the primary source of damage, and if the animal’s body cannot cope, the disease progresses, becoming a generalized form. The appearance and condition of the sick animal deteriorate significantly: without the use of systemic remedies, the cat may even die.
The criterion for cure is the absence of complaints, satisfactory condition of the skin and coat, as well as a negative result of microscopic examination. Cat owners should remember that treatment should only be carried out under the supervision of a veterinarian: self-medication only improves the pet’s condition for a short time, then becomes complicated by relapses and threatens serious health problems.
Rate and share!
Preventive actions
Even after suffering from the disease, the body does not develop immunity to re-infection with subcutaneous mites. For this reason, it is important to carry out preventive measures in a timely manner. Experts give their recommendations on this matter.
They recommend:
- to exclude as much as possible possible contacts between the pet and other animals that may have health problems;
- regularly treat the cat’s skin using anti-inflammatory drugs;
- Monitor a balanced diet, vaccinations, and the amount of minerals and vitamins consumed in order to naturally maintain the cat’s high immunity.
Attentive attitude towards the animal becomes the key to its excellent health. A cat in excellent health is much less susceptible to subcutaneous mites, so she is safe.