Cats' eyes are very sensitive. Thanks to this, they have a unique feature - to see in the dark. Due to the special structure of the retina, the cat’s pupil reacts sharply to lighting - it expands in the dark, almost covering the iris, or narrows to a thin strip, preventing light damage to the eyes.
But there are situations when the pupil remains dilated, regardless of the lighting. What causes dilated pupils in a cat? Let's try to understand this situation.
The normal state of a cat's pupils
A cat's pupils are always dilated at night, regardless of their internal state. This reaction helps the animal see better in the dark. Surprisingly, cats can even catch the light of stars.
One of the reasons for dilated pupils in a cat is physiology, or rather estrus. If during this period the animal’s pupils are constantly dilated, then this is the norm. This reaction of the body manifests itself to the hormonal changes that occur in the body during this period. At this time, dilation of the pupils is accompanied by signs of the sexual cycle - loud meowing, pressing to the floor with the tail raised up, frequent urination and constant licking.
Stress, overexcitation, fear, and aggression are also the causes of dilated pupils in a cat for a long time, regardless of lighting conditions. Experts say that cats see everything in slightly blurred outlines, and when the animal is alarmed or frightened, it intuitively looks around, trying to see sources of danger.
The reason for the cat's dilated pupils in this situation is adrenaline, which is produced whenever the animal is in an excited state. In addition to dilated pupils, such nervousness may be accompanied by hissing and flattening of the ears. Enough for the cat to calm down, the pupils “relax” and again become dependent on light.
Perhaps the owners know another reason for dilated pupils in a cat. When running, active games, jumping, trying to catch some living creature, the cat’s pupils are dilated. The animal needs to clearly see its potential prey, and also measure the distances between objects. This is a completely normal reaction to the production of active adrenaline. After the end of the games, the condition of the pupils will return to normal.
Unsteady gait
First on the list of signs indicating the development of blindness in a cat is an unsteady gait. Owners of blind cats know firsthand that their pets, deprived of the ability to see normally, are able to live varied and quite happy lives. Remaining blind, the cat will not suffer, but will be able to adapt to life. The fact is that with age, all cats sooner or later begin to go blind as a result of the development of degenerative senile processes.
Domestic cats have human-like vision. The difference is the color of the image and twilight vision. Cats are not able to normally focus their gaze on nearby objects. At the same time, objects located at a distance are visualized much better. This explains the fact that a cat can be completely indifferent to its favorite toy that lies nearby.
For most people, after 40 years of age, their vision begins to rapidly deteriorate. Therefore, a person turns to an ophthalmologist, who prescribes the wearing of glasses, at least for reading. Domestic cats, after 5 years, begin to see worse. The reason for this is a change in the flexibility of the lens, causing clouding. This leads to a disruption in the ability to focus on objects, regardless of their location.
Vision problems that come on suddenly can cause a change in gait. Unsteady walking occurs in cases where vision loss is caused by sudden changes in the lens, vitreous body or retina.
Dilated pupils in a cat after surgery
This condition should not alarm owners. Indeed, the dilated pupils of a cat after anesthesia do not react to light for some time. Within a day, their condition returns to normal. Veterinarians recommend leaving the animal in the clinic to monitor recovery from anesthesia for two to three hours. In severe cases, the length of stay in the clinic is determined by the veterinarian.
After castration, the cat's pupils are dilated for 24 hours. After anesthesia, the animal may experience vomiting and severe weakness. You can pick him up from the clinic in an hour.
Eye diseases
If a cat, at rest and in normal lighting, has one or both pupils dilated, then this indicates some kind of pathology in the animal’s health, which should alert the owner. Be sure to take your pet to the vet, as there can be many reasons for this condition. Only a specialist can identify them and make a diagnosis.
It is necessary to understand that the fact of dilated pupils in an animal is not as terrible as the lack of reaction to light.
Third eyelid
Normally, the nictitating membrane (nictitating eyelid) performs an important protective function.
