Genetics and breed
The cause of increased lacrimation may also lie in genetics. There are breeds of cats in which constant lacrimation is caused by features of the anatomical structure, and is considered within normal limits. These are breeds of Scots, British, Persians, and exotics.
All cats, whose skull structure is characterized by a short, flat muzzle and large eyes, have narrowed tear ducts and small tear grooves, which is why fluid constantly flows from the edges of the eyelids, forming characteristic furrows.
Still, you shouldn’t blame the whole problem on genetics if your pet is one of the above breeds. It is better to once again consult with a veterinarian to determine the correct diagnosis.
If a cat has water in one eye - reasons
Natural
Some cat breeds are more likely to suffer from watery eyes than others. In cats of British and Persian breeds, due to the structural features of the skull, lacrimation often occurs due to dust and various small debris getting into the eyes. It is very important to monitor the hygiene of these breeds and regularly wash your pet's eyes. Hairless cat breeds are prone to drooping eyelids. Turning of the eyelids can cause conjunctivitis and increase the risk of eye injury. Entropion of the eyelids is treated with surgical excision.
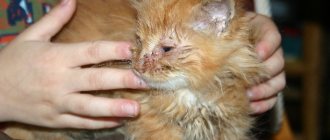
Thus, the age of the animal can be attributed to natural causes. Newborn kittens are not able to keep their eyes clean on their own, so the owner will have to take care of hygiene. It is worth noting that excessive lacrimation can also be a symptom of infections and parasites, so it is worth having your animal checked by a veterinarian.
Treatment of tearing in cats
The nature of the treatment depends entirely on the cause of the pathology. If problems are detected with the anatomical structure of the nasopharynx, resulting in lacrimation and difficulty breathing, the doctor may even prescribe surgical intervention. In other situations, treatment is not difficult.
If an allergic reaction is detected, you need to get rid of the allergen and prescribe antihistamines.
If there are injuries or a foreign object is found in the eye, the wound should be treated and the object removed.
What to do at home
The owner must create the most comfortable living conditions for the sick pet and strictly follow the veterinarian’s instructions. Under no circumstances should you self-medicate, as it can aggravate the situation.
Some traditional methods can be used for conjunctivitis, but they should not replace conservative treatment. It is acceptable to use them in combination with medications.
Most often, at home, a decoction of chamomile and calendula is used to wash the eyes. You need to take 1 teaspoon of dried plants, pour boiling water, cool and let it brew. You need to wipe your eyes with a disinfectant decoction at room temperature 2-5 times a day.
Treating a cat at home
In order to decide how to treat your pet at home and not cause further damage to it, be sure to first consult with a veterinarian. After the necessary tests and a thorough examination, your cat may be prescribed antibacterial or antiviral treatment, as well as drops, antibiotics or special anti-inflammatory ointments. In some cases, the animal is prescribed physical therapy or surgery.
If your cat has constant excessive tearing and there are scabs in the corners of the eyes, or the cat has swollen eyelids, dark discharge with an unpleasant odor, or blurred vision, then you should take her to a specialist. Pay attention to the pet's body temperature and general condition. Fever, lethargy, depression, sneezing, and refusal to feed are all symptoms of the disease that require detailed study.
You should also contact your veterinarian immediately if your cat has a foreign object in its eye. Under no circumstances try to remove it yourself, as without special tools and the necessary skills you will injure the animal.
You don't have to wait to see a specialist and have a positive impact on your cat's well-being. But keep in mind, the following tips will not cure your pet, but will only temporarily and partially alleviate his suffering until the cat is examined by a veterinarian and the appropriate treatment is prescribed.
