( 1 votes, rating: 1.00 out of 5)
5589564
06/12/2021 owner reviews 1,
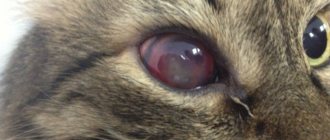
Brown spots on the eyes of cats are medically known as iris freckles, iris hyperpigmentation, melanoma, and iris melanosis. Areas of darker pigmentation appear in the iris (the colored part of the eye). The incidence of iris melanosis is quite common and usually affects middle-aged and older cats.
Iris melanosis is caused by an overgrowth of melanocytes, the cells responsible for producing pigmentation. For simplicity, we will call the benign form iris melanosis and the malignant form malignant melanomas.
Dark spots can appear in cats of any eye color and can be cancerous or benign.
Benign iris melanosis can sometimes develop into malignant melanoma when the cells undergo malignant transformation. More often than cancer, iris melanoma can lead to glaucoma, a condition caused by increased pressure inside the eyeball. Glaucoma causes distorted vision and can be very painful. Malignant melanomas can metastasize to the lungs, liver, and other parts of the body.
- Appearance
- When to contact a veterinarian
- Care
Eye neoplasms – what are they?
The delicate and sensitive tissues of our eyes, unfortunately, are vulnerable to many carcinogenic factors: radiation, chemicals, some viruses, burns and injuries. There may also be hereditary reasons for their degeneration. Tumors of the organs of vision and surrounding tissues are so diverse that they are studied by a special branch of clinical medicine - ophthalmo-oncology. Due to the many variations of eye tumors, diagnosing the problem is not always easy; this requires a comprehensive examination by a highly qualified ophthalmologist. But, whatever the diagnosis, there is no need to be afraid - modern treatment methods have come so far that there is a suitable method for every case.
Classification of tumors of the eye and surrounding tissues
The same classification applies to tumors of the visual organs as to tumors in general. They are divided into:
- Benign - slowly growing, does not metastasize, and does not have a toxic effect. They can degenerate and become malignant. Among eye tumors, this type includes: papilloma, senile wart on the eyelid, benign nevus and a number of others
- With locally destructive growth - those that do not metastasize, but have invasive growth (intermediate category). Basal cell carcinoma and progressive nevus are characterized by such growth
- Malignant - fast-growing, destroying other tissues and releasing toxins. Their cells are transported with the blood to other parts of the body and can give rise to secondary lesions (metastases). Examples: cancer of the conjunctiva, meibomian glands, melanoma and sarcomas of the eyelids.
Eye tumors are also classified according to their location in the affected organ.
:
- Tumors of the orbit (eye socket)
- Tumors of the adnexal apparatus of the eye (eyelids, conjunctiva)
- Intraocular tumors (choroid and retina).
Corneal melanosis.
Corneal melanosis, which is also called pigmentary keratitis (pigmentous keratitis), is one of the common ophthalmological pathologies of brachycephalics. The essence of the pathology is that with chronic irritation of the cornea (keratitis), melanin cells are introduced into its epithelium and the surface layers of the corneal stroma, migrating from the limbus zone. It is worth noting that pigmentary keratitis is a very general diagnosis. The thing is that the cause of this condition is chronic inflammation of the cornea (keratitis). And the main goals of treatment will be to eliminate the causes that led to keratitis.
Symptoms of the appearance of ocular tumors
Almost all tumors of the organs of vision become noticeable sooner or later. They can appear in the form of growths, thickening, pigmented areas on the skin of the eyelids, swelling, redness in the corner of the eye and around it. On the conjunctiva and cornea they look like a cloudy haze or a round whitish-yellow spot. Choroid tumors are visible as spots on the iris. But the deeper tissues of the eye affected by neoplasms cannot be seen with the naked eye. You may not be aware of them until a drop in vision occurs, pain begins, strabismus and exophthalmos develop (displacement of the eyeball forward (bulging eyes), sometimes with a displacement to the side).
