Modern medicine makes it possible not only to cure colds in humans, but also to cope with the most serious diseases in pets. Especially after major operations or, for example, such a popular procedure as sterilization.
Today we will look at one of the common ailments that affects animals that have not undergone surgical intervention. Mastitis in a cat after sterilization? What to do if your pet has swollen or inflamed nipples? How quickly does it need to act? Is it possible to get treatment at home? Why is mastitis dangerous and what does sterilization have to do with it?
Causes
Why are my cat's mammary glands swollen? The most common reasons are: :
- pregnancy;
- mastitis;
- false pregnancy;
- mastopathy;
- benign neoplasms;
- cancer.
© shutterstock
If the cat is not pregnant, then you need to contact your veterinarian to determine the cause.
Complications after sterilization
To avoid complications after sterilization, you need to make sure that the cat is healthy. Undergo a full medical examination to identify inflammation or the presence of chronic pathologies in the body. Make sure there is no ovulation, otherwise after the operation a false pregnancy may occur, which is fraught with the manifestations described above.
Before the operation, you should undergo a full medical examination.
Mastitis
Most often, a cat gets mastitis as a result of stagnation of milk in the breast. Another cause may be infection with staphylococcal infection or E. coli. Bacteria also enter the gland through the milk ducts or through the bloodstream.
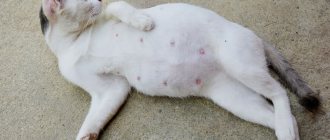
Mastitis is an inflammation of the cat's breasts. Most often this disease is characterized by symptoms :
- an increase in the size of the gland, swelling, swelling;
- increased cat body temperature;
- redness of the skin of the mammary glands;
- seals may appear;
- blood or pus can be expressed with milk;
- general deterioration in the animal’s well-being, lethargy, apathy.
If mastitis is not treated on time, then in some cases degeneration of the mammary glands may occur, which will lead to the development of tumors, including malignant ones. What should you do if your cat has swollen upper four mammary glands? First of all, it is necessary to take the animal to a veterinarian and examine it for mastitis.
© shutterstock
What to do first?
Before going to the veterinarian, you can give your cat first aid. To do this you need to do the following:
- Reduce the amount of liquid your cat drinks. This will reduce milk production. It is also better to temporarily remove wet food from the diet, giving preference to dry food.
- Express milk. This can be done with the help of kittens, placing them under all the nipples, or manually.
If there are cracks or foreign impurities have formed, feeding the litter and expressing it by hand is unacceptable. Warming up the inflamed lobes will also be no less dangerous. High humidity and elevated temperature are optimal conditions for the development of pathogenic microflora.
When a diagnosis is made, the animal is usually prescribed anti-inflammatory injections and immunomodulators. If severe swelling occurs, diuretics are required. In advanced forms of mastitis, novocaine blockades with antibacterial and antifungal drugs are needed. In advanced cases, they even resort to surgery.
Published in Diseases
False pregnancy
False pregnancy is a common occurrence in the animal world. Dogs most often suffer from this problem, but it also occurs in cats. Usually, a false pregnancy occurs after mating with a sterile male. The problem may also arise due to reproductive ill health of the cat itself. Sometimes false pregnancy occurs due to hormonal imbalances in the animal’s body.
If, some time after meeting a male, the cat’s mammary glands swell and her belly becomes rounded, this does not mean anything. The presence of pregnancy can be determined using an ultrasound machine. Usually this study is prescribed by a doctor for a period of 3-4 weeks.
Symptoms of false pregnancy in a cat:
- toxicosis;
- swelling of the mammary glands;
- abdominal enlargement due to excess fat deposition on the anterior abdominal wall;
- appearance of milk;
- false labor pains.
What to do if a cat is falsely pregnant? This condition is not so harmless, so a visit to the veterinary clinic is required. If episodes of false pregnancy occur frequently, then the cat must be sterilized.
Mastopathy
Mastopathy is a pathological change in the gland, characterized by the appearance of dense formations. This disease practically does not occur in cats that were sterilized before the age of one year. Mastopathy is a dangerous process that, without veterinary control, can further provoke the growth of a cancerous tumor.
© shutterstock
What to do if your cat has swollen mammary glands? It is necessary to take the animal to the clinic and rule out mastopathy .
Main symptoms of the disease:
- enlargement of the mammary glands;
- the appearance of bloody discharge from the nipples;
- the presence of seals in the gland;
- The animal's chest may become painful.