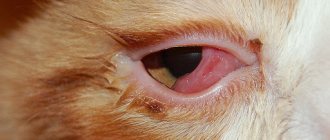
Causes of redness in cat eyes
Let's consider the possible reasons for the appearance of red eyes in a cat:
- Foreign body in the eye
. If a cat's eye is red and watery, then the reason may lie, for example, in a small pebble or speck that got into the animal's eye. You can determine that a cat has a foreign body in the eye by the following signs: usually only one eye is affected (and the other looks healthy), there is profuse lacrimation and redness, swelling around the eye, in some situations red or yellow discharge from the eye may appear, shaking the head and rubbing the eye with a paw, anxiety; - Eye irritation
. It happens that an adult animal or a kitten has red eyes due to some external influence. For example, tobacco smoke (in cats whose owners regularly smoke without going out into the fresh air) or cosmetics (pet shampoos) can cause eye irritation. May cause irritation and dust. If an animal blinks frequently, and its eyes are itchy, watery and red (both eyes at once), then irritation may be to blame; - Conjunctivitis
. A cat's eyes may be red due to inflammation of their mucous membrane. There are many reasons for the development of conjunctivitis: often the disease occurs against the background of allergies, due to regular eye irritation or due to a foreign body. In addition, this eye disease often occurs as a secondary ailment after an infection. Signs of conjunctivitis include redness of the eyes (both), swelling of the eyelids, discharge of clear and sometimes purulent secretion from the eyes (the area under the eyes is constantly wet), sticking of the eyes (due to dried pus), photophobia, and apathy. In some situations, a rise in temperature is possible; - Keratitis
. The cat's eye is red and watery due to inflammation of the cornea. The main causes of this disease include eye injuries, eye infections and allergies. In addition, some breeds are predisposed to the disease, for example, Siamese, Burmese, Persian. The main symptoms of this disease are redness of both eyes, the release of a large amount of tears or pus, clouding and roughness of the cornea, frequent blinking, itching, fear of bright light, sneezing and a runny nose are also possible, and sometimes the temperature rises; - Blepharitis
. Redness of the eyes is also possible with inflammation of the eyelids (the disease usually affects the eyelids of both eyes). The causes of blepharitis include infectious diseases, eye injuries, vitamin deficiency, and allergies. The main symptoms of blepharitis include, in addition to redness of the eyes, severe swelling of the eyelids, discharge of a large amount of pus from the eyes, peeling and sticking of eyelashes and hair, the formation of ulcers at the edges of the eyes, severe itching (cats rub their faces against pieces of furniture or rub their eyes with their paws). In severe cases, the temperature may rise; - Uveitis
. A cat's eye may be red due to inflammation of the choroid. Most often, the disease develops due to eye injury, autoimmune diseases (for example, lupus erythematosus or vasculitis), eye tumors, and other eye diseases (keratitis, conjunctivitis, etc.). How can you tell if your cat has uveitis? At first, the disease can be confused with a relatively harmless conjunctivitis, but then the following characteristic signs will be added to the redness and swelling of the eyelids with discharge: decreased vision, photophobia, discoloration and protrusion of the iris, entropion of the eyelids, strabismus, change (severe narrowing) in the shape of the pupil, severe itching , development of glaucoma or cataracts. Possible rise in temperature and refusal of food; - Entropion
. Redness of the eye (usually one, not both) often occurs when the eyelids are turned up, when the corneal layer is constantly injured by hairs or eyelashes. The main causes of entropion are genetic predisposition (in the British, Persians, Sphinxes), eyelid defects, eye injuries (including chemical and thermal burns), and paralysis of the facial nerve. Symptoms of the disease include (in addition to redness of the conjunctiva) pain, lacrimation or excessive discharge of pus, swelling of the palpebral fissure, constantly wet fur under the eye, the appearance of ulcers on the cornea, frequent blinking and squinting of the eye; - Glaucoma
. Redness in one or both eyes may be caused by increased intraocular pressure. In some situations, if both eyes are affected, the cause of the disease is considered to be genetic (the disease especially often affects Siamese and Burmese cats). If only one eye is sick, then most often this is caused by untreated uveitis. The most striking signs of glaucoma in cats are severe clouding of the eye, dilation of the pupil, an increase in the diameter of one or both eyes, swelling of the eyelids, severe tearing, fear of light, lethargy, and pain in the eyes. Sometimes vomiting may be present; - Dry eye syndrome
. Sometimes the redness of a cat's eye is associated with insufficient hydration of the conjunctiva and cornea by tear fluid. There are many reasons for this disease: infectious eye diseases (including keratitis, conjunctivitis), autoimmune diseases, kidney problems, endocrine disorders, vitamin deficiency. With the problem under discussion, the cat’s eyes turn red, the animal cannot look at the light and stay in the wind for a long time, constantly squints, rubs its eyes with its paw, at the initial stage active lacrimation is possible, but later there is no discharge from the eyes, erosions form on the cornea, vision deteriorates; - Dacryocystitis
. Brown or red discharge from a cat's eyes occurs due to non-infectious inflammation of the lacrimal sacs. Most often, the disease is provoked by any inflammatory ailments of structures close to the eyes (for example, sinusitis or sinusitis). The main signs of dacryocystitis include severe swelling of the lacrimal sac (due to the accumulation of a large amount of pus in it), the formation of fistulas on the eyelid, gluing of the eyelids and eyelashes from pus, the formation of crusts on the eyes, pain and severe itching, as well as redness of the eyes. Note that the disease can affect either one or both eyes; - Eye injuries
. If your cat has red around the eye, it may be due to injury, such as from a fight with other animals, plant thorns getting into the eye, or scratches from small pebbles. Sometimes a cat’s eye can be damaged due to a collision with a vehicle; unfortunately, human “fun” is also possible when something sharp is poked into the animal’s eye. You can recognize an eye injury by the following symptoms: severe redness (usually only one eye), severe lacrimation, which without treatment turns into discharge of pus, bleeding from the eye, swelling of the eyelids, clouding of the eye, protrusion of the third eyelid, severe itching. In some situations, blindness may develop: the cat, wandering around the house, will bump into pieces of furniture and stagger. - We have listed the most common causes of eye redness. But it is not always worth looking for the root of the problem in eye diseases. So, the cause of red eyes may be an allergy (for example, to food or veterinary medications). If the animal has a red spot above the eye, then the liver may be acting up. A cat may have red eyes due to illnesses such as chlamydia, rhinotracheitis, mycoplasmosis, and calcivirosis. An animal may also have red white eyes due to helminthiasis. But if the eyes glow red, then you shouldn’t worry too much: in some cats (especially Siamese) this is considered normal.
