The appearance of dubious spots on the skin, which sometimes itch and flake, is a serious reason to consult a doctor and check for dermatological diseases.
Pityriasis rosea (Giber's disease, roseola exfoliates, pityriasis, pithiasis) is an acute skin disease with specific rashes, a peculiar course and a tendency to seasonal relapses. It manifests itself in the formation of pink spots on the skin of the chest, back, limbs and other parts of the body, located along the lines of maximum extensibility (Langer's lines). Over time, the rashes become like large medallions. From the moment the first maternal plaque (large spot) is detected until the symptoms of the disease completely disappear, 30-45 days pass.
At CELT you can consult a dermatologist.
- Initial consultation – 3,500
- Repeated consultation – 2,300
Make an appointment
What is feline ringworm
Feline ringworm is a highly contagious (highly contagious) infection. The natural reservoir for microorganisms is often cats, although the infection can be transmitted from dogs and rodents.
Once the fungal spore gets on the skin, it germinates like a seed. Thanks to special substances on the surface of this reproductive structure, it attaches to the body. 4–6 hours after this, germ tubes form and penetrate into the surface layers of the skin.
The thread-like formations (hyphae) of the fungus grow in depth and breadth. They receive the nutrients they need for growth from the surrounding tissues. Hyphae damage the outer layer of skin, hair, and hair follicles. After about 7 days, they also begin to reproduce.
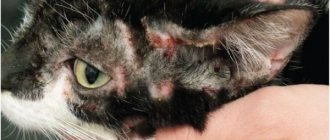
The infection is very contagious, so it is important to recognize it in time. However, feline ringworm is often difficult to detect. Your pet may have round, thickened lesions with lost hair. And sometimes lichen appears only as a gray coating under the fur.
Interesting! Feline ringworm can heal on its own if the cat has a strong immune system. But representatives of the Persian breed, as well as young individuals (up to 1 year), are more sensitive to the fungus, so it is difficult to cure it in them. In some cases, pets have to be euthanized.
Ringworm is classified as a zoonotic infection that is transmitted from animals to people. Feline lichen in humans manifests itself with unpleasant symptoms and can cause complications, so comprehensive treatment is necessary for both the pet and the owner.
Prevention
To prevent the development of lichen, it is enough to carefully care for your cat. To do this, you should not let your pet go for a walk on his own. We must protect him from all parasites. After walks, the coat should be washed and combed daily. The diet should include not only raw food, but also a variety of meats, dairy products and vitamins. When the first signs of the disease appear, it is better not to ignore them, but to immediately consult a doctor, because lichen is similar to an allergic reaction. It is recommended to take vaccines against infections.
Pathogens of dermatophytosis
The development of lichen is provoked by filamentous fungi. Depending on the main reservoir, they are divided into anthropophilic, zoophilic, and geophilic. The first can spread from person to person, the second can spread from animals to people, and the third lives in the soil.
Most often, ringworm in cats is caused by a fungus called Microsporumcanis (Latin for canine microsporia). According to statistics, it provokes the development of lichen in 92% of cats and 65% of dogs. According to scientists, other representatives of dermatophytes are transmitted to pets from the rodents they hunt.
Infection with lichen through soil occurs quite rarely.
Types of lichen in cats
There are 5 known varieties of lichen in cats:
- shearer (described above);
- multi-colored;
- pink;
- flat red;
- weeping (eczema).
How and how much lichen is treated depends on its type and the degree of neglect of the problem.
Pityriasis or multi-colored
You can tell that your pet has pityriasis versicolor by a yellow-brown spot with vague outlines that appears on the body. The variety received this name for the small scales in the affected area that resemble wheat bran.
If pityriasis versicolor in cats progresses, the spot increases in size, and the scales become different colors: pink, brown, yellow.
To eliminate the disease, the use of local antifungal drugs is sufficient. If a person or other animal has a weakened immune system, there is a risk of infection.
