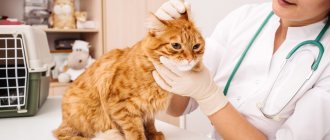
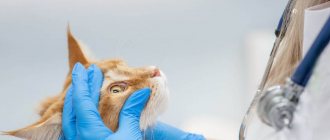
A condition such as an eye injury in a cat is dangerous due to the loss of vision and the organ itself. There are 3 types of damage, which are accompanied by redness, deformation of the eye structures, clouding of the cornea, and swelling of the eyelids. At the first signs, the owner must take the pet to a veterinarian, who will conduct a diagnosis, prescribe medications and, if necessary, perform surgery.
According to veterinary ophthalmologist O. Fedotova, cats of brachycephalic breeds are most susceptible to injury due to short extraocular muscles and a small orbit.
Symptoms of eye injury
Penetrating injury causes redness of the conjunctiva, spasm and swelling of the eyelids. If the eyelids are also damaged, there may be capillary bleeding. There is also profuse lacrimation, clouding and visible violations of the integrity of the cornea with the leakage of intraocular fluid outward. If the iris is injured, hemorrhage will occur in the anterior chamber of the eye, and if the lens is injured, it will become cloudy and a severe inflammatory process will occur inside the eye.
All the symptoms described above can lead to loss of vision, and without emergency help and the prescription of drugs that control inflammation and accelerate the recovery of the cornea, to the loss of the eye as an organ as a whole.
Foreign bodies
Foreign body entry is one of the most common causes of eye injury. Dogs are especially susceptible to this during active walks in the forest or just in tall grass.
Fragments of thorny plants dig into the conjunctival sac or into the cornea of the animal's eye. In this case, the pet experiences severe pain and may try to get rid of the splinter on its own, thereby further irritating and injuring the visual organ. Eye rinsing can serve as an emergency method for an animal in such situations. This can be done with saline solution (sold in any human pharmacy) or boiled water.
First aid “here and now” before visiting an ophthalmologist
If there is contamination of the wound (sand, wool, etc.) and bleeding, you can wash the eye with a sterile warm (room temperature or body temperature 36-37 degrees) solution of Sodium chloride 0.9% (saline). It is drawn into a syringe, the needle is removed or broken off, then the cornea and eyelids are poured. In addition to saline solution, you can use any veterinary eye lotion. If the wound is relatively clean, it is better not to rinse the cornea again, as this is very painful for the pet.
If you have antibacterial eye drops on hand, you should start using them as soon as possible (suitable options are Tobrex, Floxal, Tsipromed, Ciprofloxacin, Levomycetin, Iris, Tsiprovet).
It is not recommended to use drops with sodium sulfacyl, as their use causes severe pain, which can lead to worsening of the eye condition.
Causes and types of corneal damage
The cornea of the eye is very thin and practically unprotected, except for the movable eyelid. It can be damaged accidentally or intentionally, as a result of an accident or failure to follow safety precautions when wearing contact lenses and glasses.
The main causes of corneal damage are divided into external and internal. External ones occur due to foreign objects, substances, thermal or wave effects entering the eye. Internal - due to congenital or acquired diseases that affect the condition of the cornea and provoke a violation of its integrity.
External causes of corneal damage are considered the most numerous and varied. They are divided into several groups depending on the type of effect on the cornea:
- Mechanical injuries of the cornea
. They are sharp and dull. An acute violation of integrity is characterized by the fact that a foreign object penetrates through the layers of the cornea and reaches the vitreous body and the internal structures of the eyeball. Most often this is a scratch, puncture or cut of the cornea. Blunt eye injuries are expressed by a bruise of the cornea of the eye, which is not accompanied by radical dissection of the tissue. - Thermal damage to the cornea
is a burn of the outer shell by a hot object, excessively heated air, or steam. In rare cases, thermal burns of the eye shell are recorded due to its contact with objects that are too cold. - Chemical damage
. This cause of corneal damage is considered the second most common after mechanical trauma. It occurs when drops of acids or alkalis enter the eye. - Radiation injury to the cornea
, which occurs when unprotected visual contact with excessively bright light (so-called “bunnies”), magnetic, electrical or radiation waves.
Ophthalmologists call primary infections of the eye shell another cause of external corneal damage.
Internal processes leading to the development of pathology do not have a clear classification. These include:
- disruption of metabolic processes in the body or directly in the tissues of the eye, which cause thinning of the membrane, detachment of its outer layer from the membrane;
- dry mucous membrane due to high load on the organs of vision, wearing contact lenses, allergies or the functioning of the lacrimal glands, which provokes premature accelerated wear of the outer layer of the cornea;
- autoimmune thinning of the cornea, during which protective cells attack the tissue of the stratum corneum;
- a genetic anomaly affecting the formation of collagen in the body, as a result of which the cornea loses its firmness and elasticity and becomes brittle;
- instability of intraocular pressure, which causes a loss of strength of the cornea, provokes micro-tears that can become a gateway to infections;
- age-related changes.
They all have the same nature - they cause thinning or a decrease in the protective properties of the eye membrane. Such reasons often provoke erosion, detachment or rupture of the cornea.
Unlike external causes, which appear in one eye, internal ones can affect both eyes simultaneously or sequentially.
What will the doctor do at the appointment?
