A purulent formation on the gum is popularly called gumboil. Very often it is not taken seriously, but it is not just a small swelling that will go away on its own. Flux is an ontogenic periostitis, a complex infectious disease that affects the periosteum and jaw bone. Periostitis occurs quite often, but without adequate treatment it is fraught with serious complications, including blood poisoning.
It is almost impossible to cure gumboil without the help of a dentist. The treatment program includes therapeutic, physiotherapeutic, and surgical methods.
Have you noticed purulent formations on your gums and swelling of your cheeks? Do you have acute pain in your tooth or gum? Come for a consultation with a dentist at our clinic. Timely treatment of flux allows you to get rid of the problem within about 7 days.
Why does flux form?
Dental diseases are always the precursor to gumboil. Most often lead to suppuration:
- Untreated caries. If caries is not treated, the inflammatory process begins to spread to other tissues. Pulpitis and periodontitis gradually develop.
- Mechanical injury. Injury can lead to more than just crown destruction. Very often, an inflammatory process develops in injured tooth or gum tissues. Without treatment, purulent processes develop and gumboil forms.
- Periodontitis. In more than half of the cases, gumboil develops precisely against the background of periodontitis, as its complication. This is due to the fact that purulent processes from periodontal pockets can spread to the neck of the tooth.
- Poorly sealed canals. Before filling, the canals must be completely cleaned and the filling material must completely fill the cavity. If at least one of the conditions is violated, the infection from the canal spreads to other tissues.
Causes of the disease
Patients often blame the careless work of dentists for the development of inflammatory processes in the oral cavity. Thus, “flux after wisdom tooth removal” is one of the most discussed topics on dental forums. In fact, the most common causes of periostitis are gum trauma and untreated tooth decay. Often the situation is complicated by the patient’s reluctance to visit the dentist in a timely manner. As a result, food debris inevitably accumulates in places of damage, which eventually begin to rot. Further, the pus accumulates and then begins to rapidly spread, affecting healthy tissues of the oral cavity.
The most common causes of gumboil are damage to the gums, poor oral hygiene and caries.
Treatment of flux on the gums with folk remedies cannot guarantee a high-quality result. Most often, self-prepared medicinal products can only suppress the pronounced manifestations of the disease, and not eliminate the causes of its occurrence. For this reason, when the first symptoms of periostitis appear, it is important to undergo high-quality flux treatment in dentistry, which can guarantee complete relief of the inflammatory process.
When do you need dental help?
Flux has pronounced symptoms. The main one is the appearance of an abscess on the gum next to the diseased tooth. The abscess develops gradually. At first, the gums swell a little and a small red or whitish bump is noticeable on it. After some time, a noticeable fistulous tract forms on the lump, from which pus flows. The development of periostitis is accompanied by other symptoms:
- Swelling and swelling of the gums, lips, cheeks. Sometimes they can be so large that facial features are distorted.
- Severe cutting pain in the tooth area. Innervates the temporal region, orbits.
- The diseased tooth begins to become very loose, even if there was no mobility before or it was insignificant.
Since flux is caused by infection, it is characterized by symptoms that appear during any infectious process. The patient feels unwell, his temperature rises, his head hurts, and weakness appears. Lymph nodes on the head and neck become enlarged.
Any of these symptoms is a reason to consult a doctor. The more advanced the case, the higher the risk of complications. This disease is often accompanied by other pathological processes. For example, a cyst may form in tissues affected by infection.
Symptoms
What are the symptoms? They are quite typical, since any person who has suffered from toothache at least once in their life has felt something similar:
- The first sign is often loose teeth and the appearance of blood on the toys the cat plays with.
- The animal's mouth smells very bad, which indicates that putrefactive processes have begun.
- The cat begins to feel ill, is reluctant to eat, and often refuses food altogether (during the period of exacerbation of toothache).
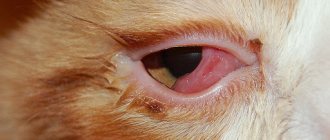
- If you look closely, you can see areas of swelling, redness, and brewing abscesses in the oral cavity. This is the most characteristic sign.
