In this article, we are going to explain the various causes of bumps on a cat's neck. We will learn about the role of the lymph nodes as part of the immune system and learn to identify tumors that will require veterinary consultation as they may be caused by an infection or tumor. Therefore, whether the lump on the neck hurts or not, we should consult a veterinarian.
If you're wondering why your cat has a lump on its neck, whether soft or hard, read on to find out the root causes and see a professional.
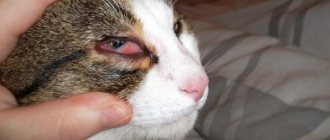
The cat has a lump under his jaw
The first thing to consider when explaining why a cat has a lump on its neck is the presence of submandibular lymph nodes. These ganglia are part of the immune system, so their function is to protect the body. If we notice that our cat has a lump on her neck, this may be inflammation of these nodes due to some pathological process.
© shutterstock
If the cat's immune system manages to control it, symptoms will no longer appear or they will be mild, such as mild discomfort or a slight fever. In other cases, the body cannot stop the pathogens and the disease develops, in which case we will need to help the cat with treatment, which, after diagnosis, will be prescribed to us by the veterinarian. Increased nodule size may be present in multiple diseases, hence the importance of diagnosis.
Risk factors
In the vast majority of cases, owners of older animals encounter neoplasms on the withers and neck of cats. The appearance of soft cones and balls is due to the natural aging of the animal’s body. Risk factors for this:
- The pet is over 8 years old;
- Endocrine disorders;
- Obesity;
- Presence of parasites.
Only a veterinarian can accurately identify the nature of the lump, the cause of its appearance and suggest treatment methods. Self-medication in the presence of formations in pets is not allowed.
Subcutaneous lumps in cats
Any subcutaneous lump, that is, under the skin that is not a ganglion, can have various origins and should be checked immediately by a veterinarian if we want to know why the cat has a lump on its neck.
In general, a hard lump on a cat's neck could be a cyst or tumor. By taking a sample from the inside, the veterinarian can determine its nature and, if it is cancer, whether it is benign or malignant. It is important to remember that if a cat has a lump in its throat, as we see it growing on the outside, it can grow inward, which can endanger its life by interrupting the flow of oxygen.
On the other hand, a soft lump on a cat's neck could be an abscess, which is a collection of pus in a cavity under the skin. These balls usually form after being bitten by another animal, so they are more likely to appear in whole venting cats who are about to fight for territory and mates. Animals have several bacteria in their mouths that, when bitten, remain in the wound. The cat's skin heals very easily, but bacteria remaining inside can cause an infection under the skin, which is the cause of the abscess.
Treatment of tumors is based on diagnosing their type and determining the presence of metastases, that is, whether the primary tumor has migrated throughout the body and affects other areas. You can choose removal surgery, chemotherapy or radiation therapy, depending on each individual case. In turn, abscesses require antibiotics, disinfection and, most difficult, drainage until they close.
What diseases cause a lump?
The list is quite large:
- cancerous degeneration of breast tissue is the most terrible diagnosis, often with an unfavorable prognosis;
- lipoma, or wen, is a benign tumor prone to spreading;
- neoplasm of the skin: papilloma, fibroma, sarcoma, lymphangioma, etc.;
- lymphadenitis – inflammation of the lymph nodes;
- hernia (inguinal, umbilical, perineal) – protrusion of internal organs under the skin;
- mastitis;
- inflammation of the paraanal glands;
- a lump may appear after sterilization - this is also a hernia, but postoperative, resulting from a violation of the technique of applying internal sutures;
- skin diseases: furunculosis, folliculitis, carbuncle formation, abscess, phlegmon, etc.;
- a lump may appear due to an insect bite (wasp, bee, bumblebee, etc.);
- pellets - although tangles are unlikely to be confused with a lump, protrusion or tumor.
Important! If the formation under the skin tends to grow rapidly, while the number of nodules increases, they bleed or are painful, then this is not a good sign and a serious reason to undergo a full veterinary examination: biopsy, urine tests, ultrasound, x-ray, etc.
Lump on a cat's neck as a reaction to a vaccine
We've looked at the most likely reasons why a cat has a ball in its neck, but also a type of tumor called fibrosarcoma can develop as a secondary reaction to the vaccine, especially in feline leukemia. Although the injections are usually in the withers area, the injection is located higher and we may notice a small nodule in the neck associated with inflammation. It should resolve within 3-4 weeks, but if it does not, chronic inflammation can lead to fibrosarcoma.
Surgery to remove it can be difficult because it is a very invasive tumor. For this reason, some professionals recommend using vaccines related to fibrosarcoma of the extremities, since this way they can be amputated in the event of a tumor.
We should also be aware that inflammation and even an abscess may occur as a side reaction in the inoculated area of any injection.
© shutterstock
Causes of subcutaneous lumps
Small round balls often appear after injection under the skin. They are called post-injection granuloma and resolve on their own a few days after the end of the injections. To avoid them, the injection site is massaged daily. Sometimes granulomas remain for life, without changing their size and position. In other cases, the reason lies in:
- blockage of the sebaceous glands;
- allergic reaction;
- infestation with parasites;
- hormonal imbalances;
- infection of open wounds;
- disturbances in the formation or functioning of connective tissues;
- injuries;
- inflammatory processes.
The risk group includes older animals, cats with chronic diseases, late castrated and sterilized pets. The risk of developing cancer increases with constant stress, low activity and poor diet. A predisposition also appears with frequent injuries in the same area of the body, infection with leukemia and regular inhalation of tobacco smoke. Cancer is often inherited and is diagnosed in animals older than 7 years.
