Veronica Igorevna Sharipova
veterinarian Petstory
Almost every day, owners contact veterinary clinics with a complaint that their cat often goes to the toilet in small quantities. But not everyone knows that in most cases this problem can be prevented! So, the rest of our article is all about the causes of frequent urination in cats and possible ways to treat it.
How often do cats pee normally?
At home, cats go to the toilet from 1 to 3 times a day, kittens can normally pee more often - up to 4-6 times a day. In outdoor conditions, uncastrated cats can walk much more often - this is how they mark their territory.
The number of trips to the toilet per day depends on the method of feeding (dry food or wet food), the amount of water drunk (some cats willingly drink water from any bowl, and some like only fresh water from the tap), as well as on the individual characteristics of the pet. But, if a cat constantly goes to the toilet, this is a reason to be wary and consult a doctor.
Diagnosing the problem
You can try to determine the cause of frequent urination yourself, but this is not the best solution, because being a non-professional, you can miss really important details and symptoms.
The problem will not necessarily be superficial - it is quite possible that extremely dangerous inflammatory processes are occurring in the animal’s body, or some other disturbances in the functioning of internal organs.
Even if the reasons seem obvious, it would still be a good idea to consult a veterinarian. If the treatment turns out to be incorrect, the disease will only progress, and in the end it can even lead to the death of the animal . With the help of a number of special studies, the veterinarian will be able to reliably determine the cause of the disease and select individual treatment. In a veterinary clinic, several types of tests, ultrasound examination of internal organs, and x-rays are used for diagnosis.
© shutterstock
If the cat often runs to the toilet little by little (even to the point that it returns to the litter box every few minutes), it is quite possible that this is due to acute cystitis. In this case, correct treatment will get rid of the disease in just a few days. Lack of treatment can lead to the disease becoming a chronic condition that will last for many months.
Noticing the problem in time and contacting a specialist is the main task for the owner.
What should you be wary of if a cat pees often?
So, what symptoms should alert the owner?
- Increased frequency of visits to the litter box. For example, if a cat always went to the litter box once a day, and suddenly began to go 3-4 times or more, this is a reason to go to the clinic, even without other health complaints.
- Presence of blood in the urine. This is a sign of damage to the wall of the bladder and urethra.
- If your pet suddenly starts drinking a lot and peeing a lot. This is a symptom of so-called polyuria and polydipsia, which may indicate a serious illness in the pet (for example, diabetes).
- If your cat constantly runs into the litter box and urinates little by little, this may be a sign of cystitis.
- If a cat sits in a tray for a long time and there is no urine or very little of it, this is quite dangerous. This condition may indicate that the cat has a blockage of the urethra, and it threatens his life. In such a situation, you should immediately contact a veterinarian.
What else can cause polyuria?
On average, an adult cat produces 100–200 ml of urine per day. An aging pet has a weaker sphincter, so it cannot tolerate it all the time. An older cat goes to the toilet more often, and this is normal. At the same time, the amount of urine excreted by animals per day does not change (pollakiuria). In case of rapid progression of urinary incontinence, the animal should be shown to a specialist and treatment should be started.
During puberty, cats mark their territory and leave small portions of urine in different places. The pungent odor of such secretions often causes the animal to be castrated.
Frequent urination in this case is a completely natural need, namely the desire to claim territory. This does not indicate that your pet is sick.
If the owner feeds the pet not with natural products, but with meat pads, he will need a triple volume of liquid. Accordingly, such a cat or kitten urinates often; the processes of removing toxins and waste from its body are much more intense than in animals that eat wet food.
Sometimes the cause of polyuria in a domestic cat is kidney failure. As a rule, this happens to animals older than 8 years.
Signs of the disease:
- paleness of the nasal triangle;
- temperature drop;
- the appearance of wounds in the oral cavity and on the surface of the tongue;
- increased secretion of saliva;
- unusual odor from your pet's mouth;
- tremor of the limbs and nausea may appear.
