Although cats are much more susceptible to these problems, swollen nipples and mammary glands are sometimes observed in male cats. An unspayed female is at greater risk than a spayed female. If unusual mammary swelling is noticed while the kittens are nursing, the kittens and their mother may need veterinary attention as the infection can easily spread between them.
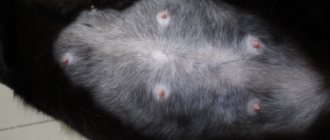
Swelling of the nipples and mammary glands are external manifestations of enlarged mammary glands. Most cats have eight nipples, and if one or more nipples become enlarged or inflamed, one or more of them may be affected. Normal events in a cat's life can cause mammary tissue to swell, such as pregnancy and lactation. However, many infections and other conditions that can be life-threatening also cause breast enlargement.
Symptoms
Typically, when a condition is abnormal and requires treatment, several signs may occur.
- Swelling of the nipples or breast tissue
- Painful nipples
- Redness
- Nipple discharge
- Ulcerations of the nipples and breasts
- Loss of appetite
- Heat
- Enlarged lymph nodes
- Swelling of the skin on the hind legs
- Refusal to feed
- Sick kittens (while nursing)
© shutterstock
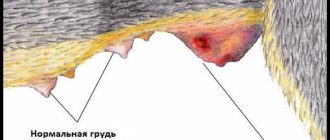
Symptoms of mastitis in cats
Mastitis in cats may be accompanied by the following symptoms:
- swelling of the mammary glands appears;
- the glands become denser and redden;
- the local temperature of the glands rises, they feel very hot to the touch, sometimes the temperature of the whole body rises;
- the cat does not allow the kittens to touch the nipples;
- the cat often licks sore nipples;
- the consistency and appearance of milk changes;
- milk may be mixed with pus, flakes or blood;
- the activity of the animal decreases;
- appetite decreases;
- The general condition of the cat is lethargic and depressed.
Such symptoms require a mandatory visit to the veterinarian. Often, owners believe that mastitis is not a big deal and will go away on its own, so if the listed signs appear, they postpone a visit to the clinic. However, such symptoms can also be signs of other diseases, in particular mammary tumors, which in cats are very often malignant and quickly metastasize, and if a diagnosis is not made in a timely manner, time for treatment can be irreparably lost. Mastitis also most often requires treatment; the inflammatory process develops quickly and can cause serious complications.
Advanced mastitis can lead to the formation of abscesses (purulent inflammation).
When mastitis occurs, the milk becomes contaminated and unsuitable for feeding kittens; at the first symptoms, it is recommended that they be switched to artificial feeding. This will also help avoid additional injury to sore nipples.
With chronic mastitis, clinical symptoms may not clearly manifest themselves, the cat’s well-being will be within normal limits, and visible changes in the mammary glands may not occur or it will be very weak. The symptom in this case may be disturbances in the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract (primarily diarrhea) in kittens, and sometimes death.
Causes
In addition to being a normal cause of pregnancy, swollen mammary glands can be a sign of a more serious internal problem in the cat. Your veterinarian will be best able to determine the exact cause of the swelling, allowing your cat to be diagnosed and treated more quickly. Reasons include:
- Pregnancy
- Mastitis (breast infection during breastfeeding)
- Galactostasis (accumulation of milk in the mammary gland during weaning)
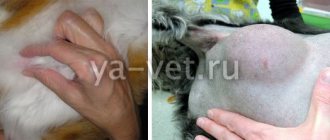
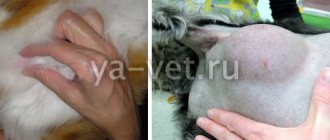
- Mammary hypertrophy in cats (benign formations)
- Mammary cancer
- Breast hyperplasia (due to high progesterone levels)
Problems with early weaning of kittens from cats
Early weaning can lead to stress and even various diseases in the cat.
If the female has the first litter, it is not recommended to select all the babies at once in order to avoid stress and, as a result, the development of diseases.
The most common problem in the case of early weaning is disturbances in the functioning of the mammary gland. The cat is not able to cope with stress on its own and the lactation process continues.
Risk of developing mastitis and mastopathy
In such situations, the cat's risk of developing mastitis increases.
Due to ongoing lactation and the inability of kittens to produce milk, the risk of developing mastitis or mastopathy increases.
At such moments the cat becomes aggressive , does not make contact with the owners, and refuses food and water. Most often, after a certain time, the stressful state fades away if the owner makes every effort to do so.
- To do this, you should create the most comfortable conditions for mommy.
- Eliminate stressful situations, eliminate noise and contact with strangers, show great care and speak in a calm, gentle voice.
If, despite apparent calm, the cat’s mammary glands are swollen, this may indicate the development of a disease such as mastitis . Prolonged ignoring of the symptoms of mastitis provokes a more serious disease – mastopathy.
Diagnostics
When you arrive at the clinic, your veterinarian will need a complete medical history of your cat. A physical examination will be performed, during which the nipples and breast tissue will be carefully examined for signs consistent with breast health. Some problems may not be serious and may resolve on their own, while other conditions may be life-threatening.
A number of diagnostic tests may be done, usually starting with a blood test. This may include a complete blood count and biochemical profile. A biopsy of the enlarged tissue may be taken for further microscopic evaluation (histopathological examination). X-rays of the chest and abdomen may be needed to check the location of the tumor and detect metastasis (spread). A urine test can be used to confirm and identify bacteria present in a cat.