The sooner pathological changes are detected, the greater the chance of completely protecting the Patient’s vision. It is better to proceed to treatment at a stage when the tumor is still small. Therefore, we recommend paying attention to various symptoms, which are not always associated with tumors: lacrimation, dark spots in the field of vision, decreased visual acuity, discomfort in the eye area. And, of course, regular comprehensive vision testing is the best protection against such unpleasant surprises as eye tumors.
Causes of chronic keratitis in a pug:
- Inability to close eyelids (Lagophthalmos)
- Macroblepharon (breed characteristic of eyelid growth)
- Enlargement of the eye (with glaucoma)
- Facial nerve dysfunction (due to injuries, frostbite, inflammation)
- Friction
- Medial entropion (common in Pugs)
- Distichiasis (common in Shih Tzus)
- Nasal folds (common in Pekingese)
- Tear film disorders
- Keratoconjunctivitis sicca (Spaniels, Boston Terriers, English Bulldogs, Pekingese, Pug, Shih Tzu are predisposed)
- Chronic autoimmune processes (for example, pannus in shepherd dogs and their mixed breeds)
Corneal melanosis is a pathological condition of the eye, which, if not properly treated, can rapidly progress, thereby depriving the animal of vision. Therefore, if you are the owner of one of the dog breeds listed above, then pay attention to the pet’s eyes. Corneal melanosis begins with whitish swirls on the cornea (first the eye becomes cloudy), and then brown pigment is deposited in these areas (brown spots appear on the eye).
Further, the pigment formations become denser and continue to grow. Please note that the area of turbidity (“eyesore”) around the pigment is also growing. This suggests that the pigment will progress.
Pigmentation processes can affect the entire area of the cornea, forming total pigment - a condition in which the animal is disoriented and almost completely deprived of vision. The animal's eye will be dark brown in color and appear normal. But if you look closely, you will not see either the pupil or the iris, but only the brown cornea.
Diagnosis and treatment of eye tumors
Typically, an eye tumor can be detected by ophthalmoscopy (examination of the fundus of the eye). To confirm and clarify the diagnosis, stages of examination are carried out
:
- Ultrasound of the eyeball
- CT scan
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI)
- Fluorescein angiography
- Tissue biopsy followed by histological analysis.
Modern methods of immunohistochemistry make it possible to accurately determine the nature of the tumor, and tomography - its location.
Diagnostics
If the owner notices brown discharge around the cat's eyes, he needs to take the pet to a veterinary clinic. In most cases, examination and history is sufficient to make a diagnosis.
Sometimes it is necessary to conduct additional tests to help rule out head and eye injuries, as well as diseases of internal organs and infectious diseases. To do this you may need to do:
- Ultrasound of the organs of vision;
- X-ray of the skull;
- blood and stool tests.
Treatment of ocular tumors
Like many serious pathologies, tumors require an integrated approach to treatment. The choice of the necessary methods depends on the diagnosis, the stage of development of the tumor, and the individual characteristics of the Patient. It is important to understand that removing a tumor may not always be sufficient for subsequent health safety. In some cases, regular prevention of its re-development will be necessary.
Methods for removing tumors
:
- Laser evaporation
- Radiosurgical removal using robotic systems
- Cryotherapy (freezing cancer cells with liquid nitrogen)
- Thermotherapy (several sessions of heating tissues up to 45 degrees)
- Brachytherapy (contact radiation technique)
- Photodynamic therapy (destruction of cancer cells by the reaction of their product to light)
- Chemotherapy
- Surgical removal
The need for surgery usually arises only in the later stages of the disease. Until then, treatment may be limited to absolutely safe and minimally invasive techniques (a technique aimed at minimizing the area of intervention in the body and the degree of tissue injury).
The appearance of a neoplasm is a reason for active action, but not for panic. Your attending physician will select a combination of techniques that will achieve the most favorable result for your health. Check your vision regularly, contact a specialist if alarming symptoms appear - and be healthy!
