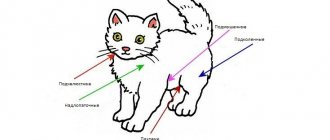
Cats, like all domestic animals, can cause a lot of trouble for their owners. Naturally, an attentive and responsible owner is attentive to all changes, often visible to the naked eye, in his beloved cat. It is for this reason that if he noticed that the cat had a hard and swollen belly, he might be scared, and rightly so.
Before you contact your veterinarian, let's find out together what could be the causes of a hard belly in cats. Here's everything you need to know.
Causes of a hard belly
If the cat’s stomach is tense for a long time, and is accompanied by other negative symptoms:
- diarrhea;
- hard stools;
- vomiting;
- the presence of blood in vomit or stool;
- apathy;
- increase in body temperature.
The animal must be taken to a doctor to establish an accurate diagnosis. Most often, helminthic infestation and constipation lead to the tone of the anterior abdominal muscles. In cats, the hardness of the abdominal wall may be due to pregnancy. In addition, there are other reasons for hypertonicity of the abdominal wall.
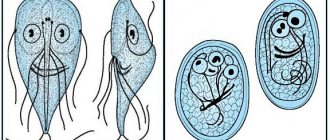
Helminthiasis
The accumulation of a large number of parasites in the intestines leads to constipation, inflammation in the digestive system, and vomiting. Worm infestations lead to disruption of the cat’s general condition and deterioration in the quality of its coat. And excessive stretching of the intestines caused by constipation causes pain and reflex spasm of the abdominal wall muscles when pressed.
Constipation and intestinal obstruction
Improper nutrition (mixed feeding of dry food and natural food, incorrectly selected food or lack of fluid), an inedible object swallowed by a cat, hairballs, intestinal spasms, colitis can cause constipation. Constipation can be accompanied by a decrease in appetite, a disturbance in the general condition of the animal, and a deterioration in the quality of its coat. Painful sensations localized along the intestine lead to reflex tension in the cat’s abdominal wall upon palpation.
In case of intestinal obstruction, there is no passage of feces, and the animal begins to vomit. The cat refuses to eat and loses activity. The causes of a hard belly are the same as for constipation.
Peritonitis and abdominal abscess
Inflammatory processes in internal organs, purulent granulomas and abscesses on the liver, kidneys, perforation of the gastrointestinal tract, viral infections can cause peritonitis. This disease can be a complication after surgery. Peritonitis is an inflammation of the mucous lining of the peritoneum. Irritation of the peritoneum when pus or blood spills into the abdominal cavity leads to reflex compression of the peritoneal muscles and the “stone belly” syndrome. With peritonitis, the animal may have vomiting, high fever, and trembling.
Ascites
This is an accumulation of fluid in the abdominal cavity. Such accumulation is a symptom of serious diseases affecting the internal organs of the animal. It's quite easy to recognize. The cat's abdomen is symmetrically distended. Sometimes the volume of the abdomen is increased significantly. The fluid that is in the abdominal cavity irritates the nerve endings in its wall and causes pain and muscle spasms.
Poisoning
Poisoning, which is accompanied by vomiting, inflammation of the mucous lining of the digestive tract, pain, flatulence, can also lead to a reflex protective reaction of the peritoneal muscles.
Abdominal injury
Blunt abdominal trauma may have no obvious signs other than resistance of the peritoneal muscles to palpation pressure and swelling. If the injuries are accompanied by internal bleeding, the cat may have additional warning signs: blood in the stool or urine, increased frequency of urination, urinary retention or involuntary passage. The cat becomes weak and lethargic, refusing not only food, but also drinking. If the bleeding is severe or prolonged, the visible mucous membranes become pale, the eyes are covered with a veil.
Biliary colic
Biliary colic is real torture for an animal. It is accompanied by severe pain, the cat’s temperature rises, and obstructive jaundice may develop. The abdominal wall is tense and painful.
Pregnancy
Pregnancy in cats usually proceeds normally, but pathological pregnancies can also occur. Normally, a cat's pregnancy leads to some changes in the animal's behavior. The cat eats little by little, but often, jumps more carefully, does not allow the stomach to be probed, and strains its muscles during such attempts.
The stomach can be “stony” even during a pathological pregnancy and self-abortion. In the early stages, it is difficult to notice a miscarriage in a cat. She eats the rejected tissue and licks herself thoroughly. Typically, such self-abortion has no consequences for the animal. The owner usually notices a miscarriage in a cat at a late stage. When behavioral abnormalities and bloody discharge from the vulva are noticeable. At the same time, the cat is constantly thirsty, its temperature rises, it can move along one particular route, and meow pitifully.
Diagnostics
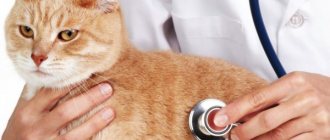
If your cat has a swollen belly and is also bothered by accompanying pathological symptoms, you should urgently take the animal to the veterinarian. During the initial examination, the doctor will try to find out why the tummy is swollen and bloated. To confirm the diagnosis, the doctor will give a referral for laboratory tests of stool and blood. If internal diseases are suspected, he will prescribe an ultrasound and x-ray. As soon as the exact diagnosis becomes known, the veterinarian will select a treatment regimen that will help solve the problem.