A complete ophthalmological examination will be performed, which includes:
- biomicroscopy of the eye (examination under magnification);
- ophthalmoscopy (examination of the retina and optic nerve head for post-traumatic damage);
- assessment of pupil reactions to light;
- An ultrasound of the eyeball is done when there is severe swelling of the cornea and it is impossible to examine the internal structures of the eye;
- fluorescein test (staining the cornea with a safe dye) - if necessary.
The test allows you to evaluate several positions at once: the area and depth of damage, the retention time of the tear film. Thanks to this, one can judge the presence or absence of dry eye syndrome and the patency of the nasolacrimal duct.
Symptoms to watch out for
Disease or common occurrence? When you notice that your cat’s eyes are running, then before taking any measures, it is worth observing and analyzing the behavior and habits of the animal in order to understand whether this is a dangerous disease, or whether your pet has a common phenomenon for their family.
© shutterstock
What should you pay attention to? Let's answer some questions :
- Does your cat still have a fun and carefree time, or has he become unsociable and is hiding even from you?
- Has your baby's appetite changed?
- How does a pet react to sunlight?
- Are there any visible injuries or scratches around the eyes?
- What color is the discharge from the eyes of cats? Are they transparent with a gray or red tint? Or is it purulent secretions?
- Has the eye color changed?
- Has your pet's temperature increased?
Perhaps when you answer these questions, you will then clearly understand that there is little reason for concern. And the appetite is normal, and the behavior has not changed, and the cat’s eyes are streaming with a substance similar to tears.
Then a completely logical question arises: why do the cat’s eyes run? And the next question: what to do to rid your pet of this?
But before we try to answer these questions, we must admit that not everyone’s forecasts are so optimistic. There are those who have noticed that their pet’s behavior, appetite and habits have changed, a wound is noticeable in the eye or the discharge is clearly purulent in nature. We are also ready to help all owners of sick animals. So, why do pets' eyes water?
Treatment of penetrating eye injuries in cats and dogs
After assessing the condition of the eye and the patient as a whole, the ophthalmologist selects an individual treatment plan. If necessary, surgical treatment of the wound with suturing of the edges is performed. Eye drops and moisturizing ophthalmic gels are also prescribed, which will help avoid eye infection and speed up the recovery of the cornea.
If the damage is more serious and deep, affecting the iris and lens, systemic anti-inflammatory and antibacterial therapy is also prescribed. These are tablets or suspensions that are taken orally. Unfortunately, in some cases the lens must be removed.
During this period, it is important to use a protective collar, as pets often want to scratch the sore eye with their paw or rub it against surrounding objects.
How to treat an injury?
Use of veterinary drugs
The treatment regimen is prescribed by a veterinarian; self-medication of the pet is prohibited. To prevent the animal from touching the injured organ, it is recommended to wear a protective collar. If the eye is scratched in a fight, you should treat it with antibacterial drops, such as:
If prescribed by a doctor, the diseased organ can be treated with the drug “Iris”.
- "Tsiprovet";
- "Iris";
- "Dekta-2";
- "Desacid";
- "Lacrimin."
Prevention of corneal injury
If there are several cats in the house or a cat and a dog, it is recommended to trim its nails regularly. How to do this correctly, watch our video. You can also wear special anti-scratch caps. A wide selection of nail clippers and anti-scratch clippers are presented in the Averia Market online store.
But, if an injury does occur, it is necessary to take the animal to an appointment with a veterinary ophthalmologist as soon as possible for examination, assessment of the severity of the injury and the appointment of timely therapy. This increases the chances not only of saving the eye as an organ, but also of preserving vision.
Eye injuries from a claw do not always occur without serious consequences, so try to avoid the possibility of fights involving your pets. This is especially important when traveling with “tails” into nature, where they may not share the territory with local street animals.
Scleritis of the eyes - what is it?
The sclera (white layer) of the eye plays a vital role in ensuring quality vision. It is part of the fibrous membrane, which also includes the cornea. The sclera is very dense and opaque in structure. This allows it to protect the inner parts of the eye from external influences. Light rays that would cause blinding if it were transparent do not penetrate the sclera. In addition, the tunica albuginea maintains intraocular pressure and takes an active part in the outflow of aqueous humor. Diseases of this part of the eyeball can cause serious complications.
Scleritis is an inflammatory process that affects all layers of the sclera and leads to its destruction.
Because of this, the outer shell of the eye begins to delaminate. The inner layers and all visual functions are at risk. If the course of the disease is unfavorable, a person may completely lose vision.
So, how to provide first aid to a cat in case of various injuries?
To begin the “treatment”, the pet must first be caught, since after the fight he is extremely excited and behaves aggressively. A better option may be to throw a blanket or soft cloth over the cat to prevent it from scratching your hands and face. After twisting, he will stop resisting, and you can begin providing first aid.
Sometimes a cat just needs first aid after a “showdown” with his relatives
Treatment of scleritis
This disease is treated with anti-inflammatory drugs and other medications, the action of which is aimed at eliminating the cause of scleritis. The patient is also prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures, including electrophoresis. In severe cases of the disease, surgery is performed. Usually it is necessary in case of purulent neoplasms, damage to the retina, the appearance of astigmatism or glaucoma.
Severe damage to the sclera, its thinning, is treated by transplanting donor tissue. It is also necessary for serious damage to the cornea.
The patient can alleviate his condition with the help of folk remedies. Of course, they should not become a replacement for primary treatment. Aloe lotions, decoctions of calendula and chamomile, sage and thyme will help reduce pain. Such remedies cannot cure the disease.