What are papillomas in cats and why do they appear? This disease is quite widespread among both animals and people. Why papillomas appear, how dangerous they are, and how to treat them - this is what our article is about today.
If your pussy has symptoms of illness, then do not waste valuable time, contact the Center for Emergency Veterinary Care for Animals “YA-VET”.
Veterinarians with a high level of education, training and many years of experience are at your service. Diagnostics are carried out using the latest generation equipment and with a very high degree of accuracy.
It is also possible to call a veterinarian to your home, where they will conduct an examination and make a diagnosis in a calm and familiar environment for the animal. To call for emergency veterinary help, call the phone and a doctor will be with your pet in the shortest possible time.
Routes of infection
The papilloma virus is most often transmitted from a sick animal to a healthy one through direct contact. Pets often become infected during mating. Therefore, before mating, it is necessary to check the cat and the female cat for the presence of papillomatosis.
However, sexual intercourse is not the only method of infection. Animals become infected through any bodily contact with a sick relative, for example during play or mutual licking. The papilloma virus can live for some time in the external environment. In rare cases, infection occurs when sharing a bowl or tray with a sick animal.
However, warts do not always appear on the skin and mucous membranes when infected. Many cats are carriers of the causative agent of papillomatosis, but are absolutely healthy. This virus is considered an opportunistic pathogen. It lives in the body of many animals, but is activated and becomes pathogenic only under unfavorable conditions. Papillomas in cats occur when immunity decreases. The appearance of warts indicates that your pet is very weakened.
Allergens in food
With a chronic latent course, the skin is constantly dry and flaky, the coat is brittle and dull, there is no itching. Although the wet type is also possible - weeping, highly inflamed and reddened areas of the skin, on the surface of which ichor constantly appears.
It is almost impossible to cure atopic dermatitis caused by a reaction to an allergen in food. However, a cat can live a full and happy life if the allergen is identified and its entry into the body is stopped. To do this, you need to take blood tests (it’s better to immediately do an extended analysis for 24 positions) and, together with a veterinarian, choose a diet.
Provoking factors
The following factors can trigger the activation of the virus:
- chronic illness;
- pregnancy and feeding of kittens;
- long-term use of medications;
- stress;
- avitaminosis;
- hypothermia;
- advanced age of the animal.
Small kittens often suffer from papillomatosis. Their immunity is still poorly developed.
It is important to remember that if papillomavirus has entered an animal’s body, it remains in the cells forever. Treatment can only reduce its pathogenicity and lead to the disappearance of external manifestations of papillomatosis. After therapy, the virus will be in a “dormant” state. It can be reactivated at any time as soon as the animal’s immunity decreases.
Diagnostics
The symptoms of papillomatosis are sufficiently pronounced that diagnosis is not difficult even for a young veterinarian. Diagnosis is made based on history and examination. At the appointment, the time of appearance of papillomas, location and quantity, age of the animal, and the presence of other diseases are determined. Complex diagnostic methods are used not to make a diagnosis, but to determine the degree of development of the pathology.
Methods for effective isolation of the pathogen have not been developed, so electron microscopy, immunological and molecular methods are used to search for the virus. The role of pathological material is removed skin papillomas, as well as smears and washes of the mucous membranes.
It is easier to find the virus not in the neoplasms themselves, but in the areas adjacent to them.
The main diagnostic methods are as follows:
- Electron microscopy. They take a biopsy and make a super-thin section. After which it is stained with 2% phosphotungstic acid. The magnification is 1:100000.
- Immunohistochemical analysis. This is a reaction of hyperimmune serum with an antibody and a pathological drug with papillomavirus.
- PCR. A method for determining the genetic chains of the virus in a biopsy specimen.
Can a person get infected from a cat?
Should you be careful when handling a sick animal? After all, it is known that papillomatosis affects not only cats, but also people. However, the animal owner has no reason to fear. After all, warts in people occur due to infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). In cats, skin lesions are caused by a completely different pathogen. People with papillomatosis also cannot transmit the virus to animals. HPV is specific to humans only. A sick cat cannot infect a dog. She is dangerous only for her relatives. Therefore, you should limit her contacts with other cats, especially with small cubs.
Symptoms and types of papillomas
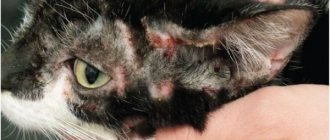
What do papillomas look like in cats? Warts are growths on the skin. They can fit tightly to the epidermis or rest on a stalk. The color of the growths can vary from flesh-colored to yellow or dark brown. The size of warts can range from 4 mm to 1 cm. In severe cases, papillomas merge and form growths similar to a head of cauliflower. A photo of papilloma in a cat can be seen below.