However, with some pathologies, the nictitating membrane may fall out and the so-called “third eyelid” may form in the cat. It begins to form in the corner of the eye and looks like a white film. In the normal state, it is visible only when the animal blinks or tilts its head. If you see this white film in other cases, a visit to the veterinarian is necessary.
Third eyelid prolapse is rarely an independent disease. Most often, this is a sign of other, more serious, pathological processes in the pet’s body.
Symptoms of eyelid loss are:
- redness of the conjunctiva;
- swelling;
- secretion of mucus, pus;
- lacrimation;
- formations in the corner of the eyes (the third eyelid itself);
- itching and fever are possible.
During treatment, medications are prescribed that relieve symptoms and also eliminate the cause of the disease.
Anisocoria
With this disease, the dilated pupils of the cat do not react to light. This is a serious reason to visit a veterinary ophthalmologist. The causes of the disease can be not only in the eyes themselves, but also in problems with the nervous system, in particular pathologies of the optic nerve or brain. This condition can lead to blindness if the cause is not eliminated in a timely manner (if the pathology is curable).
The causes of the disease include:
- posterior uveitis;
- retinal atrophy;
- lens luxation;
- glaucoma (angle-closure);
- brain tumors (rare);
- cerebrovascular accident;
- optic nerve atrophy;
- increase in intracranial pressure;
- disruption of the blood supply to the eye.
Frequent collisions with objects
Constantly bumping into objects. With a sudden loss of vision, the animal begins to collide not only with objects, but also with walls. In this regard, veterinary experts strongly do not recommend that owners of cats who have lost their vision make changes in the house.
If there is a lot of furniture in the house that has sharp corners, it is recommended to wrap them in something soft. Special film or devices are perfect for these purposes, the purpose of which is to protect furniture for small children who are just exploring the world.
Often colliding with objects, a blind animal will soon remember the route and automatically determine distances. Not all cats can remember distances and routes, so in this case they rely on their sense of touch. It is the whiskers that are very important for old and blind animals, playing the role of a kind of probe. Vibrissae allow the cat to determine at what distance an object is from the animal.
Consequences of injuries
When scarring of injuries occurs, opacities of varying intensity appear on the cornea. Because of this, insufficient light intensity reaches the retina. Behind the damaged cornea, the pupils reflexively dilate further to capture more light for improved vision. Although there is a reaction to light, it is very weak, and it seems that the pupils are constantly dilated.
Disease prevention and care
It is necessary to examine the animal's eyes daily. Regular cleansing with boiled water or chamomile decoction helps prevent clouding of the cornea of the eye. This allows you to remove contaminants that are sources of infection. A gel is applied to the eyelids to cleanse and protect the skin. The fur around the eyes is combed with a small comb and neatly trimmed. If wounds appear on the cornea, the eyes are washed with Furacilin solution.
All information posted on the site is provided in accordance with the User Agreement and is not a direct instruction to action. We strongly recommend that before using any product, you must obtain a face-to-face consultation at an accredited veterinary clinic.
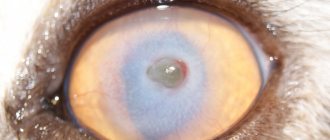
Cataract
A disease in which there is complete or partial clouding of the lens of the eye. As a rule, this occurs in the elderly animal due to vitamin deficiency, diabetes or injury. The main symptom is a gray-blue color of the pupil. Treatment is carried out only surgically, but in the early stages and for prevention they use Gamavit and Fitomin.
Refusal to jump
A cat with poor vision refuses to jump in heights, jumping onto elevated surfaces as before. The reason for refusing to jump may be the inability to calculate the correct trajectory of the jump as a result of poor vision or blindness. But refusal to jump can also occur in the event of unsuccessful maneuvers, as a result of which the animal is injured. For a long time, a cat may refuse to jump from heights or onto elevated surfaces.
It is worth drawing the attention of cat owners to the fact that the reason for refusing to jump can be not only poor eyesight or injury, but also pain in the lumbar region. Also, the appearance of discomfort in the kidney area due to the development of various pathologies can cause the animal to refuse to jump.