Pink or lichen giber
Another variety is pink or herpes zoster. Unlike ringworm, it is caused by viruses, not fungi. Initially, one itchy spot or plaque appears on the body. Then it breaks up into many small spots. The disease is characterized by severe itching and pink spots covering the entire body.
Pityriasis rosea in cats is often inherited and is contagious. The main reason for its development is weakened immunity, primarily due to poor nutrition.
Treatment is anti-allergy medications and immunostimulants. The duration of the disease depends on timely and correct treatment - from 4 days to a month.
Weeping
Eczema in a cat is often an allergic reaction to stress and physical irritants (harness, leash, collar).
The disease can begin with the appearance of a small rash, from which blisters filled with liquid gradually form. The bubbles burst, and the escaping liquid causes the fur to become wet.
Local treatment. Products with a drying effect and containing antibiotics are used. If there is no result, tinea versicolor in cats continues to be treated with antimycotic (antifungal) drugs.
Is lichen transmitted from cats to humans?
Cat lichen is dangerous for humans, as it is easily transmitted from pets to owners. You can become infected through direct contact with a cat or through various objects. The infection can be brought by a domestic cat after a walk or by its owner on shoes or clothes. Often, lichen infection occurs after contact with stray animals.
The causative agent of feline lichen is very dangerous because it is resistant to various chemicals and can also remain active in the environment for more than a year. Therefore, the cat and its owner are constantly at risk.
People from this group are most likely to be infected with shingles:
- child under 14 years of age;
- an elderly person over 60 years of age;
- women during pregnancy and lactation;
- people with reduced immunity.
Adults can also get sick, but the lichen will have a hidden course. Their immunity will quickly cope with the infectious agent.
Feline lichen in children is more complicated than in adults. According to statistics, children aged 3 to 8 years most often suffer from the disease. Their infection has an acute course, manifests itself in severe inflammation of the skin, and suppuration often forms. This is due to the fact that children have thinner and more sensitive skin, and their immunity is not yet fully developed.
The likelihood of contracting feline ringworm increases in the following cases:
- violation of personal hygiene rules;
- colds or chronic diseases in which the immune system is weakened;
- frequent contact with animals;
- the presence of wounds, scratches, abrasions, microcracks on the skin;
- increased humidity in the room;
- frequent stress;
- long course of antibiotics;
- a large number of allergens in the room.
These factors increase the risk of human infection with lichen, since the fungus enters a favorable environment where it actively develops.
Sources of infection, risk factors and pathogenesis
Dermatophyte spores also live in the soil, so they enter the house on outdoor shoes and clothes or with street air. Mice and rats become carriers.
Ringworm, regardless of the variety, is more common in animals with weakened immune systems.
The following factors predispose to this:
- chronic diseases;
- viral and bacterial infections;
- unbalanced diet;
- helminths and ectoparasites;
- long-term medication use.
The risk group includes kittens, elderly and young cats under one year old: their immune system either has not had time to strengthen or has weakened. The likelihood of infection with the fungus increases in long-haired animals and those who walk unattended.
Each type of lichen begins with a single lesion with damaged or lost hairs. Further development is different. With a disease of fungal etiology, new foci appear over time, they grow and merge. In the absence of treatment, the lesion becomes generalized and bacterial infectious diseases are added.
With rosacea, one maternal spot also appears first, then others surround it, but after 1–2 months they spontaneously disappear. The development of eczema is difficult to predict: the disease fades away if the causes are identified and eliminated in time.
How can you get infected?
Ringworm is transmitted from cats to humans through fungal spores. Main routes of infection:
- Direct contact with the animal. The largest number of spores is found on the fur or skin of a pet infected with lichen. If there are injuries (wounds, scratches) on the hands of the person stroking the cat, then the likelihood of contracting lichen seriously increases.
- Through loose particles or wool. The infection, which is transmitted through spores, can affect people even with minimal or no contact. The likelihood of contracting lichen increases when scales, dandruff, or hair from a sick animal come into contact with the skin.
- Through the soil. Infectious agents can remain viable in the soil for a long time. Therefore, there is a possibility of becoming infected with lichen when working in a personal plot, during a picnic or playing in the sandbox.
