What is pneumonia
No matter how much we dream that our cats will always be healthy, sometimes they still get sick. Often the animal's respiratory system is affected, for example, it may develop pneumonia.
Pneumonia is an inflammation of the airways that can be accompanied by a buildup of fluid, pus, or dead cells in the lungs. When the disease occurs, the body's condition seriously deteriorates and breathing problems arise.
According to many years of observations by Murkoshi specialists, this disease is more often observed in kittens or older cats, since their immunity is weakened and therefore they are more susceptible to infectious diseases. But there is no need to worry - with timely treatment and following further recommendations, the disease quickly recedes and the kitten forgets about pneumonia. The main thing is to seek help in time and prevent complications. To do this, let's understand the causes of the disease, its symptoms, treatment methods and prevention.
How owners can further help
To help your pet recover, just follow these simple rules:
- Attempting self-medication is strongly discouraged.
- It is important to follow all the veterinarian’s instructions, despite the fact that treatment can take from 3 weeks to 1.5 months. Do not make any independent adjustments to the therapeutic regimen and do not interrupt courses of taking medications without instructions from a specialist.
- Provide your pet with rest, high-quality, nutritious and balanced food during treatment, and protect him from potential stress.
- If there is a decrease or absence of appetite, forced feeding of semi-liquid food, high in protein and easily digestible, is indicated.
- Do not give your cat cold water or cold food.
- Do a light tapping massage of the chest.
- During the treatment period, try not to overload the cat with games, so as not to provoke shortness of breath, increased fatigue and oxygen starvation.
Causes of pneumonia in cats
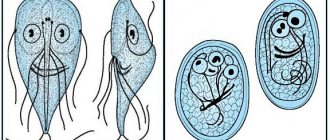
Pneumonia is considered a serious disease and can even occur from simple hypothermia, which can lead to a weakened immune system. Despite this, there are three main causes of the disease: infections, bacteria and fungi. Pneumonia can also be caused by lungworms Paragomimus kellicotti or Capillaria aerophilia, which during their life processes release toxins that lead to various problems in the body. Pneumonia can also be caused by prolonged acute respiratory or immunodeficiency diseases.
Read more: Immunodeficiency in a cat: what to do
Cats with acute and chronic forms of bronchitis and lung cancer are at particular risk. Often, pneumonia in a cat develops due to sepsis as a result of a foreign object entering the trachea or bronchi and taking a long time or unsafely to remove it from the body.
Types of pneumonia
Experts identify the following types of pneumonia:
- Focal type. The simplest and most common option. Only small, isolated areas of the lungs become inflamed. As a rule, these are areas adjacent to large bronchi.
- Segmental variety. A small educational program: a segment is a part of a lung lobe. Accordingly, in this case a separate segment becomes inflamed. As a rule, it is also adjacent to the large bronchi through which the infection has spread.
- Lobar pneumonia. The whole lobe becomes inflamed. One of the heaviest varieties.
- Drain type. This is the name of a type of pathology when lesions of several segments or lobes merge.
- Total, or generalized variety. Inflammation covers the entire lungs.
Separately, we need to dwell on the last variety. As you know, the lungs are a paired organ, and therefore the total type can be either unilateral or bilateral. Lobar or segmental lesions may also be found in both lungs.
Why is pneumonia dangerous?
Pneumonia is one of a number of diseases, ignoring which will lead to inevitable complications. In particular, many patients with pneumonia develop chronic bronchitis, swelling or an abscess. It is worth noting that complications are not always pulmonary in nature; the development of hepatitis, anemia, encephalitis and other ailments is also possible.
Read more about hepatitis: Symptoms and treatment of hepatitis in cats
In a severe form of pneumonia in a cat, most of the lung is destroyed, which leads to respiratory or heart failure, general weakening of the animal’s body and infectious-toxic shock. The amount of toxins can significantly exceed the norm - this will significantly increase the load on the liver and kidneys, and failure of these organs is quite possible. Often, for a kitten suffering from pneumonia, everything ends in death, since the body of this little creature simply cannot withstand such serious complications. It is quite easy to prevent complications and sad consequences - it is necessary to begin proper treatment at the first symptoms.
Classification of antibiotics
All antibacterial agents can be divided into 5 categories according to their characteristics and range of application. Let's take a closer look at this classification:
Mechanism of action:
- Bactericidal - the active substances of the drugs completely destroy bacteria and viruses. After taking such strong drugs, all pathogenic microflora in the human body dies.
- Bacteriostatic – inhibits the growth or spread of viruses. Thus, the cells remain “alive” without forming pathogenic flora.
Symptoms
In the initial stages, pneumonia is quite difficult to distinguish from any other respiratory tract disease: the symptoms will be very typical. The cat's body temperature often rises to 41 degrees, loss of appetite, increased thirst, depressed and depressed state, and dry nose are observed.