- Due to severe pain (with the development of pulpitis), the animal does not sleep well, sometimes, for no apparent reason, it begins to “growl”, meow hoarsely and forcefully.
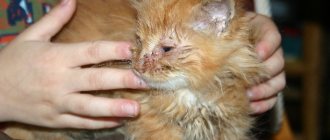
- Sometimes your pet's cheek becomes swollen (pictured). But, unlike “human” flux, this happens infrequently.
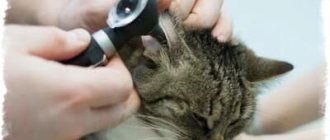
Diagnosis of the disease is quite simple, in many cases everything is limited to an external examination. If the veterinarian suspects that the process has spread to the periosteum, an x-ray and/or ultrasound examination is done, through which cavities and cavities can be detected in the bone tissue itself.
Flux treatment methods
Treatment should be started as early as possible. If an abscess on the gum opens spontaneously, there is a risk of infection entering the bloodstream. With such an infection, blood poisoning develops, and such a complication can lead to serious consequences, including the death of the patient.
Flux treatment is always complex. The treatment program depends on the degree of tooth decay and the spread of infection.
Dentistry for those who love to smile
+7
Make an appointment
How to treat flux?
If your tooth hurts and gumboil appears on your cheek, you shouldn’t panic and look for something to rinse your mouth with. “Grandmother’s” treatment methods really help get rid of acute pain and relieve some swelling, but they have not yet helped anyone cope with purulent compaction, which is the main danger. How and with what to treat flux? How to remove gumboil in case of gum inflammation? Only a qualified dentist can give detailed answers to these and other questions.
Self-medication with folk remedies will only help dull the pain and relieve swelling a little. Only a qualified dentist can completely remove pus and eliminate the cause of inflammation.
How is flux treated in dentistry? Currently, there are two main methods of treating gumboil on the cheek:
- Opening the pus sac, in which the doctor removes the accumulated pus through a small incision. The procedure is performed under anesthesia. After removing the pus, the specialist installs a drainage at the site of the incision - a special rubber strip that ensures the outflow of pus and prevents the wound from healing ahead of time.
- Cleaning an abscess through a root canal is necessary if the inflammation is a consequence of caries or a crack in the tooth.
Often in advanced stages of the disease there is a need for tooth extraction. Typically, this procedure is carried out when there is deep destruction of the causative tooth or if there is a large infected area between the tooth and the gum. Removal is also used if there is a sufficiently large crack in the tooth that cannot be treated.
Typically, the doctor begins by making an incision into the periosteum or lining of the mouth. The causative tooth is usually removed gradually, that is, in parts. For this, a special dental saw or laser is used. Modern equipment has made it possible to make the procedure for tooth extraction quick and completely painless, so there is no need to be afraid of treatment. After the operation, the sharp edges of the incision are smoothed, which is then washed with peroxide or other antiseptic agents and fixed with sutures.
Opening an abscess on the gum
The abscess is always opened. This reduces the risk of spontaneous opening, which can cause complications. The flux is opened under local anesthesia. If the patient has panic or other indications, the doctor may choose a different method of anesthesia.
A small incision is made on the anesthetized gum in the area of the gumboil, no more than 2 cm in length. After the dissection, the doctor completely cleans and sterilizes the purulent cavity and treats it with antiseptics. A crust should not be allowed to form in the area of the incision, as it will interfere with the outflow of ichor and purulent contents. To do this, a drainage is inserted into the incision. After the cavity is cleared of pus, you can begin general treatment, the purpose of which is to eliminate the causes that caused periostitis.
Basic information
Many people believe that gumboil is just an inflammation of the gums. This is wrong. Yes, the gums are involved in the process, sometimes gingivitis is even a predisposing factor in the development of this pathology, but in fact, the center of localization of the source of flux is the periosteum (its inflammation is periostitis) and the root of the tooth. This is very dangerous, since in advanced cases the disease is fraught with jaw deformation and loss of almost all teeth.