- Through clothes, shoes, various objects. Lichen spores may be present on toys, household items, furniture, shoes, and clothing.
Feline ringworm is also transmitted from person to person. To do this, it is enough to touch the skin, clothes, shoes and personal hygiene items of the infected person.
What to do at home
At home, the kitten must be isolated from other animals and from children, since lichen is easily transmitted to humans. You will have to wear gloves to treat wounds and bathe him, wash your hands especially often, and treat the room with antiseptics.
You should not allow your pet into bed; its bed must be frequently disinfected or the bedding changed, since fungal spores remain alive for a long time and can become a source of re-infection.
The kitten needs to be well fed and kept warm. He will have to wear an “Elizabethan collar” around his neck to prevent him from licking off medications, most of them toxic, or from scratching itchy wounds.
Signs and symptoms
To avoid infection with cat lichen, you need to be attentive to the health of your pets.
To do this, you need to notice the signs of infection in your cat in time:
- gray coating on the skin under the fur;
- the coat becomes dull, often becomes oily, and falls out in the affected area;
- skin manifestations in the form of round thickened formations with areas of hair loss;
- the claws become rough, scaly, and deformed.
In most cases, the head, chest, front legs, and back are affected. Sometimes a generalized infection occurs in which the fungus affects a large part of the body.
Cats infected with lichen become restless, depressed, and often scratch the affected area. Some pets refuse food.
Interesting! It is more difficult to detect ringworm in long-haired cats than in short-haired cats, since the affected areas are covered with hairs. Therefore, you need to regularly examine your pet, and if suspicious symptoms appear, visit a veterinarian.
The incubation period for lichen in humans after infection from a cat ranges from 7 to 14 days. Sometimes it can take up to 21 days for characteristic symptoms to appear.
Feline lichen in humans is manifested by the following symptoms:
- Ring-shaped formation on smooth skin. It looks like a pink round or oval spot with a red rim of small papules, which peels off in the middle.
- Plaques on the scalp. They look like bald spots that peel and turn red in the center. Their shape is irregular, the boundaries are barely noticeable.
- Itching, enlargement of lesions. Primary plaques on the head are itchy and grow, they affect a large area of skin, break off hairs at a height of 1–2 mm, which are covered with whitish scales. Several rounded formations with a rim on smooth skin merge.
- Ulcers. In the later stages or with severely weakened immunity, suppuration appears in the affected areas.
Feline ringworm in humans can manifest itself as damage to the nails (onychomycosis). Then they thicken, exfoliate, their color changes, spots and tubercles appear, they gradually become deformed and subsequently collapse.
Ringworm may be accompanied by a general deterioration in health, drowsiness, sometimes fever, and inflammation of the lymph nodes.
The fungus in humans is localized on the hands, face, scalp (temple, back of the head), torso, groin area or buttocks.
The symptoms described above are a reason to visit the veterinarian. After all, complications from lichen can be very dangerous (abscess, visual impairment up to blindness, tumor processes, hearing problems).
Common signs of ringworm
To properly begin treatment for lichen, it is necessary to carefully study the symptoms of this disease:
- Formation of small bald patches. They are very difficult to notice, because the loss of a piece of hair can be confused with anything. At this stage, the pet behaves as usual and does not lose its appetite, so it is very difficult to notice the disease at this stage.
- Baldness begins to manifest itself more strongly, forming individual spots. White spots that peel off begin to appear on some parts of the body.
- In later stages, baldness is pronounced and spots begin to spread throughout the skin. In the photo of ringworm, we can see that these spots are gray, yellow or red in color.
In advanced cases, the pet’s behavior changes and the appetite completely disappears. You should contact a veterinary clinic as soon as possible so that the doctor can correctly diagnose the disease and prescribe treatment.
