The occurrence of vomiting in a cat without vomiting can be a consequence of both physiological and pathological factors. If, apart from this symptom, nothing indicates a disease, and the animal remains active, then there is no need to worry. But the depressed state of the pet, unnatural body position or pain syndrome is a reason for an urgent visit to the veterinarian.
Despite the fact that only a specialist can identify the exact cause of a cat’s gag reflex without vomiting, it is important for owners to know the warning signs that indicate the development of pathology.
Current problem
For most people, heartburn is simply an occasional discomfort. Approximately 20% of the population of highly developed countries experience it at least once a month.
But for the 6% of people who have a chronic form of heartburn known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), unresolved (untreated) symptoms can lead to various health complications. People with erosions in the lining of the esophagus due to acid reflux often do not realize the harm of GERD until they have advanced stages of the disease.
If you experience frequent or prolonged heartburn (twice a week on a regular basis), consult your doctor. Here are nine reasons why you shouldn't ignore the symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease.
The cat often burps: reasons
Regurgitation in cats is normal and occurs for the following reasons:
- Regurgitation of semi-digested food by a lactating cat occurs in order to accustom kittens to solid food.
- Toxicosis of pregnancy: occurs after two decades of gestation, when other signs have not yet appeared.
- Gluttony: wild ancestors did not have a successful hunt every day. Therefore, the animals ate for future use. But, too much food is worse than not enough. The same thing happens if the owners try to give dry food according to the norm. Or there are competitors in the apartment. The animal attacks the pellets and eats too quickly. He doesn’t have time to drink anything, dry food absorbs moisture from the gastric mucosa. The body expels dangerous food to prevent dehydration.
- Residual effects of drugs. If the animal is fed after surgery, it will vomit.
- Hungry vomiting occurs in the morning, when an animal that is accustomed to eating by the hour forgot to feed it on time. A white foamy mass appears.
- Motion sickness in transport after feeding. Pieces of food shake and irritate the walls of the stomach.
- Hairballs that a long-haired pet swallows while licking can mix with food, form trichobezoars and block the intestinal lumen. To prevent this from happening, the cat begins to cough, vomit and regurgitate dangerous lumps.
- Soured or moldy food. With improper or prolonged feeding, peroxides are formed, which the body perceives as poisons and tries to get rid of them in every possible way. An opened bag of dry food can be stored for 40 days, and a can in the refrigerator can be stored for 36 hours.
- An excess of cereals or bread with a lack of meat and vegetables is perceived by the body as spoiled food.
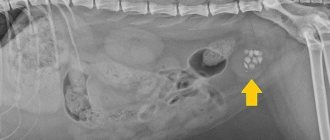
- Foreign object: if it comes out, vomiting stops. Otherwise, urgent veterinary attention is required.
Be sure to read:
Vomiting in a cat: causes, what different types of vomit indicate, first aid, treatment, when it is not dangerous
Development of inflammation in the esophagus (esophagitis)
In gastroesophageal reflux disease, food, acid, and digestive juices back up into the esophagus. Over time, this causes irritation and swelling of the mucous membrane lining the inside of the esophagus. This is esophagitis. If acid exposure in the esophagus is observed for just a few weeks, then inflammation of the mucous membrane can already develop. This can cause discomfort and even pain along the midline of the abdominal wall, “in the pit of the stomach,” where the right and left ribs meet at the sternum. This inflammation makes the esophagus vulnerable to even more dangerous conditions - erosions or scars.
Esophageal stricture
If esophagitis continues for too long, the resulting scar tissue can narrow the esophagus. This stricture can lead to difficulty passing and swallowing food, which can become stuck at the level of scar tissue, causing pain.
Large pieces of food may become stuck and this situation may require endoscopic intervention to remove them. The stricture may cause frequent choking when eating. Because of this, patients often refuse to eat and lose a lot of weight.
