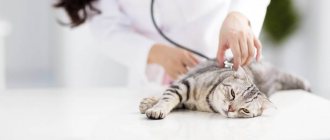
Cat flu is a term used by veterinary specialists for diseases caused by pathogens of viral infections and accompanied by damage to the upper respiratory tract.
Like human flu epidemics, cat flu is a highly contagious disease affecting the cat family in a city, region, etc.
Which cat is most susceptible to the flu?
Considering the fact that feline influenza is one of the most common viral diseases among the cat family, it is almost always present in this animal population. Among cats, the most common cases of influenza are:
- Elderly cats and kittens over 2 months of age.
- Cats kept in nurseries, shelters, etc., where there are conditions for the rapid spread of influenza.
- Cats with reduced immunity (feline immunodeficiency virus, patients with leukemia).
- Not vaccinated against viral infectious diseases.
Influenza: description of the pathogen
In 90% of cases, calcivirus (FCV) and herpesvirus (rinotracheitis) are “to blame” for the appearance of flu symptoms in cats. Pathogens are especially dangerous for animals with reduced immunity, kittens under 6 months, weakened or older pets. Hypothermia and poor nutrition also contribute to the rapid spread of the disease, so a greater number of sick cats are found among stray cats or those kept in shelters and nurseries with poor living conditions.
For reference! Upper respiratory tract infection (URI), or influenza, is a general term used to describe a pathological condition affecting a cat's respiratory tract. Virus (“poison”), a non-cellular pathogen that reproduces its own kind only inside a living cell of the body.
How does infection occur?
Cat flu is most common:
- in stray cats;
- in animals that are often outdoors;
- those living in one room in numerous groups.
To a greater extent, the virus attacks kittens, old cats, and animals with weakened immune systems and chronic diseases.
Healthy, strong cats with good immunity are also susceptible to infection, but their disease is milder.
The virus is transmitted through close contact with other individuals through airborne droplets. This happens during joint games, when using a common bowl for eating or drinking. The virus is quickly destroyed in air, but cases of transmission of infection through bedding, toys or care items have been observed.
The likelihood of infection can be reduced by carrying out disinfection measures in cat habitats. The virus is easily destroyed by treating the room and cat's belongings with a weak bleach solution.
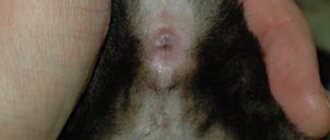
Symptoms of the disease in cats
The symptom complex directly depends on which virus became the provoking factor of the flu. So with calcivirus (calcivirosis) it is noted:
- runny nose;
- sneezing;
- ulcers on the mucous membrane of the mouth and tongue.
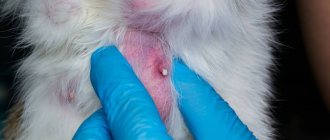
With herpesvirus (rhinotracheitis), damage occurs to the upper and lower respiratory tract (trachea, nasopharynx, lungs). Against the background of a prolonged illness or flu, secondary infections (pneumonia) develop in kittens, weakened animals or after the age of 8 years.
Possible symptom complex for influenza:
- nose (discharge, sneezing);
- eyes (reddened, inflamed, mucopurulent discharge, itching);
- mouth ulcers;
- no appetite, loss of smell due to nasal congestion;
- dehydration;
- fever (increased temperature, this is how the body reacts to the introduction of a pathogen).
Other representatives of a viral infection (influenza) may include chlamydia and bordetella, which provoke discharge from the nostrils of a serous or mucopurulent nature. Cough and conjunctivitis are also noted.
Do domestic cats get the flu?
Whether cats get human flu is a question that cannot be considered categorically. It was already mentioned above that all strains of the influenza virus do not pose a threat to pets. But there are many other viral infections that can affect people and pets at the same time.
In addition to the fact that some viral infections cause illness in pets, there is also an alarming tendency for dangerous strains of human influenza to mutate. Scientists do not make predictions regarding the activity of mutated strains of the virus, therefore, it is possible that in the near future cats will have to be protected from these pathogens.
Transmission routes and risk group
The feline influenza virus is transmitted by airborne droplets from a sick individual to a healthy one. There are two routes of pathogen transmission:
- contact, when the animals communicated with each other, and it is not necessary that the sick individual have all the signs of influenza; the incubation period of the disease is from 2 to 10 days. It is during this period that the cat is a carrier of infection, but remains outwardly healthy;
- indirectly (fomites), such infection is more often present in nurseries, foster care, shelters, anywhere where quarantine, sanitary and hygienic standards may not be observed, or there is overcrowding of animals. The virus enters the upper respiratory tract when using the same bowl or bed.
When FHV and FCV are detected, cats that have had similar strains of the virus become carriers of the infection. That is, while they appear healthy in appearance, they spread the flu through saliva, nasal fluid or tears. Under stress, a cat that was previously ill and recovered may again show mild signs of the disease due to decreased immunity.