Diagnosis of the disease
If you suspect feline lichen, you should visit a doctor. The dermatologist will conduct a visual examination of the skin, collect anamnesis, and prescribe the necessary tests:
- Luminescent diagnostics. The sick person sits down, the doctor turns off the light, and then illuminates the affected areas with a Wood's lamp. When fungus is detected, an apple-green glow appears. However, this method is not very reliable.
- Trichogramma. Hairs and scales are removed from the affected areas, which are then examined under a microscope. This method allows you to detect spores and hyphae of lichen.
- Sowing. The veterinarian collects biomaterial from focal formations and places it in a nutrient medium. After 3 days, the fungal colony grows.
The latter method is considered the most accurate, as it allows you to determine the causative agent of feline lichen in humans in the early stages. Cultures are also used to confirm recovery after a course of treatment.
Pityriasis rosea in pregnant women
Pityriasis occurs more often in women than in men. It is especially dangerous when the skin disease occurs in pregnant women. If you notice any rashes, it is important to immediately visit a dermatologist and undergo treatment. It is unacceptable to risk the baby’s health and expect the plaques to disappear on their own. If the disease is not treated, then bacterial infections appear, which are much more difficult to deal with.
If a pregnant woman has not been diagnosed with pityriasis rosea, it is nevertheless important to adhere to the following recommendations:
- clothing made from cotton and linen is preferable to synthetic and woolen fabrics
- limiting heavy physical activity
- For hygienic purposes, use only warm water
- timely moisturizing of damaged skin areas
Treatment methods
Treatment of lichen from a cat in humans should be comprehensive:
- systemic antifungal drugs;
- topical medications;
- sanitary and hygienic treatment of the premises.
Important! Self-treatment or monotherapy using folk remedies is ineffective and often even dangerous, as it can lead to the proliferation of lichen throughout the body. Then you will have to eliminate the consequences of the infection, and the treatment will be delayed. Therefore, it is better to immediately carry out competent therapy under the supervision of an experienced veterinarian.
A sick person should minimize contact with healthy family members. It is important that both the owner of the cat and the animal itself that infected it with lichen undergo treatment. The treatment plan is drawn up by a veterinarian, taking into account the severity of the disease, age, and characteristics of the body.
During the treatment of feline lichen, the following recommendations must be followed:
- Cut the hair on the damaged area of the head short to stop the spread of the infectious agent. It is recommended to repeat this procedure every week.
- Eat properly. A sick person should give up sweets, spicy, salty, fried foods. It is recommended to supplement your diet with fresh vegetables, fruits, herbs, cereals, lean meat, and fish.
- Drink at least 1.5 liters of filtered water per day to speed up metabolic processes.
- It is recommended to use antifungal shampoos to wash your hair.
- It is necessary to regularly disinfect clothes, shoes, and personal hygiene items.
- Wear comfortable clothes made from natural fabrics.
- Avoid excessive sweating and change clothes if necessary.
- Strengthen the immune system with vitamin and mineral complexes.
- Remove allergen sources from the sick child's room, such as soft toys.
- Ventilate the room daily.
- Replace bathtub with shower. Do not soak plaques for a long time or rub them with a washcloth.
These recommendations will help speed up the healing process.
Treatment for feline lichen in humans takes an average of 6–8 weeks. In advanced cases, it drags on for several months. To speed up this process, you need to start treatment in the early stages, and also strictly follow the doctor’s recommendations.
Important! Veterinarians recommend treating feline tinea until the person has 2 negative culture results. Otherwise, asymptomatic carriage or relapse of infection is possible.
Local antifungal therapy
You can treat cat lichen at home using topical medications. They are used in the early stages of infection, as well as as part of complex therapy.
The following drugs are used to treat lichen:
- Sulfur-tar or sulfur-salicylic ointment for lichen. It has a thick consistency, relieves inflammation, and has an antimicrobial effect.
- Clotrimazole, Amyclone, Candibene, Dermazole, Lamisil, Mycoseptin and other drugs based on clotrimazole and micoconazole. They stop the further spread of cat lichen and destroy the fungus. The drugs are produced in the form of ointments, creams, and solutions.