For mastopathy, conservative treatment is most often prescribed, which is well tolerated by cats. If an animal has swollen mammary glands, it is better to take it to a doctor as soon as possible for diagnosis.
Diagnostics
When you arrive at the clinic, your veterinarian will need a complete medical history of your cat. A physical examination will be performed, during which the nipples and breast tissue will be carefully examined for signs consistent with breast health. Some problems may not be serious and may resolve on their own, while other conditions may be life-threatening.
A number of diagnostic tests may be done, usually starting with a blood test. This may include a complete blood count and biochemical profile. A biopsy of the enlarged tissue may be taken for further microscopic evaluation (histopathological examination). X-rays of the chest and abdomen may be needed to check the location of the tumor and detect metastasis (spread). A urine test can be used to confirm and identify bacteria present in a cat.
Benign neoplasms
Veterinarians call the most common causes of benign neoplasms hormonal imbalances, injuries to the mammary glands and genetic predisposition. Unsterilized cats and overweight animals are at risk. The use of hormonal contraceptives increases the likelihood of breast tumors.
Symptoms of the disease:
- the cat's mammary glands are swollen;
- upon palpation, a compaction is felt under the skin;
- lymph nodes may be enlarged;
- sometimes there is discharge from the nipples;
- the behavior of the animal may change.
If an animal's mammary glands are swollen, this may be a symptom of tumor development. In cats, most neoplasms are malignant, so it is necessary to consult a veterinarian as soon as possible.
Treatment
At home, help can be provided only in the initial stages of the disease. Although it is worth noting a number of nuances.
Firstly, it is important to treat only catarrhal and serous forms at home. Secondly , nulliparous cats must visit the clinic. A common cause of mastitis is stagnation of milk followed by infection, which is accompanied by inflammation. But, if the swelling of the nipples goes away without discharge, then the reason is different. It can only be determined in a veterinary clinic.
Thirdly, if not all mammary glands are swollen, then the affected parts can be sealed with a bandage or bandaged. If necessary, isolate kittens. Under no circumstances should babies be fed contaminated milk. Especially with purulent mastitis.
External signs of illness when it is reasonable to treat at home:
- The cat's temperature is normal.
- There is no purulent, bloody or other unusual discharge.
- The nipples are a little swollen.
- Only part of the mammary glands is affected.
- The cat does not experience pain upon palpation.
- The milk ducts in the nipples are not blocked.
If after a few days the cat's condition does not improve, you should contact your veterinarian. We list the most effective ways to help alleviate your pet’s condition.
Express milk
IMPORTANT! Under no circumstances should you do this with your hands! Any touch during mastitis is extremely painful.
You should use a regular 5-10 ml syringe. We remove the piston and cut off the upper tip. Then we treat the resulting space with fire. A regular lighter will do. Level the surface with your fingers.
We insert the plunger, applying the syringe to the nipple. The milk will be expressed unless there is a blockage. The procedure will require the help of a partner. If your cat is in severe pain and tries to escape, you should immediately consult a doctor.
The milk is expressed until the nipples become flaccid. Light pressure should not cause pain to the cat. The lumps disappear, the swelling decreases in size.
Light massage
Don't be overzealous. A high-quality massage is similar to gently scratching the abdomen, avoiding the most sore spots if possible.
Warm compresses
Use a decoction of chamomile, oak or sage. A tablespoon of the mixture is brewed with 200 ml of boiled water and left for 30 minutes. Cools to a comfortable temperature. A bandage or napkins are moistened with the broth and applied to the affected areas. Covered with cellophane and bandaged loosely.
Rubbing with ichthyol or camphor oil helps effectively. The treated areas are also covered with a bandage. It is also needed to prevent the cat from licking the oil.
Limit food and water
When using dry food, water is given only after meals. Otherwise, the cat is given water once until it is completely saturated. The next day, it is advisable to switch the animal to dry food. The diet is maintained until the first symptoms of recovery.
In a clinical setting, in most cases, drug treatment is used. It depends on the type of mastitis. Let's note some of the ways:
- Intravenously or intramuscularly - 10% sodium gluconate (1-3 ml repeated every other day), 10% catozal (0.5 - 2.5 ml for 3-5 days), gamavit (0.3-0.5 ml per 1 kg of body for a week), mastomethrin (0.5-2 ml 1-2 times a day for 2 weeks), traumatin (0.1 ml per 1 kg of body 1 time a day for 5 days).
