What is cat scratch disease?
One of the human infectious diseases that can be contracted from an animal is cat scratch disease or felinosis. The source of infection is infected cats. In cats, these bacteria do not cause the disease, or its symptoms are practically undetectable. However, when scratched or bitten by such a cat, accompanied by minor damage, bacteria enter the skin with saliva, and then into the lymph, with the current of which they spread throughout the human body. The occurrence of the disease is also possible when the saliva of an infected animal gets on the mucous membrane of the eyes. The disease is characterized by summer-autumn seasonality. Young people and children are considered the most vulnerable.
The incubation period (the period from the moment of infection to the onset of symptoms of the disease) for cat scratch disease is on average 1-2 weeks, but can be shortened to 3 days or extended to 4-6 weeks. The typical form of infection has a certain cyclicity - the presence of three periods:
- Initial period;
- The period of the height of the disease;
- The period of convalescence (recovery).
Causes and risk factors
The causative agent of cat scratch disease is Rochalimaea henselae. Polymorphic non-motile gram-negative bacterium; is morphologically similar to representatives of the genus Rickettsia and exhibits similar properties to Afipia felis. A motile, non-fermenting, gram-negative rod-shaped bacterium. It is fastidious for in vitro cultivation, preferably grown on HeLa cells.
Risk factors for developing the disease:
- Disorders of cellular immune responses
- HIV infection, especially when the CD4+ lymphocyte count is below 100 in 1 μl
- Long-term use of GC, azathioprine, cyclophosphamide, cyclosporine, alcohol abuse.
Penetration of the pathogen through damaged skin or, less commonly, through the mucous membrane of the eye subsequently leads to the development of an inflammatory reaction in the form of a primary affect. Then, through the lymphatic ducts, the microbe enters the regional lymph nodes, which is accompanied by the occurrence of lymphadenitis. Morphological changes in the lymph nodes are characterized by reticulocellular hyperplasia, the formation of granulomas, and later microabscesses. The disease is usually accompanied by hematogenous dissemination with the involvement of other lymph nodes, liver, central nervous system, and myocardium in the pathological process. A severe and prolonged, and often atypical course of the disease is observed in patients with HIV infection.
Various mammals (cats, dogs, monkeys, etc.) are considered the reservoir and source of infection. The disease is registered everywhere. In regions with a temperate climate, an increase in incidence is noted from September to March. Considering the nature of the infection, the main contingent is persons under 21 years of age; 90% have a history of bites or scratches caused by kittens. Studies conducted on animals have shown that the microorganism does not cause the development of any pathology in them and they do not respond with the development of hypersensitivity reactions when the pathogen antigen is administered intradermally. Incidence: 10:100,000 population (25,000 cases annually).
Manifestations of cat scratch disease
At the site of the bite or scratch, swelling and redness occur, then skin papules form, which soon become suppurative. A rash may appear around the wound. At the same time, inflammatory changes occur in the lymph nodes close to the lesion. A person’s temperature rises and symptoms of intoxication occur (weakness, headaches, malaise, sweating). At the height of the disease, the liver and spleen may become enlarged. After some time (2-3 days), festering elements appear in place of the papules, which open, and subsequently crusts appear. The crusts dry out and fall off, after which no defects or skin pigmentation remain. This process can last from 1 to 3 weeks. Over time, the inflammation resolves, and sclerosing lesions form at the site of damage. If the immune system is insufficiently active, the pathogen can penetrate the blood and spread throughout the body, and various internal organs (liver, heart, vascular system and others) can be affected, with the development of similar foci of inflammation in them.
Atypical form
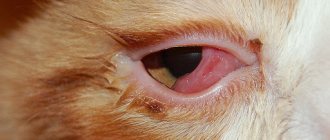
When infectious agents come into contact with the mucous membrane of the eye, there is a high risk of developing conjunctivitis. Symptoms in case of contact with skin:
- fever;
- the appearance of ulcers;
- suppuration of injuries;
- After healing, scars form.
This form of felinosis occurs in 10% of cases. It is usually diagnosed in children, as well as the elderly (people whose body reactivity is reduced). The duration of the disease is from 6 to 8 weeks.
Prevention
Prevention comes down to the following rules:
- After a cat bite, you should immediately wash the area with soap and water to disinfect the wound.
- Wash your hands with soap and water every time after playing with cats, especially for people with weakened immune systems.
- Since kittens under one year of age are most at risk of infection due to the presence of bacteria in the blood, people with weakened immune systems should adopt cats older than one year.