In general, compared to dogs, cats are more prone to oral pathologies . This is due to the structure of their teeth. Most of them are long, sharp fangs. They do not have “platforms” for chewing and grinding food; cats only tear apart their prey and swallow its pieces without chewing.
General treatment
Methods depend on the reasons that caused the flux. The only exception is periostitis, which develops against the background of periodontitis. In this case, immediately after opening the abscess, the doctor begins periodontal treatment. No medical manipulations with the tooth are required. In other cases of dental disease you need to treat:
- Pulpitis. First, the dentist drills out carious cavities and performs pulp removal. After this, endodontic canal treatment is performed.
- Periodontitis. Treatment depends on whether depulpation and canal filling have been previously performed. If periodontitis has developed for the first time, the doctor will remove the pulp, clean and fill the canals. If filling of the canals has already been performed previously, they need to be unfilled and treated again. Since it is very important that the pus comes out of the flux completely, when treating complicated pulpitis and periodontitis, a temporary filling is not placed.
- Tooth after restoration. At the first stage, the doctor is faced with the task of completely removing inflammation. After this, the damaged tissue of the root apex is removed. If the condition of the root allows, the tooth is restored again using a core tab or pin and an artificial crown. When the damage is very severe, it is more advisable to remove the tooth.
Anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics
The use of antibiotics helps relieve pain and stop acute inflammation. You can use antibiotics such as Trichopolum, Lincomycin, Ciprofloxacin, Flemoxin, Biseptol, Amoxiclav, Tsiprolet. Antibacterial drugs should not be used for more than five days to avoid microbial resistance in the body.
To reduce swelling and redness, you can additionally take Diazolin, Nimesil or Diclofenac, which have a local anti-inflammatory and decongestant effect.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic methods are used as additional ones. They allow you to quickly cope with the infection and stop the inflammatory process. The following methods can achieve good results:
- Fluctuarization. The inflamed tissues are exposed to low voltage current.
- Electrophoresis with lidase. Electrical current is applied to the tissue, allowing the drug to be effectively distributed.
- Ultrahigh frequency therapy. The method is based on the influence of an electromagnetic field.
- Ultrasound therapy. The effect of ultrasound on infected tissues accelerates their regeneration.
- Laser therapy. Damaged tooth tissue is treated with a laser beam.
Diagnostics
Before proceeding with dental flux treatment, the doctor must conduct an appropriate diagnostic examination. The exact diagnosis is determined based on data obtained during a clinical examination and x-ray diagnosis. Laboratory tests allow you to accurately determine the stage of the inflammatory process. Only after making an accurate diagnosis will a specialist be able to decide what to do with gumboil and which method of treatment in this particular case will be optimal.
Rinse
They are used as an additional treatment in order to completely remove pus and ichor from an opened abscess and prevent the infection from spreading to healthy areas. Soda-salt baths and rinsing with antiseptic solutions help make treatment more effective and speed up gum healing. When rinsing, you must adhere to the following rules:
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
- During the day, do 4-5 gentle rinses or baths. To do this, just take the solution into your mouth and hold it for about 30 seconds.
Compresses and lotions for periostitis
Compresses and lotions have a local anti-inflammatory and disinfecting effect, they destroy pathogenic microbes and will help get rid of swelling on the mucous membrane. You can use the drug Dimexide, which is diluted with water until a concentration of 20-30% is reached. The compress is applied to the area of inflammation and left for about an hour.
Soda lotions also help a lot. Baking soda is diluted in a volume of two teaspoons in 200 ml of water. You can moisten a cotton pad or several layers of gauze with the solution and then apply the lotion to the affected area of the gum.
Good therapeutic effectiveness is also observed when using salt compresses. It is enough to dissolve a couple of teaspoons in 100 ml of warm water. A gauze swab soaked in the solution should be applied to the inflamed area and held between the gum and cheek for at least half an hour.