Stricture is treated by widening or stretching the esophagus (bougienage or dilatation). These treatment procedures can have multiple effects on the stricture. But taking stomach acid blockers (proton pump inhibitors, PPIs, or H2 blockers) may prevent scarring in the esophagus from returning in the future.
Throat and voice problems
The main symptom of gastroesophageal reflux disease is heartburn, but not all people feel or report it. They may have other symptoms that are more difficult to diagnose. Doctors call these cases "silent reflux," or asymptomatic reflux. The patient may not have heartburn as classically described in textbooks, but they may have various other problems that occur outside the esophagus, such as hoarseness, voice changes, sore throat, or chronic cough. They feel as if there is a lump or hair in their throat and constantly have to clear their throat by coughing and clearing their throat.
Breathing problems
If stomach acid accidentally flows into the windpipe after gastroesophageal reflux disease causes it to enter the esophagus, GERD can worsen asthma or pneumonia. Even without lung problems, GERD can cause shortness of breath and difficulty breathing. And treatment in this situation can be a double-edged sword. Because GERD medications, such as proton pump inhibitors, may actually increase the risk of pneumonia. (They can promote bacterial growth and suppress coughing, which is designed to help clear the lungs.)
Pay your doctor's attention to your lung function when treating reflux.
Types of cough in cats
Coughing in cats is always a symptom of some disease or condition; it occurs infrequently and looks like an alarming indicator of a cat’s health problems. Smart cats skillfully avoid situations that provoke coughing - they show less physical and emotional activity, try to stay in places with good ventilation, so coughing will not always be the initial sign when a disease occurs.
The cough is reflexive in nature and appears when the respiratory tract receptors are irritated; it helps cleanse the mucous membrane from various irritants of a mechanical, chemical and microbial nature. A cough usually manifests itself quite characteristically: by contracting the diaphragm and respiratory muscles, the cat draws in its stomach and arches its back, its neck is usually stretched down; she makes abrupt coughing and wheezing sounds.
It is necessary to pay attention to the nature of the cough, the circumstances causing it, as well as other symptoms that help identify the disease.
When coughing, the cat takes a typical pose
According to the main parameters, cough can be divided into:
- dry and wet: a wet cough is accompanied by sputum production; with a dry cough there is no phlegm, it is more severe;
- by sound: the sound can be muffled or ringing;
- by duration: a cough that occurs for the first time, the duration of which does not exceed a week, is considered acute. Chronic cough may be present for months;
- in connection with the time of day or year: morning, daytime, evening and night cough;
- spring, summer, winter, autumn;
Cough with a foreign body in the throat
A foreign body in the upper respiratory tract in cats is rare and manifests itself as a sudden attack of severe coughing, suffocation, and cyanosis of the mucous membranes, which is never observed, for example, when a cat tries to regurgitate a hairball from the stomach. The pet should be taken to a veterinary clinic as quickly as possible to remove the foreign body.
Cough from inhaling irritants
Inhaling the odors of household chemicals, perfumes, and cigarette smoke can provoke a coughing attack in a cat, which is usually accompanied by sneezing. Coughing and sneezing occur directly under the influence of an irritating odor.
The first thing you should make sure of when a cat suddenly coughs is that there is no foreign body in the respiratory tract, which is manifested by difficulty breathing, cyanosis of the mucous membranes
Cough due to illness
Cough is a valuable diagnostic sign for a number of diseases.
Respiratory viral infections
Cough appears in infectious diseases that involve the respiratory system. Along with a cough, the following is usually observed:
- fever;
- general oppression;
- lack of appetite;
- depending on the type of pathogen, it may be: conjunctivitis;
- diarrhea;
- elements of a skin rash or lesions of the mucous membranes.
The nature of the cough changes during the course of the disease: from dry it becomes wet.