Important! Most experts consider polyuria not an independent disease, but a symptom that indicates functional malfunctions in the body.
Causes of frequent urination in cats and kittens
Next, let's take a closer look at the reasons why a cat may pee frequently:
Stress
Oddly enough, frequent urination or cystitis due to emotional experiences is the most common problem detected by a doctor at the initial appointment. In this case, doctors diagnose idiopathic cystitis. As a rule, the disease is typical for young pets. The causes of stress in cats can be very diverse - not only obvious (a car ride, a visit to the veterinarian, a noisy party at the house), but also chronic (boredom, an inconvenient litter box, lack of scratching posts).
Bacterial cystitis
Microflora enters the bladder and, as a result, cystitis develops. This disease is quite rare in cats and usually occurs as a complication after bladder catheterization.
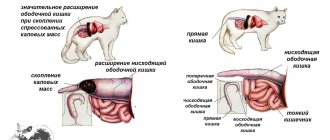
Urolithiasis disease
This is the scourge of modern domestic cats. In a cat, this problem may manifest itself as a frequent urge to urinate. The disease is associated with impaired fluid intake of the animal at home, as well as obesity and lack of activity in the home. When cats drink little and exercise little, they begin to go to the toilet rarely. Accordingly, urine accumulates in the bladder for a long time, salt crystals begin to precipitate, forming stones. With the development of the disease, blockage of the urinary canal or inflammation of the bladder wall, due to abundant salt deposition, the cat begins to urinate frequently.
Mechanical damage to the bladder
After catheterization, it quite often leads to the development of cystitis and, as a consequence, to the fact that the cat often pees.
Presence of a tumor in the bladder
Unfortunately, neoplasms in cats can occur at any age, even at a very young age, and the reasons for their appearance are unknown.
Kidney diseases
Such diseases in the final stages and, as a result, a decrease in the density of urine, lead to the fact that the cat begins to pee a lot. The fact is that secondary absorption of urine ceases to occur in the kidneys, and all the water that the cat drank transits into the bladder. In such conditions, despite drinking plenty of fluids, cats are usually severely dehydrated.
Diabetes
With this disease, the pet begins to drink a lot and, as a result, often runs to the toilet. The disease is typical for overweight older cats who lead a sedentary lifestyle. Therefore, if a cat begins to drink and pee a lot, then it is necessary, first of all, to measure the sugar in his blood.
Hormonal diseases
Hyperthyroidism and hyperadrenocorticism are quite rare pathologies and lead to increased thirst and, as a consequence, increased urination.
Treatment: what to do and how to help the cat?
If a problem is detected, you should consult a doctor who, after a comprehensive examination, prescribes appropriate treatment.
Frequent urination in cats should not be ignored, since complications develop very quickly and can cause death. Therapeutic measures are selected by the veterinarian individually for each pet after conducting a comprehensive examination and identifying the cause of the problem. The table presents methods of treatment for disorders of various nature, as a result of which the cat develops frequent urination:
| Problem | Therapy |
| Urolithiasis disease | Inserting a catheter into an animal under general anesthesia to ensure normal urine outflow |
| For large stones, surgery is performed to remove them. | |
| Prescribing veterinary drugs to relieve symptoms | |
| Diabetes | Using insulin to stabilize a cat's condition |
| Correction of nutrition and the fight against excess weight if present | |
| If diabetes and frequent urination are associated with impaired pancreatic function, then medications are prescribed to improve the functioning of the organ | |
| Stress | Elimination of provoking factors |
| Providing peace for the cat | |
| Marking territory | No special treatment required |
| It is possible to perform sterilization or castration, after which frequent urination for this reason goes away |
Associated symptoms
Depending on the cause of frequent urination, it may have various accompanying symptoms:
Against a background of stress
, in addition to the fact that the cat often pees, it can hide in closets, under the bed, and refuse food and water.
For bacterial cystitis
The cat usually doesn't feel well. She is lethargic, eats little, and may even vomit.