- Travocort, Triderm are combination drugs that contain steroid hormones. They are used under the supervision of a veterinarian and only in severe cases. They have anti-inflammatory, antifungal, antipruritic, antiallergic effects.
- Ketoconazole is a 2nd generation drug for the treatment of mycoses. This is an effective but toxic remedy.
- Bifonazole is a broad-spectrum antifungal drug.
The medications described above have an impressive list of contraindications and can also cause adverse reactions. Therefore, they are included in the treatment plan only for medical reasons.
To wash your hair when treating feline ringworm, you need to use special shampoos, for example Nizoral, Sebozol, Sulsena, Dermazol, Exoderil, Keto Plus. They contain antifungal components.
To dry out lesions, relieve inflammation, and accelerate tissue regeneration, a person infected with lichen should use drugs based on iodine or alcohol in the form of a solution: Iodipron, Iodinol, Degmicide, Nitrofungin. They are suitable for treating lichen lesions on scalp areas of the body.
Sprays are used to eliminate large areas that have been affected by lichen. Lamisil, Lamicon, Kanesten, Fungoterbin are most often prescribed.
Systemic therapy
Feline ringworm in humans in advanced stages should be treated with antifungal drugs in the form of tablets and capsules:
- Fluconazole is a synthetic antifungal drug for the prevention and treatment of infection.
- Lamisil is an antimycotic with a broad spectrum of action and a low likelihood of adverse reactions.
- Orungal is effective against dermatophytes and other fungi.
- Griseofulvin has antifungal and fungistatic effects.
- Mycozoral demonstrates a fungicidal or fungistatic effect.
Antimycotics, together with topical drugs, give faster results in the treatment of feline lichen. However, medications should only be taken after veterinarian approval as they are toxic and can also cause serious adverse reactions. The treatment regimen and dosage are selected by a specialist.
Antifungal drugs are often combined with immunostimulating agents, for example Amiksin, Likopid, Tamerit.
Treatment of premises and care items
Fungal spores on infected hairs, skin flakes or dandruff are regularly released into the environment. To clean the house, speed up recovery, and also protect healthy family members from infection, you need to regularly carry out sanitary and hygienic treatment.
A cat with shingles is isolated in a room where it will be easier to clean up after it. And it is better for the infected person to live in a room where there are no carpets and little furniture. This will simplify the task, since cleaning must be done daily.
It is recommended that an animal infected with lichen be cut short during treatment, and then regularly treat foci of infection to reduce the risk of its spread. After this, you need to thoroughly vacuum the floor, as well as the furniture in the room. Then wash all surfaces with water with added bleach (4 liters of water per 500 ml of chlorine bleach).
This concentration is suitable for washing floors; to treat other surfaces, you need to reduce the dose of bleach.
Clothing that has touched the lichen lesion should be washed using disinfectants every day. This applies to shoes, household items, such as towels and combs. Trays and bowls of cats infected with shingles should be disinfected daily.
Traditional methods
Traditional medicine is effective only as part of complex therapy. They are not suitable for self-treatment.
Folk remedies for the treatment of feline lichen in humans:
- Mix iodine with vodka in a 1:1 ratio. Plaques need to be lubricated 2-3 times a day.
- Combine birch tar with fish oil (1:1). The mixture is rubbed in twice a day.
- Ringworm spots are rubbed with moistened tar soap, the product is left for 5-10 minutes, and then washed off and dried the affected area of the skin.
- A piece of bandage or gauze is moistened with apple cider vinegar and applied to the area affected by lichen for 10–15 minutes. The procedure is repeated 5–6 times a day.
- 2 Aspirin tablets are crushed and added to a bottle of iodine. The mixture should be applied to the areas of infection in a thin layer twice a day.
- Lichen plaques are wiped with propolis tincture 3-5 times a day. You can also use calendula tincture.
- 2 tsp. Birch buds are filled with 250 ml of alcohol. Then they are left in a dark place for 2 weeks. Apply the tincture 3–5 times.
Folk remedies for the treatment of feline ringworm are used after the approval of a doctor.