Asthma
Asthma is a chronic inflammatory disease of the respiratory tract, in which cells of the immune system take an active part. The cause of asthma is an allergy, very often to pollen, household chemicals, but, theoretically, it can be any substance. Asthma is characterized by attacks of spastic contraction of the bronchi, which is manifested by convulsive cough and shortness of breath; the cat breathes with its mouth open. The cough manifests itself in attacks, with no cough in between. There is also no fever or other manifestations characteristic of the development of an infectious disease. Asthma is characterized by seasonality - spring-autumn, as well as a tendency to night coughing attacks, this is due to the weakening of natural sympathetic innervation at night, which prevents the narrowing of the bronchi.
In asthma, the cough has a paroxysmal character, often associated with exposure to an allergen, for example, pollen.
Pneumonia
Pneumonia usually occurs as a complication of an ongoing infectious disease and is characterized by a deterioration in the condition in the form of increased fever, progression of general depression, and severe cough with sputum. Sometimes pneumonia is caused by nonspecific flora, for example, when a cat is severely hypothermic, if it has heart failure or immunodeficiency conditions.
Helminthiasis
With some helminthiasis, cough occurs when worm larvae migrate and are carried into the bronchi and lungs through the bloodstream. Cough due to helminthiasis is short-lived and moderate in nature, and may result in vomiting. In some cases, with massive infection by helminths, they penetrate into the stomach and esophagus, which also causes coughing.
Heart diseases
With heart disease, its size gradually increases; the enlarged heart puts pressure on the trachea, causing coughing. A cough in heart disease sounds muffled and is not accompanied by sputum production; develops gradually and intensifies with physical activity. In parallel, you can find other symptoms of heart disease:
- weight loss;
- pallor or cyanosis of the mucous membranes and unpigmented nose;
- increasing weakness and lethargy of the cat;
- heart rhythm disturbances;
- with the development of ascites, the size of the abdomen increases;
- fainting.
Chest injuries
In case of chest injuries, surgical emergencies may occur, accompanied by coughing:
- pneumothorax - accumulation of air in the pleural cavity as a result of injury to lung tissue by a broken rib;
- hemothorax - accumulation of blood in the pleural cavity due to injury to a blood vessel;
- chylothorax - if, as a result of a chest injury, the thoracic lymphatic duct ruptures, lymph accumulates in the pleural cavity;
- diaphragmatic hernia - in case of severe injuries, the diaphragm ruptures and the abdominal organs exit into the chest; At the same time, shortness of breath and cough develop.
These are severe life-threatening conditions in which shortness of breath, cardiac dysfunction, and shock are observed. The cat's life depends on how quickly it is taken to the veterinarian. The veterinary clinic carries out a complex of anti-shock measures and drainage of the damaged pleural cavity with the removal of air or accumulated fluids, which helps to straighten the lung and restore its function.
Esophageal ulcers
Stomach acid can erode the lining of the esophagus, causing sores and ulcers. Esophageal ulcers are different from stomach ulcers, which are usually caused by bacteria. People with wounds and sores may spit up blood and may also vomit blood. They may see blood in their stool. The blood may be red, cherry red, or like coffee particles. In stool, blood from the esophagus and stomach usually turns black when passing through the small intestine, the color and appearance of oil - viscous, slippery, and difficult to wash off.
Contact your doctor immediately if you have these symptoms. Endoscopy can detect ulcers of the esophagus. Acid-blocking or acid-lowering medications may make them disappear.
Preventing regurgitation after eating in cats
To combat regurgitation, the following measures are taken:
- do not overfeed your pets, it is better to reduce portions and give them more often;
- prevent food spoilage: an opened bag of granules should be fed 40 days in advance, canned food 36 hours in advance when stored in the refrigerator;
- do not feed your pet less than 2 hours before traveling in a car;
- comb long-haired pets to minimize hair getting into the stomach when licking;
- To ensure that the hairs do not clump and come out with feces, use Malt paste or specialized super premium food.