For urolithiasis
, especially when it is completely difficult to empty the bladder, cats stop eating and drinking. They constantly run into the tray, sometimes even sleep there, regularly strain on the tray and meow pitifully. As a rule, cats also have severe stomach pain, and they do not allow it to be touched.
With mechanical damage to the bladder
After catheterization, a sharp deterioration in the cat’s condition may be observed. There is urination with blood, cystitis, or, conversely, its complete absence. Also, due to the pain factor, the cat may refuse to eat and generally be sad.
Presence of a tumor in the bladder
, as a rule, has no other symptoms other than frequent urination. The condition is characterized by a gradual deterioration.
For kidney diseases
cats begin to lose weight, their coat becomes dull and dirty. Cats often refuse to eat and vomit occasionally. It is also common for cats with kidney disease to have bad breath. Cats become sad, don’t play, and sleep all day.
For diabetes
, in addition to profuse thirst and constant urination, the pet is characterized by significant obesity and the so-called perverted appetite - cats may begin to eat foods that they have never eaten before. But at the same time, with an excessive increase in blood sugar levels, on the contrary, cats may become lethargic and refuse to eat.
In the presence of hormonal diseases
cats can have a variety of symptoms. Often this is a sharp decrease in weight, poor coat quality, and the belly may be enlarged. At the same time, appetite, as a rule, does not disappear, and may even increase.
Obesity in castrated cats
The probability of accumulation of excess weight and obesity in neutered cats is very high. This can even be called a common phenomenon that brings discomfort to the animal. Excess weight accumulates due to a sedentary lifestyle, since castration makes cats sedentary and lethargic, but they continue to eat a lot and with pleasure.
A cat's excess weight is easily visible and noticeable. This is a layer of fat on the abdomen, poor palpation of the spine and ribs. Obesity in an animal can cause various diseases of internal organs, the cardiovascular system, and hormonal imbalance. Obesity also has a bad effect on bones and joints.
It is impossible to start this disease and not reverse its influence. It is better to start treating obesity in the early stages. An important role in the treatment of the disease lies in the physical activity of the cat. Pay more attention to the animal, play with it, give it more opportunity to run and jump, because cats love this very much.
Organize proper and balanced nutrition, take more care of your pet. Add lean meat, vegetables, and dairy products. Use food specially formulated for neutered cats.
Treatment
For cystitis due to stress
sedatives are prescribed, such as “express calm” for cats or special diets (royal canin calm). But it is important to understand that treatment will be ineffective if the cause of stress is not eliminated.
Bacterial cystitis
treated with antibiotic therapy. But it should be noted that to make a diagnosis and select a drug, it is necessary to conduct a special study. This is taking a sterile urine sample through a puncture of the abdominal wall and submitting it for bacteriological culture with antibiotic titration (that is, selecting a drug that best copes with the found bacterium). Only in this case is it possible to defeat the infection, prevent its reoccurrence and the development of antibiotic-resistant strains of microorganisms.
Treatment of urolithiasis
completely depends on the nature of the stones that are found in the cat, so analysis is indispensable. For example, if struvite salts (synonym - tripel phosphates) are detected in a urine test, it is sufficient to prescribe a special diet (for example, royal canin urinary) and improve the cat's drinking regime (switching to wet food, purchasing special fountains for cats, from which they drink water more readily, than from a bowl). Other types of salts (for example, oxalates) require an individual approach and a treatment regimen depending on the concomitant diagnoses in the cat (for example, these salts are often found in cats with kidney disease).
Mechanical damage to the bladder
after catheterization requires the development of treatment tactics in each specific case. Pain medication, antibiotics, and even possible surgery may be needed.
If you suspect a tumor in the bladder
First, a histological analysis is taken to determine the type of tumor. Depending on the results, treatment is prescribed - chemotherapy, removal of the tumor or the entire bladder.
In most cases of kidney disease
, unfortunately, are incurable and require only supportive treatment. But, in modern conditions, with timely treatment, it is possible to extend the life of a cat with kidney disease by several years!