Despite the fact that herpes and calcivirus are considered viral pathogens and appropriate treatment is prescribed, they are accompanied by secondary infections - bacterial, which provoke rhinitis, conjunctivitis and pneumonia. In this case, flu symptoms are accompanied by signs of secondary infections, which often complicates the diagnosis. Sometimes cats that have had the flu remain chronically ill (chronic rhinitis).
Cat flu: symptoms
Cat flu, the symptoms and treatment of which raise many questions, has an incubation period of 2-10 days. The virus can be transmitted from a sick animal, for example, in a nursery, or from a carrier through airborne droplets. The principle of virus penetration into the body is the same as in humans - through the mucous membranes of the oral cavity and through the conjunctiva of the eyes. The contact variant is less common - through products, sleeping accessories, cups, etc.
Article on the topic
Medical battalion at home. How to organize treatment for a pet
A clear sign of cat flu is a runny nose. Also among the symptoms indicating pathology are:
- sneezing;
- conjunctivitis;
- increased body temperature;
- febrile conditions.
Also, a sick cat will be tired and weak; it will eat less or refuse to eat at all. If the cat's flu is caused by a calcivirus, it is milder. The situation becomes much more complicated if a bacterial infection is added. Then the cat may develop:
- pneumonia;
- bronchitis;
- chronic rhinitis.
This situation may occur if there is an outbreak in the cat population.
The hamster has infected! What diseases are transmitted from animals to people? More details
How is influenza diagnosed?
An accurate diagnosis can only be made in a veterinary clinic equipped to modern standards, such as RosVet. A cat with typical signs of damage to the upper respiratory tract is examined by a specialist, consistently excluding all known pathologies that occur with signs of rhinitis, tracheitis, etc.
The final diagnosis of feline influenza is made based on test results for the presence of the FCV or FHV virus. An analysis is carried out using samples of discharge from the eyes and nose of the cat using PCR.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is carried out in a veterinary clinic after a comprehensive assessment of the animal’s condition, taking into account the epidemiological situation in the cat’s place of residence. The doctor examines the animal, assesses its condition, and analyzes the clinical picture of the course of the disease.
Additionally, laboratory tests are carried out:
- urine and blood analysis;
- PCR – growing virus strains from swabs taken from a cat’s mouth and eyes;
- Ultrasound;
- radiography.
Additional diagnostics are necessary in severe and advanced cases, when signs of a secondary disease are clearly expressed.
How to treat flu in cats?
Therapy consists of symptomatic elimination of signs of the disease, action on the cause and supportive treatment. Prescribed:
- interferon;
- antiviral drugs;
- L-lysine (amino acid);
- ointment and eye drops;
- saline drops in the nose.
The cat is transferred to a warm room and given soft, easily digestible food. In case of complete refusal, the cat is transferred to the clinic’s hospital for feeding through a tube. In case of dehydration and lack of fluid, infusion therapy is carried out. Antibiotics are prescribed to eliminate secondary bacterial infections. When concomitant pathologies are identified, parallel treatment is carried out and complications are prevented.
Cat flu: treatment
Cat flu, which must be treated without fail, requires an integrated approach. To begin with, a sick pet must be separated from others, if there are any in the house. The treatment room should be draft-free. The entire treatment system is prescribed by a veterinarian. And here it is important to understand that drugs for humans are not suitable for animals.
If we consider the general principle of treatment, the following drugs are usually prescribed:
- immunomodulators that increase the body's defenses;
- symptomatic therapy in the form of drops, ointments and sprays;
- antiviral therapy;
- antipyretic therapy if the cat has a fever.
If a secondary infection develops, antibiotics are offered. And the owner will have to monitor compliance with the drinking regime to avoid deadly dehydration. Sometimes you have to force yourself to drink. If the cat refuses to eat and is already close to exhaustion, he may need IVs.
Cat flu is a disease that is not fatal in itself for a four-legged animal, but entails serious consequences in case of complications. Therefore, it is necessary to seek qualified help as quickly as possible and carry out all measures prescribed by the veterinarian.
How to prevent flu correctly
The risk of developing influenza in cats can be reduced if the animal is promptly vaccinated against calcivirus and herpesvirus. But this does not reduce the likelihood of disease, so it is necessary to comply with sanitary and hygienic standards and rules for keeping cats in the house, nurseries, and shelters.
It is especially difficult to prevent influenza in stray pets, therefore, the only option is to reduce the number of stray cats through sterilization.
If you notice that your cat is unwell, there are signs of damage to the upper respiratory tract, or discharge from the eyes and nose - do not hesitate! Call the RosVet VC by phone: +7 (495) 256-11-11, 24 hours a day. The clinic is available 24 hours a day, and if necessary, a veterinarian will come to your home.
Prevention
It is impossible to completely protect your cat from this disease, but you can reduce the risk of infection by following these simple prevention rules.