As the disease progresses, the signs of pneumonia will become more characteristic. You will begin to notice increased salivation, frequent coughing and wheezing will appear (at first the cough will be dry, but over time the release of phlegm from the lungs will begin). A febrile state is also likely due to a constantly high temperature; mucus may be discharged from the nose.
Another characteristic symptom of pneumonia in a cat is cyanosis , which is the acquisition of a bluish tint by the mucous membranes. When the pet has pneumonia, it becomes very difficult to breathe; the tongue will constantly stick out. Sometimes pneumonia is accompanied by painful sensations in the lung area when coughing - the cat may meow pitifully. Do not delay contacting the veterinary clinic, do not wait for a whole bunch of symptoms to appear, otherwise the likelihood of successful treatment will be less.
Brief description and main symptoms
The risk group includes old animals and kittens - those cats whose body’s defense system is weakened. However, young, energetic animals can also fall victim to the disease. If the disease is detected in time and treatment is started, negative consequences can be avoided.
A responsible owner needs to know the first signs by which the disease can be identified:
- The cough is dry at first, then wet.
- Breathing with whistling and wheezing.
- Apathy. The previously active pet now tries to hide, remain alone, and does not want to play with the owner.
- Refusal of food. The cat may consume liquid, but may also refuse water.
- Significant increase in heart rate.
- Dry nose or discharge.
After detecting these symptoms, it is important to contact a veterinarian who will prescribe treatment.
Diagnostics: tests, x-rays and bronchoscopy
Diagnosis of pneumonia begins with a visual examination of the cat, measuring body temperature, and listening to the sternum area with a phonendoscope for the presence of wheezing. The veterinarian will definitely take a general blood test to determine the level of leukocytes (during inflammatory processes in the body, their level is usually higher than normal).
One of the effective methods for diagnosing pneumonia in a cat is radiographic examination, which is a method of dynamic examination using x-rays. In real time, using this device, the veterinarian is able to monitor the condition of the animal’s internal organs and select the most suitable projection for the image in order to determine the presence or absence of inflamed elements in the lungs.
In cases where the results of radiographic examination are in doubt, veterinary medicine resorts to bronchoscopy. This is the introduction of a thin bronchoscope into the trachea and bronchi for direct examination and a more detailed examination of their condition. This type of diagnosis can also be used to perform a biopsy for further histological examination and removal of foreign bodies (if necessary).
Diagnosis of inflammation in a clinical setting
In practice, owners and veterinarians are often faced with a typical problem: despite the severity and brightness of the symptoms, it is impossible to make a diagnosis based on the clinical picture alone. A serious diagnosis of inflammation in a clinical setting is necessary:
- First, the specialist will carefully examine the animal and collect a detailed history (when the cat got sick, what preceded it, etc.).
- If pneumonia or other diseases of the respiratory system are suspected, listening to the chest using a phonendoscope will always be a mandatory diagnostic step. A competent specialist will already be able to determine the source of inflammation and its area at this stage.
- Chest percussion (tapping) may also be used. Again, for an experienced veterinarian, the method can provide a lot of valuable information about the location and size of the inflammatory focus. But! When it is located deep in the pulmonary lobes, beyond the reach of percussion, this technique gives results of dubious value.
- But still, the main diagnostic methods are fluoroscopy and ultrasound examination of the chest.
Treatment of pneumonia in cats
After diagnosis, the veterinarian decides whether the cat needs to be treated in a hospital or in intensive care, since in severe cases of pneumonia it is important to constantly monitor the patient’s condition. But very often owners of mustaches do not delay contacting a veterinary clinic, and treatment can be done easily at home.
A course of antibiotics, antipyretic and anti-inflammatory drugs must be prescribed. The duration of treatment is approximately three to six weeks. If we are talking about pneumonia in a kitten, then it is necessary to prescribe more gentle remedies so as not to damage the immune system at such an early age.
Throughout the entire treatment, the cat must be created with special conditions: ensure complete rest, the room should be warm, no drafts or cold floors, and a humidifier will not hurt. Often, to maintain intestinal microflora when taking antibiotics, vitamins and preparations containing lactobacilli are prescribed. It is very useful for a cat with pneumonia to carry out a special massage, which consists of lightly tapping the sternum with your fingertips to facilitate coughing. The water must be slightly above room temperature, no tap or refrigerator water.
How to prepare a cat for an x-ray
There is absolutely nothing complicated about how to prepare a cat for an x-ray:
- It is highly advisable to keep your pet hungry before x-rays. The fact is that in some cases general anesthesia (anesthesia) may be required, since during the examination the animal must be absolutely calm. Without anesthetic drugs, this can be difficult or even impossible to achieve. The problem is that during anesthesia the peristalsis of smooth muscles changes. If there are food masses in the stomach, vomiting will occur. And vomit will almost certainly end up in the lungs, which further contributes to the development of aspiration pneumonia. To avoid this, the animal is not fed five hours before the procedure, and water is not given two hours before the test.