- The use of antibiotics - cephalosin (20-25 mg every 8 hours for 5 days), cephalexin (10-30 mg 2 times a day for 5 days). Often a novocaine blockade is used with the addition of penicillin or bicillin for 2 days.
- In severe cases, surgical intervention is resorted to. Remove pus, express milk, get rid of affected areas.
Each case is individual and only after a full examination will the veterinarian be able to prescribe effective treatment
Malignant neoplasms
Mammary cancer in cats is a malignant neoplasm that in the later stages begins to metastasize to other organs. If detected early, animals are much more likely to survive. Malignant neoplasm is one of the most dangerous diseases of the mammary glands in cats.
© shutterstock
Most common symptoms in the early stages:
- the cat has swollen mammary glands;
- upon palpation, compactions are felt;
- enlarged lymph nodes;
- the animal may become lethargic and lazy.
In later stages, the tumor is already visible to the naked eye. It increases in size and grows into the surrounding tissue. With the blood flow, its cells spread throughout the animal’s body. In feline breast cancer, metastases are most often found in the lungs, liver and brain. The tumor begins to disintegrate, and a little later the animal dies. Veterinarians are powerless here; euthanasia is recommended.
Mastopathy in a cat
It happens that some time passes after sterilization and the owner notices swelling of the mammary glands in his pet.
With more careful palpation, you can feel small compactions with a soft or springy consistency . This is how mastopathy manifests itself. The initial stage of the disease does not cause a painful syndrome, so timely diagnosis of the pathology is of great importance.
If such a symptom is detected, you should immediately contact the clinic for a correct diagnosis and treatment.
If symptoms of mastopathy appear, you should immediately contact a veterinarian!
Diagnostics
Diagnosed using histological examination.
Histological examination.
Risk group
Females who have been spayed after at least their second heat are more at risk.
Younger females who have had their ovaries removed before their first estrus are very rarely susceptible to developing this disease.
Young cats are less susceptible to the disease after surgery.
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed depending on the severity of the course.
If the disease is diagnosed late, surgery is recommended, during which the affected tissue or completely swollen gland is removed.
If the disease is detected late, surgical intervention is recommended.
The initial stage is amenable to drug treatment. The use of immunomodulatory drugs to enhance the body's resistance is indicated. Iodine-containing medications are prescribed to stop the growth of pathological tissue.
To prevent secondary infections and eliminate pain, treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs is recommended.
homeopathic remedies are used to restore the female’s hormonal levels. Under no circumstances should you use warm compresses or lotions for mastopathy. Heat provokes the proliferation of diseased cells.
Which doctor should I contact for examination?
You should know that mastopathy and mastitis can cause the development of cancer. Regular examinations by a specialist will help avoid dangerous pathologies. If you have pain or lumps in the mammary glands, you should contact a mammologist. After an accurate diagnosis, he will prescribe appropriate treatment.
For preventive purposes, it is recommended to visit a mammologist annually. In case of complicated heredity, due to individual characteristics, in the presence of concomitant pathologies, additional visits to the doctor are required.
What does pain indicate?
For most women, burning and mutual dull pain in the chest is a consequence of premenstrual syndrome. A burning sensation and pain in the chest is observed at the beginning of pregnancy.
Lumpiness and tenderness in the breasts occurs when milk accumulates in the mammary glands of a nursing mother. When cracks form in the nipples, there is a risk of infection and the development of mastitis.
Localized pain and burning in the chest can be the cause of the development of benign formations. This pain intensifies in a certain position of the body.
Burning and pain in one side of the chest may indicate the development of cancer. Tumor formations of the breast are most often located in the upper outer quadrant.
Medical indications for cat sterilization
The main reason for sterilizing a cat is to exclude unwanted pregnancy. But there are a number of medical indications for such an operation:
- Violation of the sexual cycle: estrus occurs once every 1-2 months or more often; prolongation of the estrus period itself;
- Diagnosed pathologies of the reproductive system: purulent endometritis (pyometra), cysts or neoplasms of the ovaries and uterus.
Pros of cat castration
The main advantage of surgery to remove the uterus and ovaries is to stop sexual activity and prevent pregnancy. But there are other positive aspects of this operation:
- Statistically, the life expectancy of castrated cats increases.