Mastopathy
Chronic mastitis can cause mastopathy.
It is generally accepted that the main cause of mastopathy is hormonal disorders. However, this pathology can occur as a complication of chronic mastitis.
Clinical signs
The main symptoms are associated with enlarged mammary glands.
- The provoking cause, the factor of which is a stagnant process, is characterized by fibroepithelial hyperplasia of a diffuse form .
- The entire area increases in size with the presence of multiple compactions, and not only individual compactions are painful, but also the entire inflamed area.
- If ulcers begin to appear, help will be very difficult and the effectiveness of the prescribed treatment will remain in question.
What to do
Depending on the current condition, various treatment methods are available. If your cat is suffering from an infection (as is the case with mastitis), it may require emergency medical attention. Immediate attention is necessary to ensure the cat is stabilized and can receive treatment.
© shutterstock
- Mastitis . Treatment for mastitis includes antibiotics to clear up any infection and pain medications to help your cat cope with the pain associated with the condition. Your veterinarian may also recommend that you apply a warm compress periodically to help with drainage.
- Mammary cancer . This type of cancer is very aggressive and spreads frequently. This usually occurs in several nipples at once. Surgical removal of the affected glands (mastectomy) is recommended, especially if the cancer is in the early stages. If the cat is not suitable for surgery, chemotherapy may be the only treatment option.
- Mammary hypertrophy in cats . The recommended treatment for this condition is complete sterilization (ovariohysterectomy). Although these operations are more routine, if the cat is suffering from general poor health, the procedure can be very tedious.
- Breast hyperplasia . To solve this problem, you need to remove the source of progesterone. This usually results in an ovariohysterectomy. If ulceration of the glands has occurred, they can be removed if the cat is stable enough. Pain medications will be prescribed to help your cat survive the days following surgery.
- Pregnancy or Galactostasis . Both of these causes of breast enlargement will disappear on their own over time.
First aid and treatment
If you notice hard mammary glands in a cat during feeding, you need to contact a veterinarian for further diagnosis and proper advice. It is recommended to call a doctor at home so as not to separate the mother cat from her offspring. In addition, a trip to the veterinary clinic can cause a nervous breakdown in your cat.
The doctor may prescribe a biopsy if a malignant tumor is suspected. Diagnostics is necessary in order to determine possible metastases in other organs and draw up a further action plan.
In addition, before starting treatment, laboratory tests are carried out:
- general blood test (makes it possible to identify the bacterial nature of inflammation);
- biochemical blood test (determines the state of the hepatorenal system).
Providing first aid for mastitis is advisable only in the first stages of the pathology. You can express the stagnant gland separately by hand, or use the most active kitten with a good sucking reflex. It is not advisable to put too much pressure on the gland or apply warm compresses.
By pressing hard on the mammary gland, you can damage it, and when applying warm compresses and with a bacterial infection, complications develop. It is better to treat swollen mammary glands with neutral solutions with a temperature no higher than 38 degrees.
Swollen mammary glands in a cat with lactostasis associated with increased milk production are treated with a special diet, including reducing fluid intake and pulling the mammary glands with a clean cloth. The nipples must be tied so that the animal can move freely.
Water can be completely removed for 24 hours, instead of wet canned food and soups - dry food or porridge.
When it develops into a purulent form, the kittens are switched to milk substitutes, and the cat is prescribed antimicrobial agents. Only a veterinarian can prescribe an antibiotic, taking into account the individual characteristics of the body.
Babies are not separated from their mother, and in order to prevent them from tormenting her nipples, a special blanket is put on the cat that covers the entire belly. Cracks in the nipples must be lubricated with special healing antibacterial ointments. In order to increase the cat's body's defenses, it is recommended to administer drugs that stimulate the immune system.
Why does the disease develop?
There are many reasons, and they are often associated with weakened immunity. Factors such as:
- Diseases of the reproductive system during pregnancy or after childbirth.
- Hormonal disturbances against the background of empty estrus (without fertilization) or during false pregnancies.
- Stagnation of milk in the glands, if there is an excess. This happens when kittens are taken away from a mother cat too early.
- Mechanical injuries or bruises.
- Bacteriological or fungal infections that penetrate through cracks or other injuries to the nipples.
- Hypothermia.
- Complications after childbirth or sterilization.
It happens that pathology is inherited by a cat, so before buying kittens, be sure to check what the parents were sick with.
What is false pregnancy in dogs and cats, its causes
False pregnancy in cats and dogs occurs due to excessive synthesis of progesterone, the hormone responsible for gestation and embryonic development of the individual. When there is a hormonal imbalance, all the signs of pregnancy appear, but the fetuses themselves are absent.
The reasons for the violation are different. Among them:
- neoplasms of the uterus or ovaries;
- cysts;
- inflammation;
- mating with a male whose reproductive function is impaired;
- resorption of embryos up to 4 weeks of pregnancy. The death of the offspring may be due to incompatibility of partners, changes in the diet or maintenance of the female;
- diseases of the endocrine system.
False pregnancy is sometimes provoked by severe, prolonged stress, caused, for example, by moving, changing owners, or the appearance of a new pet in the house.