- It is not recommended to play with or pet stray cats.
- Cats should not be allowed to lick open wounds or scratches on the skin.
- Cats' nails should be trimmed.
- Veterinarian-approved flea control products should be used at all times.
- Cats should be kept indoors to reduce their exposure to fleas and avoid infestation.
If, however, you or your child are exposed to the infection described, do not risk self-medication, consult a doctor!
Where to go?
On the same or the next day, you must contact the City Center for the Prevention and Control of AIDS and Infectious Diseases at the address: emb. Obvodny Canal, 179-a, metro station "Baltiyskaya", tel.: 251-98-35; 251-98-27; 575-44-05.
Anonymous office: 4th floor, room. No. 7 and No. 12 from 9:00 – 19:00 daily, except weekends.
On weekends and holidays, you can contact the emergency department of Infectious Diseases Hospital No. 30 named after. Botkin at the address: st. Mirgorodskaya, 3; tel.: 717-27-15.
For the children's population: pediatricians are accepted at the address: Bumazhnaya str., 12; metro station “Narvskaya” from 9:00-16:00; tel.:786-66-39.
Eye injuries in children
Our nimble, restless children... They want to know so much. Constant movement is natural for babies. The largest number of “everyday” eye injuries occur on the street, in courtyards, i.e., where they spend their free time and, as a rule, are left to their own devices. Bumps, bruises and scratches are inevitable. What if your eye is damaged?...
An eye injury is a very serious injury. It can lead to complete blindness. In the structure of children's eye pathology, injuries occupy almost 10%. According to statistics, the greatest number of eye injuries occurs between the ages of 7 and 15 years. Eye injuries are most common in boys, since their games are generally more aggressive in nature. Most often, eye injury occurs due to the ingress of various small bodies into them: fragments of metal, stone, grains of sand and specks, husks of seeds, ears of grain, etc. Damage to the eyes of children from piercing and cutting objects: forks, scissors or explosives, often occurs during games and pranks due to parental oversight. The causes of injury can be: a blow to the eye with a stick, ball, puck, snowball, fist, etc. the eye is often injured by toys, the child may fall on the glass; or damage your eyes with school supplies - pencil, fountain pen, compass, ruler.
Depending on the source of injury, there are: mechanical injuries, eye burns, radiation damage to the eyes.
What's happening?
Common signs of eye injuries are pain and pain in the eye, lacrimation, photophobia, hemorrhage and automatic spasm of the eyelids.
Foreign bodies (grains of sand, midges, etc.) that get into the eye, lingering on the conjunctiva, cause lacrimation and an acute burning sensation in the eye, which intensifies with blinking.
The severity of a contusion (bruise) of the eye is determined by the location, force of the blow, the area of its application, and the shape of the wounding object. Non-penetrating injuries can cause hemorrhage into the eye, bruising, retinal and choroidal rupture, retinal detachment, and traumatic cataracts. Most often occurs due to impacts with blunt objects and bruises.
With penetrating injuries, a foreign body may remain in the membranes of the eyes. In this case, the victim feels a sharp pain in the eye and watery eyes. A person cannot look at the light, his vision decreases sharply. A penetrating wound and a bloody stain are visible on the eyeball. With a penetrating wound, complete destruction of the eyeball and loss of vision is possible.
Treatment of eye injuries
Treatment of victims should be carried out by an ophthalmologist, depending on the nature and severity of the injury.
First aid for a mild eye injury consists of instilling anti-inflammatory eye drops into the eye, applying a sterile bandage to the eye and urgently referring the victim to a specialist.
If there is a speck! Even such a seemingly insignificant problem can cause a lot of trouble if you do not respond in time. Is your baby complaining about pain in his eye and crying? That's when tears bring relief. There is a good chance that they will wash away debris and dust. You need to wash your eyes. Use warm, boiled water. Didn't have it at hand? Even tap water will do! The main thing is to get rid of the trouble as quickly as possible. Lay the baby on its side, spread the eyelids of the affected eye with your thumb and forefinger. Then pour clean water from a cup, you can use a new rubber bulb or a large syringe (without a needle). Under no circumstances should you rub the affected eye!