Barrett's esophagus
If left untreated for many years, persistent acid reflux can form changes in cells known as Barrett's esophagus, which is considered a precancerous condition. This condition does not cause many symptoms other than those of reflux. A doctor can diagnose it by performing an endoscopy.
If you have heartburn more than twice a week for a long time, or if you have symptoms of gastroesophageal reflux disease that are getting worse or you have discovered new ones that you didn't have before, these are all reasons to get checked and have an endoscopy.
What can you do at home?
Rare episodes of vomiting in a cat without deterioration in general health should not cause concern. However, if a cat shows signs of nausea and sits for a long time in an unnatural position, as if choking, this becomes a serious reason to contact a veterinarian.
Important! If cats are vomiting, you should call a veterinarian at home. Firstly, transportation can additionally provoke a vomiting reaction, and secondly, if the pet has swallowed a sharp object, then transportation is unacceptable.
Before the doctor arrives, you need to carefully monitor all changes in the cat’s behavior and well-being. It is worth checking the integrity and presence of medications, household chemicals and other toxic substances that your pet may have swallowed. You should also make sure that the cat is not chewing on indoor plants.
Note! If large stocks of industrial dry food are stored in the house, then it is worth making sure that they are safe. Often vomiting and poor health are the result of such overeating.
It is forbidden to give cats medications that prevent vomiting, painkillers and other drugs that can hide the symptoms of the underlying disease. But at the same time, owners should know what to do when a cat has the urge to vomit, but does not vomit:
- Provide the cat with a starvation diet, remove all food from the animal’s field of vision, since in some cases even the sight of food can trigger an attack of nausea.
- Provide your pet with free access to water (it should be clean and fresh).
- Isolate the cat from other animals - move it to a quiet, dark place where there are no drafts.
- In case of frequent vomiting and fluid refusal, it is necessary to inject a saline solution subcutaneously into the withers area and on both sides along the spinal column (in the form of a pearl necklace). If you have experience, it is better to do an intravenous injection.
If nausea is caused by intoxication, the cat may begin to shake. In this case, it must be covered with a warm blanket.
You need to monitor whether the cat goes to the toilet. You must inform your doctor about prolonged absence of urination or the presence of blood in the urine during the telephone call. If we are talking about an attack of urolithiasis, then the animal needs urgent hospitalization.
Esophageal carcinoma
In very serious cases, untreated gastroesophageal reflux disease (and subsequent Barrett's esophagus) can lead to esophageal cancer. The main risk factors are alcohol consumption, smoking, poor nutrition, and chronic esophageal diseases with reflux.
Symptoms include weight loss, trouble swallowing, or gastrointestinal bleeding. This is something that happens over decades of untreated reflux (30-40 years), so those who are 30 and otherwise healthy have no reason to suspect cancer. But if you're over 50 and have had heartburn for years and suddenly lose weight, for example, this is definitely what your doctor will suspect first.
A cat spits up after eating: what to do?
The cause of vomiting is the presence of food in the gastrointestinal tract. Therefore, to stop vomiting, you need to eliminate the cause - that is, food. The cat is not fed for half a day, or better yet, for a day. But you shouldn’t get carried away, because after a two-day fast, the mechanism for extracting energy from fat depots turns on. Reserve nutrients rush to the liver and a dangerous disease develops - lipidosis.
You must show your will and not react to your pet’s extortion; even a small crumb of food causes reflex vomiting. If the animal reacts to drinking, it is removed, a veterinarian is called, and before his arrival, a saline solution is injected subcutaneously in unlimited quantities.
Be sure to read:
A cat is vomiting yellow liquid: normal or pathological, first aid, what to do, best medications, diet
The next day, the pet is given some easily digestible food in an amount of no more than 1/3 of the norm. They give him plenty of water and monitor his behavior. If no new vomiting follows, increase the portion, bringing it to normal.
During diet therapy, the use of dry granules is suspended and wet nutrition is used. It is not necessary to use Smecta or Enterosgel, however, sorbents will help normalize digestion.