Allergies and parasites
The cause of lacrimation may lie in allergies. Yes, cats, like people, can be susceptible to allergic reactions to dust, food, flowering house plants, and even their own fur. If both eyes of a cat are watery, and he often sneezes and itches, then this may be a reaction to some allergen. In this case, a veterinarian must make a diagnosis to confirm the allergy.
By the way, allergies can be triggered by infection with helminths, the presence of which has a detrimental effect on the pet’s immunity. In Murmansk, you can contact the Favorit veterinary clinic for initial diagnosis, consultation with a veterinarian and purchase of anthelmintic drugs.
How to prevent lacrimation?
Owners are advised to examine their pets' eyes daily. They should have the same shape, be clear, and have no discharge or other signs of inflammation.
If you have a small kitten, you need to provide him with the necessary hygiene. You can wipe your eyes with a bandage containing warm boiled water or any antibacterial solution. Furacilin is perfect. You can also use special drops. If an adult cat does not take good care of its own hygiene, then conjunctivitis is possible. In this case, you can use ointment or drops containing chloramphenicol. If the problem does not resolve itself within a few days, it is worth taking the animal to the veterinarian. Long-haired cats sometimes need the fur around their eyes trimmed. It is also very important to monitor the claws so that the pet does not accidentally injure its eyes when washing. Food and hygiene products must be properly selected.
If the owner follows all these rules and contacts the veterinarian for routine examinations, he will be able to avoid any eye problems in his cat. It is important to understand that prevention is simpler than any treatment. Following the tips described above will keep your pet's eyes healthy and clear-eyed for many years!
Diagnostics in a veterinary clinic
Diagnosis in a veterinary clinic is aimed at identifying the cause of conjunctivitis. In addition to a visual examination and medical history, the veterinarian conducts a number of diagnostic tests to differentiate inflammation of the conjunctiva from other diseases of the organ of vision.
Necessary diagnostic measures include taking samples of discharge from the conjunctiva and a biochemical blood test.
Determining the nature of discharge from the eyes is of great importance. So, purulent means the development of a bacterial infection, mucous means an allergic reaction, serous means a virus that has developed in the body.
Symptoms of a pet's disease
When a pet gets sick, accompanying symptoms immediately appear. If the owner notices one or more of the following signs of disease in the kitten, he needs to urgently contact a veterinarian.
- The pet has become aggressive and angry, very often rubbing its eyes with its paw:
- The kitten refuses to eat and sleeps poorly;
- In the light, the pet closes its eyes and tries to stay in a dark corner;
- Increased body temperature;
- The eyes water, become red, and purulent formations flow out of them;
- The fur takes on a brownish tint after about a century.
Other signs of pathology
Tearfulness in cats and cats can occur with varying intensity. If both eyes are watery, the skin around is changed, signs of eczema or dermatitis appear, and hair falls out, then you should immediately consult a veterinarian. In non-inflammatory processes (glaucoma, cataracts, etc.), one eye often becomes watery. Sometimes tearing is associated with a foreign body entering the eye.
The consistency of the discharge from the animal's eyes also matters. Thick discharge may accumulate in the corners of the eyes. With the inflammatory process and conjunctivitis, itching and redness of the mucous membrane may occur.
If your pet avoids sunlight, refuses food and has an elevated body temperature, behaves lethargically and unnaturally, it is necessary to show it to a veterinarian. Perhaps all these signs are the reason for the lack of competent treatment.
Establishing diagnosis
Before starting treatment, it is imperative to conduct a diagnosis that will help identify the true cause of excessive lacrimation and carry out effective treatment therapy. Only a veterinarian can conduct a correct and thorough examination.