When is a visit to a veterinary ophthalmologist necessary?
Cat owners should be attentive to their pets and if the following signs appear, show them to an ophthalmologist:
- Swelling and redness of the eyelids.
- The animal constantly scratches its eyes.
- The cat developed photophobia.
- Redness of the eyes.
- Increased tear production.
- Cloudy, purulent discharge from the eyes.
Important!
Do not delay your visit; untimely treatment can lead to partial or complete loss of vision.
Stages of cataract development
- Initial . Cloudiness occurs at the edges of the eye. The cat is able to see objects and the environment around itself, but not quite clearly.
- Immature . The middle zone of the lens gradually becomes cloudy. The animal still distinguishes objects around it, but its vision drops quite significantly.
- Mature . The entire surface of the lens becomes cloudy. As a result, the cat is unable to distinguish objects or navigate in an unfamiliar room.
- Overripe . The cat completely stops seeing. She does not distinguish whether it is dark or light around her. The lens is completely destroyed. It breaks down into fibers.
The sooner you contact a good veterinary clinic in Moscow, the greater the chance of returning your cat to full vision!
What cat breeds are at risk?
In 8 out of 10 cases, cataracts occur in older cats - over 8-9 years old. Animals that have crossed this age threshold often face serious illnesses, metabolic disorders, and large amounts of free radicals in the body. The result of these changes is a disruption of the structure of the eye lens.
Has your pet been diagnosed with diabetes? Be careful - this disease increases the risk of cataracts by 20%!
As for the breed predisposition of cats, brachycephalic breeds are most prone to lens clouding:
- British,
- exotic shorthair,
- Persian,
- Scottish Straight and Fold,
- Himalayan
First aid
Of course, the first and most urgent measure is to remove the eye from the influence of the damaging factor and deliver the victim to the nearest specialized medical facility as soon as possible.
At the same time, in most cases (EXCEPT FOR LIME BURNS!) you can rinse the eye with clean water and drip any antibacterial drops (Albucid, Levomycetin, etc.). It will be useful to apply a bandage (not pressing) to reduce the movement of the victim's eyes.
3.What should you pay attention to?
Eye moles do not affect vision in any way. However, a spot in the eye requires special attention and consultation with an ophthalmologist. Normally, the edges of the nevus are clearly defined, the surface is velvety in appearance, and the shape and color do not change significantly. If growth and changes in the spot become noticeable, it is necessary to undergo a series of examinations, and, if necessary, treatment or even removal of the pigment spot. Also alarming symptoms should be:
- blurred vision;
- limited field of view;
- sensation of a foreign object in the eye.
Even if the nevus in the eye is stable and does not cause a person any concern, one must remember that, like any mole, it is extremely undesirable to expose it to ultraviolet radiation and other influences that provoke mutations. In sunny weather, it is very advisable to protect your eyes with dark glasses or at least wear a hat with a visor.
About our clinic Chistye Prudy metro station Medintercom page!
Chemical burns
They occur upon contact with any substance (in any state of aggregation - from steam to solid crystals or powders) that corrodes or dissolves living organic tissue. The most common burns are caused by acids (usually in hazardous industries) and alkalis (usually in everyday life - ammonia, quicklime, caustic soda, etc.). In this case, a burn with a concentrated alkali, as a rule, is much more dangerous and severe than an acid one: the acid destroys only the volume of tissue with which it reacted, while the alkali continues to corrode the tissue and penetrate deeper and deeper until it is completely removed from the eye.
Therefore, in case of any chemical burns, the key importance in saving the visual organs is the speed and literacy of pre-medical medical (self) help.
Eyesore
Syphilis
Herpes
12812 August 17
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. An eyesore: causes of occurrence, what diseases it occurs with, diagnosis and treatment methods.