Chemical burns
Little researchers often get into trouble because of their insatiable curiosity. Of course, we, adults, must protect them in every possible way: hide household chemicals, cosmetics, medications and other dangerous substances higher up or lock them with a key. If trouble does happen and one of the chemicals gets into your eye, call an ambulance. And at this time, actively rinse yourself: the more, the better (15–20 minutes). The procedure should be carried out long and patiently, since it is important to remove everything that gets there. The substance, remaining on the mucous membrane or inner side of the eyelid, will harm the entire time it is there and cause a burn.
Bruise, scratch, splinter
Children often suffer various injuries during play or fighting. Serious and not very serious. In any case, it is important to know what to do. Breastfed babies can injure their eyes even with their nails if they are not trimmed in time. Or did the baby get his finger in the eye? You can apply bactericidal drops. This will help stop the inflammatory process. If you accidentally hurt your eye, apply ice to it for 15–20 minutes as first aid. What if a shard of glass or a piece of metal gets into your eye? Do not touch anything and hold your baby's hands so that he does not touch the affected eye. You can apply a sterile bandage, but under no circumstances apply pressure. Call an ambulance. Cat scratches are very dangerous and quite common. Such wounds take a long time to heal. If the claw touches the eye deeply, instant infection occurs and inflammation quickly develops. What to do? Rinse with boiled water, apply drops, apply a bandage and again - see a doctor!
In general, the slightest damage and injury to a baby’s eye is best resolved together with a doctor. It’s truer and... calmer.
Summer is coming, time for holidays and holidays. Therefore, adults should have special control over the behavior of children at home and especially on the street! Health to your eyes!
Ophthalmologist Olga Yurievna Smagina
Print Email
Causes for concern
Cats can quite often scratch or bite their owners severely during play. This becomes almost a habitual part of communication with your pet. Most often the arms and fingers are affected, less often the legs and torso.
You should pay closer attention to the scratch if:
- scratched by a street cat;
- the scratch was caused by an unvaccinated cat;
- bleeding does not stop for more than 10 minutes;
- the wound site hurts, blood, pus, and ichor are released from it;
- bubbles appear in the area of scratches;
- the skin around the scratch is swollen and red;
- temperature rises;
- weakness appears;
- lymph nodes enlarge.
© shutterstock
Features of the incubation period
The virus does not immediately detect its presence in the body. The latent incubation period after rabies infection can range from 30 to 45 days. The insidiousness of the disease is that the cat shows absolutely no signs of infection, but poses a danger already on the eighth day after the virus enters the body.
You can easily become infected with rabies from such an animal.
A lot depends on the strength of the cat’s immune system. In a healthy animal, the latent period can last up to a year. The rate of development of rabies is influenced by the following factors:
- location of the wound: the closer to the head and neck, the higher the risk of early development of the disease;
- number of bites: the more severely the cat is affected, the faster symptoms will appear.
In cats with low immunity, symptoms of rabies appear much earlier. The incubation period will be short:
- in small kittens, because their immunity is not yet formed;
- in chronically ill animals and allergy sufferers;
- in older cats;
- in cats weakened after injuries and surgical interventions.
What not to do
If you are scratched or bitten by a cat, it is quite possible to provide yourself with the necessary first aid yourself. But you should not overdo it, as some actions can only aggravate the condition. To ensure healing goes quickly and without consequences, remember that :
- There is no need to stop the bleeding quickly. With the first drops of blood, an infection can potentially come out and inflammation can be avoided.
- There is no need to apply a tight bandage, and you should not cover the wound site with dressing material. This increases the likelihood of inflammation and suppuration.
- There is no need to remove swelling on your own. Swelling of the tissue indicates a high likelihood of infection developing in the area where the cat scratched you. Delaying seeking medical help may result in the need for serious medical intervention.
What to do if scratched or bitten by a cat
If you receive a bite or deep scratch from a cat, especially an outdoor cat, you should immediately wash the wound with soap and water. It should not contain flavors or dyes. The ideal choice is laundry soap. In an alkaline environment, the rabies virus loses its activity.
For this procedure, you should prepare a soap solution, direct a strong stream of it directly to the damaged area. This can be done using a syringe or a syringe without a needle. After thorough washing, the wound should be covered with a sterile gauze pad and bandaged not too tightly.
It is strongly not recommended to cauterize or tighten the bite site. You can wash the wound with alcohol and treat it with an antiseptic.
The next mandatory step is going to the emergency room. The patient will have his wound treated and will receive anti-tetanus serum. He will also be prescribed rabies vaccine prophylaxis. These measures are quite sufficient to prevent the development of a dangerous disease.
Important! Do not take lightly injuries sustained from a domestic cat, even your own cat.