This viral infection is accompanied not only by the appearance of warts. Other signs of the disease are also noted:
- loss of appetite;
- lethargy, apathy;
- skin itching in the area of the rash;
- ulcers at the site of torn warts.
A general deterioration in health occurs more often in small kittens. Papillomatosis can be difficult for pups to tolerate.
Rashes can be localized in different areas of the skin and mucous membranes. Papilloma on the ear in cats most often occurs due to tick-borne infestation - otodectosis. In this case, the appearance of warts is accompanied by severe inflammation and itching in the ear. This combined disease requires persistent and long-term treatment.
Papilloma in a cat's nose can cause pain. After all, the animal’s nostrils are very sensitive. A large wart in the nasal passage can significantly complicate breathing.
Tumors by location
It is possible to guess the origin of the tumor based on its location, but this diagnostic method does not always work.
But there are still pathologies that most often appear on the front/hind legs.
On the front paw
Most often, tumors develop on the front paw for the following reasons (taking into account the possibility of the appearance of tumors):
- Injuries, including fractures.
- It is in the soft tissues of the front paws that splinters are most often found. They can cause both traumatic swelling and abscesses. The latter develop due to pathogenic microflora entering the wound canal. In the latter case, the tissues swell, become hot and thicken. As the abscess matures, it softens.
- Possible formation of hematomas. Due to strong impacts or other traumatic influences, blood vessels may be damaged. The blood coming out of them accumulates in the subcutaneous tissue and under the skin. In the first days the swelling is soft, after a few days it thickens and hardens.
On the hind leg
Tumors on the hind leg develop due to:
- The hind limbs very often become swollen and swollen in diseases of the heart and kidneys. The swelling is cold and dense.
- In addition, swelling of allergic origin often develops in the hind legs.
- Sometimes this is how myositis (muscle inflammation) manifests itself. These cases are characterized by severe pain.
All described pathologies can develop with equal probability on all paws.
Between the fingers
A tumor between the fingers is a common consequence of fungal pathologies. Malassezia is especially famous for this. This pathology, caused by yeast, is not typical for cats, but in practice it still occurs. Characterized by the following symptoms:
- Strange, lumpy growths appear in the spaces between the fingers.
- They are soft and “cheesy” to the touch.
- A strange, moldy, musty smell emanates from the paws of a sick animal.
Tumors in the interdigital spaces can be the result of allergies and abscesses due to foreign bodies entering the soft tissues. In the first case, the pathology is accompanied by severe itching, in the second, severe pain develops.
On the joint
A swelling or large lump on a joint is a sure sign that an animal’s limb is affected by arthritis, bursitis, arthrosis or other joint pathology.
All these diseases are accompanied by a pronounced pain reaction and severe lameness of the animal. In all cases, the tumor does not appear suddenly, but over a fairly long period of time. Older cats are most often affected.
How to distinguish a wart from a tick
During a walk, a cat may be attacked by ixodid ticks. These parasites are carriers of serious diseases that are dangerous to both animals and people.
How to determine: a tick on a cat or papilloma? Large grayish warts may resemble parasites in appearance. You need to take a close look at the formation on the animal’s skin. If necessary, use a magnifying glass. If there are legs around the “wart”, then it is an ixodid tick.
In addition, papillomas grow slowly, and the tick, having sucked blood, quickly increases in size. However, in such cases, you cannot passively watch the growth of a strange growth on the skin. The parasite must be immediately removed from the pet's body, otherwise the cat may become infected with dangerous infections. Therefore, if you have any doubts, you should immediately contact a veterinary clinic.
Symptoms
Neoplasms in cats differ in that seals appear on the body. But it is quite difficult to notice them, since usually no one probes their animal every day.
When internal organs are damaged, significant changes in the pet’s condition are noted:
- disorders of the gastrointestinal tract;
- metabolic disorders;
- neurological symptoms;
- changes in blood composition;
- respiratory problems.
Secondary characteristics:
- ascites;
- cough;
- shortness of breath, vomiting.
If a tumor in cats forms in the skin, its growth is slow. Metastasis is observed only in late stages. When a tumor grows on the mucous membranes, it grows faster and metastasizes to the lymph nodes. Melanoma in this case is prone to bleeding.