Definition
An eyesore, or leukoma, is externally manifested by clouding of the cornea of the eye that occurs after injury or an inflammatory process. The cornea is the anterior, most convex part of the eye capsule, consisting of a thin avascular membrane through which refracted light enters the posterior parts of the eye. There are three stages of corneal opacification depending on the size and depth of the lesion: a cloud, a spot and a cataract, but all of them affect visual acuity, and in some cases a person can become completely blind in the affected eye.
The success of treatment largely depends on timely seeking medical help.
Types of eyesores
There are congenital and acquired eyesores:
- congenital cataract is formed during the period of intrauterine development of the embryo and is often combined with other congenital eye diseases;
- the acquired form is the most common, occurring equally often in both men and women.
Depending on the depth of the lesion, the following types of cataracts are distinguished:
- corneal cataract without affecting other parts of the eye; there are scars of different shapes and lengths in the cornea;
- a thorn welded to the iris; a cloudiness appears on the cornea, sprouting with small vessels, spreading to the area of the iris;
- a cataract in combination with true clouding of the lens, that is, cataract;
- cataract with secondary cataract;
- intense clouding of the cornea of the eye, which is characterized by adhesions of the cornea with the iris and/or lens, clouding of the lens;
- a thorn complicated by retinal detachment and the development of eye atrophy.
Possible causes of eyesores
Doctors consider keratitis, an inflammation of the cornea of the eye, to be one of the possible causes. The most common cause of keratitis is a viral infection (herpes viruses, chickenpox). Often, bacterial infections, as well as non-compliance with the rules of wearing contact lenses, lead to an inflammatory process in the cornea.
Keratitis is characterized by redness of the eye, pain, lacrimation, photophobia, clouding of the cornea already in the initial stages of the disease, and decreased visual acuity.
If treatment is not started on time, the inflammation will spread deeper and an eyesore will begin to form.
Corneal injuries are another common cause of eyesores. Injuries can be mechanical, thermal or chemical (alkali or acid burns). Alkaline burns are the most dangerous.
The first symptoms of injury are pain, lacrimation, sensation of a foreign body, drooping of the eyelid.
Any injury to the cornea requires immediate medical attention.
Infectious diseases of the conjunctiva can lead to damage to the cornea and the appearance of a cataract. The conjunctiva is the connective membrane of the eye that covers the inner surface of the eyelids and extends from the outside to the cornea. One of the most dangerous diseases of the conjunctiva is trachoma. It occurs when a chlamydial infection enters the eye, is chronic and causes blindness in almost two million people in the world. Children are most susceptible to this eye disease.
Tuberculosis is an infectious disease that, despite the successes of domestic medicine, is still often diagnosed in patients of all ages. Tuberculosis can affect any organs and systems of the body, including the infection that can spread to the eyes, lead to deep damage to the cornea and cause the formation of a cataract.
Cases of cataract formation after eye surgery have been described. This is due to a violation of the integrity of the cornea, which increases the risk of infection.
Diseases leading to the formation of eyesores
- Congenital pathologies, for example, limbal dermoid, sclerocornea.
- Keratitis.
- Injuries (chemical, thermal burns, penetrating wounds).
- Trachoma.
- Corneal ulcers.
- Tuberculosis, syphilis.
Which doctors should you contact if an eyesore appears?
An ophthalmologist deals with the treatment of eyesores. He will order tests and conduct additional examinations. If you suspect an infectious etiology of the cataract, you may need to consult an infectious disease specialist or phthisiatrician.
Diagnostics and examinations for the appearance of an eyesore
To clarify the diagnosis, the doctor may prescribe the following examinations:
- a clinical blood test with a detailed leukocyte formula will help identify inflammatory changes in various infectious and inflammatory diseases;
Symptoms
If brown spots and formations appear on the cat's eyes, symptoms may appear, which are definitely recommended to be closely monitored. Visual acuity may decrease, the animal may not get into the bowl, it may skid when turning, and orientation in space may also be disturbed. The second aspect is considered to be increased irritability and nervousness of the pet. The cat begins to behave aggressively towards its owners and other pets in the house. Often a person notices the development of strabismus in a cat, the appearance of watery discharge from the eyeball. There is severe swelling of the cornea and redness on the iris and eyelids.