Lump on cat's neck due to thyroid gland
Finally, another explanation for why our cat has a lump on her neck could be an increase in the size of the thyroid gland, which is located in the neck and in some cases can be felt. This increase in volume usually occurs due to a benign tumor and consequently leads to excess secretion of thyroid hormones, which cause hyperthyroidism, which affects the entire body.
An affected cat will exhibit symptoms such as hyperactivity, increased hunger and thirst, but thinning, vomiting, poor hair coat, and other rather nonspecific symptoms. It can be detected with a hormonal test and treated with medications, surgery, or radioactive iodine.
The cat has a bump on his face
Finally, once we've identified the most common reasons why a cat has a lump on its neck, we'll see why lumps can appear on their face as well. The cancer, squamous cell carcinoma, can cause nodular lesions, as well as the less common disease cryptococcosis.
Both require veterinary treatment. Cryptococcosis with antifungal drugs, as it is a disease caused by a fungus, and carcinoma can be operated on. As we can see, it is very important to contact a veterinarian as soon as possible in order to begin treatment as early as possible to avoid complications.
Diagnosis and treatment of neoplasms
Diagnosis is carried out when any neoplasm appears. After a thorough examination, the doctor determines the level of danger of the resulting compaction and selects the appropriate therapy.
In addition to a clinical examination and history taking, it is necessary to check the functionality of the heart, study a general analysis of urine and blood, and also do a bacteriological analysis of the contents of the lump-vesicle. Using ultrasound and x-rays, the doctor determines the depth, exact location and size of the tumor. At an early stage, cancer is often asymptomatic, so biopsy and endoscopy are used to detect it.
The location of oncology development directly depends on the sex of the animal. Cancer in cats most often affects the testes, and in cats - milk bags. If the disease is detected at an early stage, therapy is reduced to taking special medications and gives positive results. At later stages the prognosis is negative. The patient is given painkillers and euthanized.
Table of primary and additional therapy
Drug or surgical therapy depends on the diagnosis, the state of immunity and the stage of development of the disease. Recommended treatment methods can be found in the example table.
| Type of pathology | Therapy | |
| Main | Additional | |
| Lipoma | Surgical excision of large lumps | Lipomas located near the spinal column or neck are not recommended to be touched. Intervention is allowed only if the lipoma is growing steadily |
| Hemangioma | Non-interference and surveillance | Complete surgical removal on an individual basis |
| Adenoma | Subcutaneous and intramuscular injections of antibiotics, antiviral and antifungal drugs | Surgery for increasing size |
| Mastitis | The animal is given a novocaine blockade, physiotherapy, a course of antibiotics and compresses are prescribed. | In advanced forms, surgical intervention is used |
| Cancer | In addition to special medications, the doctor prescribes radiation or chemotherapy followed by removal of the tumor | In later stages, pain management is used and euthanasia is recommended. |
| Abscess | An autopsy is performed and pus is removed using antiseptics. The treated area is isolated with a sterile bandage. Any remaining infection is treated with a course of antibiotics. | Long-term use of antibiotics is dangerous for the developing organism of kittens. If the animal is less than 1 year old, the veterinarian tries to reduce the recommended duration of antibiotic therapy as much as possible. |
| Cyst | For small formations, observation is recommended; for large ones, removal | Sometimes parasites are found in the growths. In this case, surgery is necessary even for a small cyst |
| Hernia | To remove a hernial lump, massage sessions are prescribed, the prolapsed organ is put back in place | For large formations, the doctor performs surgery to stitch the diverging ring |
| Inflammation of the paraanal glands | The accumulated fluid is squeezed out, facilitating the production of secretions | If pain occurs, the animal is injected with novocaine. If a predisposition to inflammation is identified, the cat will have to be taken for the procedure several times a year. |
| Eosinophilic granuloma | Based on the cause of the pathology, the cat is prescribed antibiotics, antihistamines or steroids. | A large weeping wound is usually excised to preserve the appearance of the affected area |
| Lymphadenitis | The disease is not independent and occurs against the background of another pathology. Painkillers, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial drugs are used for treatment | A large number of inflamed lymph nodes indicates leukemia. This pathology is not fatal, but requires long-term drug treatment |
Syringoepithelioma is not considered dangerous to health, so treatment is not provided. Hematomas resulting from minor injuries usually go away on their own or are eliminated with healing ointments.
In addition to traditional scalpel work, surgeons use laser excision, electric shock, or freezing at low temperatures with liquid nitrogen. Young and healthy animals with strong immunity often heal on their own. In this case, they receive immunity, eliminating subsequent relapses.
After surgery, the animal is prescribed a course of immunomodulators that stimulate the functioning of immune cells. The remaining wound is treated with healing ointments. Bandages can be changed yourself or at a veterinary clinic. Be sure to consult a doctor if pus continues to leak from the bandage after surgery. Some tumors found in cats are dangerous not only for animals, but also for humans.
What to do with purulent and bleeding seals?
The appearance of bleeding and purulent discharge is a symptom of cancer. Immediately upon discovering a problem, take your pet to see a veterinarian.
Before visiting a doctor, it is prohibited to treat wounds with alcohol-containing solutions, squeeze out or puncture the lump. It is also not allowed to use any ointments without prior consultation. Even plain water can make the situation worse, so do not try to rinse or wet the swelling.
If the seal breaks on its own, provide first aid to the animal. To do this, you need to treat the wound with an alcohol-free antiseptic and apply a sterile bandage. All these actions do not exclude a veterinary examination.