Treatment
Treatment can be conservative or surgical. This will depend on the cause of the hard belly syndrome. For example, in case of helminthic infestation, it will be necessary to carry out specific antiparasitic therapy; in case of constipation, a special diet and mild laxatives will be required. Antispasmodics are often recommended as symptomatic therapy. These remedies help relax the muscles of the abdominal wall, but can neutralize many symptoms and complicate diagnosis. Therefore, it is better for the veterinarian to show the animal before trying to help it. The most competent method of first aid would be to provide the animal with rest and deliver it to a veterinary hospital.
Why do cold sores appear on the lips?
Those who suffer from herpes have noticed that exacerbations begin along with ARVI. Herpes occurs when immunity decreases, the protective forces of which are used to suppress ARVI. Colds on the lips also appear when the body’s defenses are weakened: with chronic fatigue, lack of sleep, frequent stress, poor diet, alcohol abuse and active smoking, in women at the beginning of pregnancy and in the first 5-7 days after childbirth.
Photo: Colds on the lips can only appear if the immune system is weakened
Abdominal masses
Why does my cat have a bloated belly? Perhaps your pet has a tumor in one of the abdominal organs. Such pathologies are more common in adult cats. A neoplasm in the abdominal cavity can be benign or malignant. To make an accurate diagnosis, a comprehensive examination is necessary.
Depending on the location and type of tumor, treatment may include surgery to remove the tumor, chemotherapy, or observation and supportive care with medications.
Foods that cause flatulence in cats
Considering that in 90% of cases, flatulence is a consequence of poor nutrition, let’s consider foods that are at risk. If you have already encountered a problem, it is recommended to disassemble the diet “piece by piece” and, using the method of elimination, identify the product that is not digestible. Each organism is individual; if, after excluding obviously harmful products, the accumulation of gases bothers the cat, then we include everything in the “circle of suspects,” even meat.
In general, in order to reduce the risk of diseases of the digestive tract to a minimum, it is necessary to create a diet close to the “wild” way of life. Let's look at foods that are not typical for an adult cat:
Milk and dairy products - no matter how strange it may sound, some cats cannot digest the product due to lactose intolerance. In nature, a cat receives milk only from its mother, and when it grows up, it eats exclusively meat. However, if your pet tolerates milk or “live” yogurt well, go ahead, it is a source of many beneficial substances and friendly bacteria.
Fish - again, breaking stereotypes. Cats are not adapted to fishing in nature. If you manage to enjoy river fish at least occasionally, then there is no question of ocean fish. Tuna, sprat, herring, raw goby are delicacies that are allowed rarely and in very limited quantities. With daily feeding of fish, disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system and kidney failure are possible due to an excess of phosphorus.
Cereals – feeding your pet soybean or wheat, corn, barley, semolina “porridge” is the first cause of flatulence. Gluten and large amounts of carbohydrates are an excellent source of food for bacteria. Of the grains, rice and buckwheat are recommended for cats. Bread is a cereal product and also contains yeast (big fans of releasing gases), so it is also not recommended for “muchriki”.
Garlic, onions, fatty, fried, spicy foods, expired foods and cheap industrial feeds irritate the intestinal walls. The inflamed intestinal mucosa is unable to support beneficial bacteria and “gas” bacteria take their place.
Possible complications
Trichobezoars do not pose a health risk to cats. However, if they enter the intestines, the situation requires immediate resolution. The wool plug tightly clogs the intestines, making defecation difficult and causing intestinal obstruction.
In addition, hairballs injure the mucous membranes (even to the point of necrosis), poison the body with decay products, cause destructive changes in the intestinal walls and atony (depression of intestinal motility).
Note: cat hair can not only form trichobezoars in the stomach and intestines, but also accumulate behind the fangs. The cat will not be able to pull them out of these hard-to-reach places on his own, so the furry cat’s mouth should be inspected and cleaned regularly. If this procedure is neglected, an inflammatory process may develop in the oral cavity.
Intestinal parasites
Causes of bloating in cats may include gastrointestinal parasites, notes the Cornell Feline Health Center. This is more common in kittens, as they are more likely to become infected with worms. Your veterinarian can identify intestinal parasites by testing your cat's stool. Treatment usually involves taking oral antiparasitic medications.
What should the owner do
Under no circumstances should you play Aibolit or give your pet medications without consulting a veterinarian. Only a specialist can prescribe medications and set their dosage, based on the severity of the pathology, general condition and age of the animal.
Uncontrolled use of medications can lead to potassium being excreted from the body along with urine. This will worsen the cat’s well-being and lead to complications, even to the point where the animal dies. Human diuretics are especially dangerous in this regard.
Increasing their dosage independently can lead to disturbances in the level of electrolytes and leaching of fluid from the microcirculation network. This is fraught with the possible development of encephalopathy.
At the first opportunity, you should take the animal to the clinic so that the doctor can examine it and prescribe appropriate treatment.
A cat with abdominal hydrops is prescribed a therapeutic diet that involves limiting the consumption of water and any other liquid. The food of a sick pet should be nutritious, balanced in vitamins, minerals and carbohydrates and consist mainly of proteins.
The diet includes meat, poultry, sea fish, cottage cheese, kefir. You can add salt to food, but the amount of salt should be minimal.