In order to find out exactly the reason for this behavior in your pet, it is recommended to seek help from a veterinary specialist. After conducting a detailed examination of the animal and a number of necessary laboratory tests, the doctor will be able to find out the cause and prescribe treatment if necessary.
Blepharitis
Due to external influences or vitamin deficiency, inflammation of the eyelids develops. Consultation with a specialist is necessary to determine the type of disease. Blepharitis can be simple, meibomian, which is characterized by inflammation of the sebaceous glands on the eyelids, ulcerative. The main symptoms of the disease include: thickening of the eyelid, scratching around the eyes, crusts of pus on the surface, dilation of the pupil, and the cat suffers from severe itching.
First of all, the animal’s eyelids are freed from crusts using a solution of soda and oil. Vaseline oil is most effective for softening. The eyelids are treated with brilliant green and mercury yellow ointment. As an auxiliary therapy, the daily diet is enriched with Phytomins.
Treatment methods
The choice of treatment method depends on the cause of the cloudy eye:
- Antibacterial therapy. Prescribed in the presence of infectious diseases caused by bacteria. Therapy can be carried out at home. Broad-spectrum drugs, for example Ciprofloxacin, are administered intramuscularly. Levomycetin drops are instilled into the eyes.
- Anti-inflammatory treatment. Quickly eliminates swelling, redness and cloudiness. Anti-inflammatory drugs (Onsior, Cymaldzheks) are administered orally or intramuscularly. They have a negative effect on the cat’s body, so they should be used in short courses.
- Surgical interventions. In case of glaucoma, corneal ulceration and other diseases, surgery becomes the only way to save the animal’s life. They often resort to drastic methods of treatment, including removal of the affected eyeball. In case of ulcerative lesions, only the affected areas of the cornea are eliminated. After surgery, scars remain that reduce visual acuity.
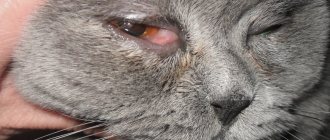
Conjunctivitis
This inflammation of the eyes is divided into subtypes: allergic, arising due to the ingress of a foreign body, infectious. It manifests itself as liquid discharge from the eyes, often purulent, general restlessness of the animal, photophobia, and the formation of crusts after sleep.
The pupils can both become very narrow and pathologically dilate. With such symptoms, it is very important to provide timely assistance to your pet, independently, but under the supervision of a veterinarian. The cat's eyes are washed with a weak solution of potassium permanganate or Miramistin. Then drops of “Iris” are instilled. If crusts appear around the eyes, they should be soaked and removed with a damp cotton swab. Then the lacrimal canal is washed generously with drops of “Iris” or “Neoconjunctivet”. The procedure is repeated three times a day until recovery. The course of treatment lasts ten days.
For conjunctivitis caused by infection, your veterinarian will prescribe antibiotics. As an addition to the treatment of moderate and mild forms of the disease, you can use hygienic lotions from the “Phytoelita” series, as well as medicinal herbal infusions, to wash your eyes.
What should the owner be wary of?
A change in habitual behavior is not normal for an animal, it means something is bothering him
The owner usually always notices changes in the behavior of his pet. Serious diseases, as a rule, are accompanied by other symptoms in addition to enlarged pupils.
It is important to observe the animal. If your pet’s behavior begins to differ from what is usual and unusual for the animal:
- no appetite;
- stool disorder, stomach upset, vomiting;
- depressed state of the animal: does not play, is inactive;
- aggressive behavior: hisses, presses his ears to his head, ruffles his fur, actively scratches or licks himself, reacts to any sound, hides, attacks animals and people;
- lacrimation, clear or purulent discharge from the eyes, not associated with the pores of the animal;
- inflammation of the eyelid, blood vessels of the eye, darkening of the membrane or the presence of a film on the eye.
By noticing changes in your pet's behavior in time, you can promptly determine the causes and presence of diseases, and as a result, avoid serious consequences from blindness to the death of the animal.