- Antitussives may be needed to suppress the cough reflex. Only a veterinarian prescribes them, since these drugs are not always needed!
New generation antibacterial agents
The difference between the latest generations of antibiotics and their earlier versions is a more advanced formula of the active substance. Active components specifically eliminate only pathological reactions in the cell. For example, new generation intestinal antibiotics do not disrupt the microflora of the gastrointestinal tract. At the same time, they fight an entire “army” of infectious agents.
The newest antibacterial drugs are divided into five groups:
- Tetracycline – tetracycline.
- Aminoglycosides – streptomycin.
- Penicillin series - amoxicillin and others.
- Amphenicols – chloramphenicol.
- Carbapenem group – meropenem, imipenem, invaz.
Let's consider several well-known antimicrobial agents of imported and Russian production.
Amoxicillin is an imported antimicrobial drug from the penicillin group. Used in medical practice to treat bacterial infections. Effective for intestinal infections, sinusitis, sore throat, Lyme disease, dysentery, sepsis.
Avelox is the latest generation of medications from the group of fluoroquinolones. It has a strong effect on bacterial and atypical pathogens. Does not harm the kidneys and gastrointestinal tract. Used for acute and chronic diseases.
Cephalosporins are third generation antibiotics. This group includes Ceftibuten, Ceftriaxone and others. Used to treat pyelonephritis and pneumonia. In general, these are safe products with few side effects. However, they should be taken only after consulting a doctor. There are many medications, but a specialist will recommend which one to choose.
Doriprex is an imported antimicrobial drug of synthetic origin. Showed good results in the treatment of pneumonia, advanced intra-abdominal infections, pyelonephritis.
Invaz is an antibacterial agent from the carbapenem group. Available in ampoules for parenteral administration. Shows a rapid effect in the treatment of bacterial disorders of the skin, soft tissues, urinary tract infections, pneumonia, septicemia.
Augmetin is a third generation semi-synthetic penicillin with the addition of enhancing inhibitors. Pediatricians recognize it as the best comprehensive medication for the treatment of childhood sinusitis, bronchitis, tonsillitis and other respiratory tract infections.
Cefamandole is a Russian-made antibacterial agent. Belongs to the group of third generation cephalosporins. Used to treat intestinal infections, pathogens of genital infections. As an antimicrobial agent with a wide range of effects, it is used for colds.
By composition
Antibacterial drugs are divided into 6 groups:
- Penicillins are the first antimicrobial drugs, obtained back in 1928 from a biological substance (Penicillium fungi). For a long time they remained the most popular medicine for the treatment of infectious diseases.
- Cephalosporins belong to the group of the most powerful antimicrobial agents with a wide range of applications. They completely destroy pathogenic flora and are well tolerated by humans.
- Macrolides are the name of a group of narrow-range antimicrobial agents. They do not destroy the diseased cell, but only stop its growth. This category includes the following drugs: erythromycin, spiramycin, azithromycin.
- Tetracyclines are good drugs for the treatment of infectious diseases of the respiratory and urinary tract.
- Fluoroquinolones are antimicrobial agents with a wide range of effects. Completely destroy pathogenic microorganisms. You can find 1st-2nd generation medications on sale. Doctors usually prescribe them to combat Pseudomonas aeruginosa.
- Aminoglycosides are antimicrobial drugs with a wide range of applications. Popular drugs in this group - streptomycin (therapy of tuberculosis, plague) and gentamicin - are used as ointments, eye drops, and injections for ophthalmic infections.
Generations of drugs. Advanced antimicrobial drugs already have six generations. For example, penicillin was the first drug of natural origin, while the third or sixth generation is an already improved version, which includes the strongest inhibitors. The relationship is direct: the newer the generation, the more effective the effect of drugs on pathogenic microflora.
By method of administration. Oral – taken by mouth. These are various syrups, tablets, soluble capsules, suspensions. Parenteral - administered intravenously or intramuscularly. They work faster than oral medications. Rectal medications are injected into the rectum.
Important! Taking antibiotics is allowed only after consulting a doctor, otherwise antibiotic resistance will develop.
Summary
We reviewed Russian and imported broad-spectrum antibiotics and briefly described the classification of drugs. Let's answer the question: which antibacterial agents to choose?
It is important to understand that antimicrobial drugs for extensive use are toxic and therefore negatively affect the microflora. In addition, bacteria mutate, which means the drugs lose their effectiveness. Therefore, antibacterial agents with the latest structure will be a priority over their earlier counterparts.
Self-medication with antibiotics is dangerous to health. In case of an infectious disease, the first step is to consult a doctor. The specialist will determine the cause of the disease and prescribe effective antibacterial agents. Self-medication “at random” leads to the development of antibiotic resistance.