Diabetes
in cats, as in people, it requires insulin injections, and necessarily a special diet and weight loss. With timely treatment, constant monitoring of blood sugar levels and individual selection of insulin dosage, in about half of cases, diabetes in cats can be completely cured!
Various hormonal diseases
require constant monitoring of blood tests and selection of the dose of hormonal drugs. In some cases, if the disease is caused by a tumor, surgery to remove it is recommended. Only an endocrinologist can deal with such patients.
Kidney stone
This is probably the most serious reason that can cause this behavior in cats. Bacteria present in the kidneys can cause urinary tract infections, and the acidic nature of urine can form several types of crystals.
These crystals can cause blockage in the urinary tract and can also lead to urinary tract infections. If you suspect any symptoms in your cat, you should take your cat to the vet as soon as possible.
This urinary tract blockage can lead to kidney or heart failure within 24 hours. If a cat has intestinal cystitis, the cat may constantly urge to urinate.
You need to be attentive to your cat and take him to the veterinarian if you suspect any of these ailments.
© shutterstock
Prevention
Unfortunately, not all diseases can be prevented. For the development of a tumor in the bladder
, genetically determined
kidney disease
or
hormonal diseases
cannot be affected.
Bacterial cystitis
usually occurs as a complication of other diseases. But we can follow simple rules to avoid other reasons why a cat may often go to the toilet in small ways:
Firstly, it is very important to prevent the development of stress
in the house, for this you need:
- from a very early age, accustom the kitten to being carried, traveling, visiting guests, and ideally to having other pets in the house (a dog and a cat can be great friends if they have known each other since childhood);
- if there are several cats in the house, each one must have a tray, a separate bowl, several drinking bowls, several houses and scratching posts. Also, every cat should have the opportunity to hide in a safe shelter to be alone;
- Before guests arrive or go to the clinic, if the cat is not accustomed to noise and crowds of people, it is advisable to use sedatives.
Prevention of urolithiasis
is to provide the cat with an active lifestyle and plenty of fluids. It is very important to monitor what your cat drinks from. If she doesn't drink much, it might be worth changing the bowl, buying a special water fountain for cats, etc.
Prevention of diabetes
– this is control over the pet’s excess weight and proper feeding.
How much urine should cats produce?
It's strange, but every living thing with a bladder has a "normal" amount of urine they produce in a given day. When the body produces more urine than normal, it is called polyuria.
But anyway, how much urine should a cat produce in one day?
Well, according to a study conducted by Dr. Delmar R. Finco at the University of Georgia Department of Physiology and Pharmacology, the average cat produces between 10 and 20 milliliters per kilogram of body weight in 24 hours .
This is slightly less than the amount suggested by conventional wisdom, which states that cats produce an average of 28 milliliters per kilogram of body weight every 24 hours.
© shutterstock
Features of kittens
A kitten may need to go to the toilet frequently for a variety of reasons. In very young kittens, the problem may be associated with congenital pathologies such as malformations of the bladder, diverticulum of the ureteral orifice, urethral stricture, urethrorectal fistula, atony or hypertonicity of the sphincters. In older kittens, cystitis can be caused by stress. Also, kittens aged 7–8 months have episodes of urolithiasis.
Causes not directly related to the disease
Infectious diseases and inflammation of internal organs are not always the reason why a cat often visits the litter box. This is especially true for kittens and young animals under the age of one year, since cystitis occurs extremely rarely in them. So, there are several possible reasons for frequent visits to the toilet that are not related to infection or inflammation:
Below, all of these problems are discussed in more detail.
Main
- There are many reasons for frequent urination, from cystitis to serious systemic diseases.
- Regardless of age, if a cat pees often and little, this is always a pathology that needs to be understood and treatment selected.
- To make a diagnosis, a comprehensive diagnosis is required. In most cases, this is a urine test, blood tests, and ultrasound of the genitourinary system.
- There is no symptomatic treatment in this situation, since in each specific case it is necessary to look for the cause of the disease and treat it.