- The possibility of developing purulent endometritis, ovarian cysts, and neoplasms of the female reproductive system is prevented;
- Due to the lack of sexual heat, the cat stops meowing for days on end during estrus, thereby trying to attract a male cat. This behavior in domestic cats leads to sleepless nights for owners;
- Behavior is corrected due to the absence of sexual hunting, and there is no need to mark the territory;
- The risk of contracting infectious sexually transmitted diseases is eliminated.
Causes of lumps and nodes in the mammary gland
The appearance of lumps in the mammary gland may be associated with an imbalance due to the use of contraceptives, pathological disorders of the thyroid gland, ovarian dysfunction, and mastitis. Injuries, chest bruises, and stress lead to the formation of knots. The consequence may be abortion, menopause, and disorders in the reproductive system. You should not wear a tight bra.
The lump can be the size of a small pea or the size of a grapefruit. Small size is not a reason to ignore the problem. Often small tumors grow to gigantic proportions in a short time. If you notice a lump in your breast, make an appointment with your doctor immediately. It may save your life and certainly keep you healthy.
Inflammatory diseases
More common inflammatory pathologies of the mammary glands include mastitis caused by staphylococci.
Types of mastitis:
- Non-lactational. Has an acute or chronic form. Develops with bruises, hypothermia, burns.
- Lactational. Consequence of lactostasis during breastfeeding.
- Galactophorite. Inflammation of the ducts.
- Purulent. Abscess or phlegmon of the mammary gland, followed by the formation of a compaction.
- Non-purulent. Inflammatory process with serous sweating of tissues.
Mastitis is accompanied by pain, tissue swelling, lump formation, fever, weakness, and signs of intoxication.
Specific infections
Nonspecific breast infections include tuberculosis and syphilis. With tuberculosis, hypertrophy and thickening of the breast, hyperemia of the skin and enlargement of regional lymph nodes are observed.
Syphilis of the mammary glands is rare, has a long course and is characterized by systemic damage to the body. Develops in three stages. The causative agent is a pale spirochete that penetrates through microcracks and has the ability to reproduce rapidly. The disease is contagious at any stage. This type of syphilis is not transmitted to men.
Traumatic injuries
Chest injuries are common among women of all ages. Bruises are accompanied by aching and severe pain. Damage may be open or closed. The traumatic factor leads to damage to blood vessels and bleeding into the tissue, resulting in the formation of hematomas with clear boundaries of blue or maroon color.
If the areola or nipple area is bruised, traumatic shock may occur. Open wounds carry the risk of infection.
Consequences of illnesses, injuries and operations
The seals formed after a bruise are not malignant in nature, but can subsequently degenerate. Breast injuries are especially dangerous if a woman has nodular mastopathy. If you do not consult a doctor in a timely manner, dangerous complications develop.
These include:
- Fat necrosis. Focal death of breast tissue, with the appearance of a painful lump. There is deformation of the breast, retraction of the skin and a change in its color. A benign tumor does not degenerate into a cancerous tumor on its own, but can become a provoking factor.
- Calcifications. Calcification of soft breast tissue. The accumulation of calcium salts in the mammary gland develops against the background of some disease, including cancer (in 20% of cases). On palpation they are detected with an increase of more than 1 cm.
- Capsular contracture. Growth of fibrous tissue around the implant after mammoplasty. Compression of a foreign body leads to breast deformation, the appearance of a seal in the gland area, contouring of the implant, and discomfort.
- Polyacrylamide gel knots. Complicated condition after breast surgery using polyacrylamide gel. The transformation of the gel into capsules in the form of subcutaneous seals and movement to other parts of the body is observed. The development of a massive inflammatory process with purulent discharge is possible.
Bruising of the mammary glands is accompanied by swelling and pain. Sometimes injuries lead to clear or bloody discharge from the nipple. Any breast should be a reason to contact a mammologist for a detailed diagnosis.
Diagnosis of the causes of lumps and nodes in the mammary gland
- Consultation with a mammologist. The mammologist will examine the patient, palpate, identify a lump or nodule, prescribe all the necessary tests and, if necessary, refer for consultation to other specialists in our center - oncologist, gynecologist, geneticist, endocrinologist, surgeon.
- Instrumental studies : Ultrasound of the mammary glands;
- ductography;
- digital and MR mammography.
- biopsy followed by histological examination;
If the examination revealed one or another pathology, the mammologist will draw up an individual treatment program.
Most breast lumps are not ultimately cancerous. However, to be sure of this, it is necessary to undergo a high-quality examination. By making an appointment now, you will have the opportunity to undergo diagnostics using the latest equipment at a time convenient for you.