Important! Before going to the veterinarian, be sure to prepare a pet card, which should indicate all vaccinations, anthelmintic treatments, and past illnesses. It is advisable to write down symptoms of malaise and other suspicious signs on a piece of paper.
Sometimes the veterinarian may be interested in the following important questions at the appointment:
- how long the symptoms last;
- how did the first symptoms of tearing from the eyes appear and the peculiarities of the course of this condition, for example, did two eyes immediately begin to water at the same time, or vice versa, first one began, and then the other, and whether there are other additional symptoms;
- when the last procedures to eliminate helminths, fleas, ticks and other parasites were carried out.
To make an accurate diagnosis, the veterinarian will definitely take a urine and stool test. It is advisable to already have the research material with you before going to the doctor. Also, at the appointment, he will definitely take mucus from the eye for examination; for this reason, there is no need to first rinse the pet’s eyes with various solutions.
Differential diagnosis
Differential diagnosis is carried out, first of all, with conjunctivitis. Conjunctivitis often accompanies many ocular and periocular pathologies: primary keratitis (ulcerative and non-ulcerative forms), dry eye, blepharitis, uveitis, glaucoma, dacryocystitis. It is necessary to distinguish between hyperemia of episcleral and conjunctival vessels in order to differentiate dangerous eye diseases (such as glaucoma or uveitis) from superficial and less dangerous processes (for example, from superficial keratitis). [29], [30], [31], [32]
Treatment
The vision of cats is considered an important function that animals require for a full life. The vision of cats is considered an important function that animals require for a full life. For this reason, it is important to carefully and regularly monitor the condition of your pet's eyes. And if you detect excessive lacrimation, and even more so discharge with signs of pus, there is no need to self-medicate.
It is worth noting! The veterinarian prescribes medications depending on the condition of the eyes and the type of discharge in the animal. For local effects, drugs are usually prescribed in the form of drops.
You can treat your cat’s eyes at home using special products that can be used without a doctor’s prescription:
- You can wash your animal’s eyes with furatsilin with a concentration of 0.2%. This remedy can be used for conjunctivitis. You can also use other solutions with antiseptic effects;
- Levomycetin (aqueous solution). This remedy is used for bacterial conjunctivitis. Drugs in the form of drops - Kanamycin or Sofradex - also have a good effect;
- ointments containing antibiotic components. The main thing is to apply the ointment correctly to the eyes so as not to cause even more harm. This remedy should be applied several times a day;
- solution of hydrocortisone or novocaine. These drugs should be administered by injection. They help reduce pain;
- use of an anesthetic and sodium chloride with a concentration of 8.5%. If a foreign body, speck, or debris gets into the animal’s eyes, then he needs to be given an analgesic. After the drug has taken effect, you need to take a cotton swab, turn out the cat’s eyelid and carefully remove the speck using cotton wool;
- For allergic reactions in cats, treatment is accompanied by the use of hormonal drugs.
First aid and treatment
To completely cure an animal, you need to make a correct diagnosis. Treatment is usually carried out using drops and ointments, and immunity-supporting drugs are often included. Before determining the cause of lacrimation, you can clean the animal’s eyes yourself, using napkins or cotton pads. They should be moistened:
- chlorhexidine solution;
- infusions of herbs, such as chamomile or sage;
- boric acid solution (2%).
Such cleaning will not help cure the animal, but it will make the pet’s condition easier if its eyes stick together due to secretions, interfering with orientation in space.
A veterinarian will tell you how to properly care for your pet’s eyes in her video from Lina Vet’s Vet Tips channel.
Medicines
The doctor decides how to treat the animals after an examination: you should not do this yourself, because it can cause harm. So, little kittens can not do everything that is freely prescribed for adult animals. Eye drops such as:
- "Leopard";
- "Diamond Eyes";
- tsiprovet;
- anandin.
The last of the drugs stings noticeably, so the kittens scratch their eyes and get worried after the procedures. For bacterial conjunctivitis, it is recommended:
- chloramphenicol;
- kanamycin;
- sodium sulfate;
- sofradex (contains a hormone and is not recommended for corneal damage).
But, it is worth emphasizing that in case of allergies, none of the drugs listed will help - you will only torture the animal in vain. For proper treatment and advice, you should contact a veterinarian.
Traditional methods
If a cat’s eye is leaking, then treatment with folk methods, at best, can only help cleanse the organ of vision, preventing infection from developing. With already developing inflammation, this method of fight is unlikely to help. Experts recommend cleansing with decoctions of useful antiseptic plants: chamomile, St. John's wort, sage.