If such symptoms appear, it is recommended to immediately take your pet to an appointment with a veterinarian. When examining a cat, a specialist will prescribe appropriate treatment and tell you about methods for preventing the development of such diseases. Self-medication is prohibited.
4. Treatment methods
If for some reason, together with a doctor, a decision is made to remove pigment on the cornea of the eye, modern medicine offers gentle methods. Until recently, eye moles were operated on only with microscalpels and radioscalpels under a microscope. Currently, laser coagulation is widely used.
The procedure has become as safe as possible for nearby tissues, painless and effective: an ideal cosmetic result is achieved.
Sign up for a consultation
Signs by which you can determine clouding of the lens of the eye
Visually, at the first stage of cataract development, it is impossible to notice changes in your pet. This is due to the fact that the deterioration of visual function is compensated by well-developed hearing and sense of smell. Therefore, the symptoms of the disease are noticeable when the surface of the lens is already severely damaged.
Symptoms that may indicate the development of cataracts in an animal:
- the appearance of a small cloudy spot or film on the surface of the eye;
- the cat ceases to navigate indoors (especially in the unknown);
- the animal moves poorly;
- constantly bumps into furniture and objects;
- He practically doesn’t play because he doesn’t orient himself in space.
General information
A cataract is any opacity of the cornea; Previously, this concept also included cataract - clouding of the lens - however, taking into account the fundamental etiopathogenetic and anatomical difference, currently these two diseases are separated and considered as independent.
As you know, a healthy cornea is transparent. Being the outermost, open part of the eye's optical tract, the cornea performs both protective and focusing functions. In fact, this is a natural concave-convex lens with a diameter of 1 cm, a thickness of 0.5-1 mm (thinner in the central part, thicker towards the points of diffuse transition into the sclera) and an optical power of 40 diopters.
Any damage, any changes in shape and refractive parameters, degeneration of the multilayer structure of the corneal tissue inevitably and automatically lead to a pronounced and, as a rule, uncorrectable decrease in vision. With all the variety of causes of cloudiness or complete opacity of the cornea, this condition can only be treated surgically, and it is necessary to take all necessary, available, and possible measures to protect the cornea and prevent the formation of a cataract.
2.Types of age spots
Based on the location of the spots, they are divided into conjunctival nevi
(visible on the mucous membrane of the eye) and
choroidal nevi
(identified only during eye diagnostics, since they are located on the fundus).
According to their structure, eye pigment spots are divided into three groups:
- vascular spots (reddish or pink spots formed from the blood vessels of the eye);
- pigmented nevus (clusters of melanin pigment that are brown, yellowish or black);
- cystic nevus (a node of lymphatic vessels, often a discolored area that makes the corneal pattern look like a honeycomb or bubbles).
Visit our Therapy page
Operations for corneal opacities
Various techniques and protocols are successfully practiced, selected “according to indications” depending on the specific clinical situation. Typically, penetrating or partial keratoplasty is used - respectively, complete (over the entire thickness and area) or partial, more gentle replacement of the affected area or layer of the cornea with a donor keratobioimplant. Such operations are well established and, as a rule, effective, especially if all instructions for the rehabilitation period are followed, which in some cases can last up to a year or more.
According to statistics, the most successful, in terms of short-term and long-term prognosis, are operations for keratoplasty of cataracts caused by infectious ulcerations/scarring. A necessary condition is sanitation and prevention of recurrence of infection.
As for the prevention of the cataract itself, the first and main rule should be to contact a qualified ophthalmologist for any signs of conjunctivitis or other inflammatory process (before the cornea is involved in it), for any injuries and burns of the eye. In a very significant proportion of cases, the cataract could have been prevented without delaying the situation and without bringing the situation to ophthalmic surgery.