Preventive actions:
- Vaccination. Vaccinations do not provide a 100% guarantee, but they significantly reduce the likelihood of infection. You should follow the vaccination schedule recommended by your veterinarian.
- Strengthening the immune system with vitamins and immunostimulants.
- Follow the rules of kitten care and hygiene. Regularly wash and disinfect the litter box, dishes and the cat’s area.
- Protect your pet from hypothermia.
- Provide quality food.
- Do not let cats roam, avoid contact with stray cats and dogs.
When the first signs of illness appear, the animal should be quarantined and shown to a veterinarian.
Vitamins to strengthen the immune system
Special blood tests help determine which vitamins the body lacks. The main marker of stable immune function is considered to be normal levels of vitamin D hormone. It enters the body with food and is synthesized by skin cells under the influence of sunlight. Considering the deficiency of ultraviolet radiation in most Russian regions, it is recommended to take the vitamin hormone in the form of a dietary supplement. To prevent respiratory diseases, the immune system needs B vitamins, ascorbic acid, and fat-soluble vitamins A and E.
Products that contain vitamins for the prevention of ARVI and influenza
Ascorbic acid (vitamin C):
- sauerkraut
- bell pepper
- citrus
- cranberry
- currant
- rose hip
Group B:
- nuts
- milk
- legumes
- buckwheat
- oats
- tomatoes
Tocopherol (E):
- sea buckthorn
- spinach
- broccoli
- bran
- eggs
- vegetable oils
Retinol (A):
- carrot
- green onions
- parsley
- peaches
- apricots
- melon
Replenishing vitamin reserves through nutrition alone is an impossible task. To maintain the immune system in a state of combat readiness, an additional source is needed - pharmacy vitamin complexes:
• Supradin Immuno Forte; • Doctor More; • Multi-tabs Immuno Plus; • Pediakid syrup; • Superum Echinacea Vitamin C Complex.
The most modern and effective means for strengthening the immune system can be ordered with home delivery.
Caring for a sick cat
Home care includes not only drug treatment.
Tips for owners:
- Give all prescribed medications as directed.
- Provide your mustachioed pet with access to clean drinking water. If the animal cannot drink on its own, inject the liquid using a syringe. This prevents the body from becoming dehydrated.
- If you lose your appetite, you should purchase good quality food for your pet. It is better to choose a diet food for kittens.
If the cat does not eat on its own, it is fed liquid food using a special tube.- Thoroughly wash the area where the cat rests and eats, and regularly disinfect the litter tray.
- Isolate your pet from other healthy animals.
- Avoid active games with the cat.
Causes of infection
The disease can develop if the following viruses enter the animal’s body:
- Calicivirus (Feline calicivirus). Affects the upper respiratory tract. Both domestic and wild individuals can become infected. Can be compared to the human cold.
Herpesvirus (Feline Herpes Virus) or rhinotracheitis. The infection spreads through the respiratory tract throughout the animal's body. In addition to breathing problems, it affects the organs of vision. Often has complications, accompanied by a bacterial infection.- Chlamydia Chlamydophila felis. Acts as a pathogen in cases of weak immunity.
The disease can also occur with the development of concomitant diseases that influence the development of the disease - obesity, leukemia, immunodeficiency.
Which cat can get sick?
Cats that have previously suffered from pneumonia are at risk. Their immunity is weakened, and the virus attacks the body faster. May get sick:
- kittens who have not received the vaccine;
cats over 10 years old;- adults not vaccinated against infections;
- pets from shelters walking on the street;
- cats who have suffered serious illnesses or surgeries;
- animals living in private houses.
Vaccination can keep an animal safe, so domestic cats and pets living in shelters should be vaccinated to prevent an outbreak of infection.
Means for the prevention of acute respiratory viral infections and influenza
Preventive measures against acute respiratory infections are divided into specific and nonspecific. Specific prevention is vaccination. The Russian Federation is immunizing the population against influenza and coronavirus. There is no vaccine for other viruses, of which medical virology numbers more than two hundred. Non-specific methods include drug protection of the body, home remedies to strengthen the immune system, rules for the prevention of influenza and ARVI, recommended by WHO.
What to do if you get sick?
Fever, weakness, soreness, lacrimation are early signs of infection. When they appear, it is not recommended to leave the house. Firstly, so as not to spread viruses, and secondly, so as not to worsen your health. You can call a therapist or pediatrician by phone. In case of extreme temperatures, it is better to call an ambulance. Before the doctor arrives, the sick person must be put to bed and given warm tea (fruit juice). It is advisable to put a medical mask on the patient, provide him with a separate room, dishes, and hygiene items. To prevent complications, it is important to follow medical prescriptions - take medications, drink plenty of fluids, ventilate the room, eat foods rich in vitamins, phytoncides, and protein. In the first days of illness it is necessary to observe bed rest. If you have the flu, physical activity can trigger the development of acute respiratory distress syndrome, an extremely life-threatening condition.