The tumor metastasizes through the blood or lymph. Those nodes that are located close to the formation are most often affected. Metastases into the dermis may be observed; they look like small dark rashes. Metastases that are transmitted through the blood can appear in various organs. The adrenal glands, brain, and liver are most often affected.
Shortness of breath may be a visible symptom of malignancy in cats over 10 years of age.
Possible complications
As already mentioned, warts in animals can lead to serious consequences. Papillomatosis is often accompanied by itching. Animals scratch the affected areas and tear off tumors. Bleeding ulcers appear on the skin. This can lead to malignant cell degeneration and skin cancer.
Oncological diseases are the most dangerous, but far from the only complication of papillomatosis. When large warts are injured, severe bleeding may occur, leading to anemia. Also, sores and scratches can become infected and fester.
Treatment
For the treatment of papillomas, immunomodulators and vitamins are prescribed:
- "Vitafel";
- "Gamavit";
- "Maksidin";
- "Ascorbic acid" (injections).
Drugs are also used for symptomatic treatment. In case of severe itching, the animal is recommended to take Suprastin. If there are scratches on the skin, it is recommended to lubricate the damaged areas with antiseptic ointments and solutions:
- "Levomekolem";
- "Betadine";
- "Chlorhexidine."
Treatment with immunomodulators takes quite a long time. If the tumor grows strongly or prevents the animal from breathing and eating, then removal of the wart is indicated.
Most often, removal of papillomas in cats is carried out using Novocaine injections. Injections of the drug are prescribed intravenously or at the base of the wart. The amount of medication is calculated by the veterinarian and depends on the weight of the cat. The injections are repeated three times with an interval of 2-3 days.
Surgical treatment of papillomas in cats is carried out in the absence of effect from the use of novocaine. Warts are removed using the following means:
- liquid nitrogen;
- laser;
- ultraviolet radiation.
After removal of the tumors, it is necessary to undergo a course of treatment with immunostimulants and vitamins. This will help prevent relapses of papillomatosis.
Can warts cause discomfort or even illness in a cat?
The side effects of warts will largely depend on your cat's health. Usually warts don't cause any more problems, just an irritation while they last, but if your cat can't mount a sufficient immune response, the warts may be causing some pathology or they may not go away. Normally immunocompromised cats are cats that have had a previous illness or have a serious infection or have been exposed to radiation.
On the contrary, when your cat is healthy, warts usually do not spread to other parts of the body and also disappear on their own.
In cases where the warts do not go away or if you want to remove your cat's warts as soon as they appear, you can contact your veterinarian for surgical removal. This is especially recommended when the warts are inflamed or infected, as they need to be removed as soon as possible to prevent them from causing more serious consequences for your cat.
Traditional methods
Is it possible to treat papilloma in cats at home? You should not rely completely on folk remedies. After all, papillomatosis is a viral infection, and it is impossible to do without drug therapy. Folk remedies can be used only after consulting a specialist. They are used only in combination with veterinary drugs and sometimes with surgical treatment.
For small papillomas, the following remedies are effective:
- Iodine. This antiseptic should be applied to a cotton swab and cauterized the stem of the wart.
- Rowan. Ripe fruits are crushed to a paste and applied to papillomas twice a day.
- Celandine. You need to squeeze the juice out of the plant and treat the new growths with it.
- Acetic acid. The product is applied to a cotton swab and the papilloma is cauterized.
- Garlic. You need to squeeze the liquid out of the garlic clove and lubricate the wart.
Folk remedies are effective only for single tumors. If papillomas affect large areas of the skin, then only drug and surgical treatment can help.
Reviews
Animal owners leave positive reviews about the treatment of papillomatosis with novocaine injections. After 2-3 injections, the warts completely disappeared. However, cat owners emphasize that after the course of treatment it is necessary to give their pets immunomodulators. Otherwise, papillomas may grow again.
You can find positive reviews about the treatment of papillomatosis with ascorbic acid injections. Vitamin therapy helps strengthen the immune system and mobilize the body's defenses to fight the virus. However, such remedies are effective only for mild forms of the disease.
Experienced cat breeders recommend resorting to surgical methods for treating warts only in extreme cases, if the tumor prevents the animal from breathing or eating. Surgery is also necessary if there is a risk of malignant changes. This is a rather expensive procedure that is not available to all cat owners.
The pharmaceutical drug “Cryopharma” also received good reviews. It comes in aerosol form and contains a mixture of dimethyl ether and propane. This product is used to freeze and remove warts. Its action is similar to that of liquid nitrogen. However, this drug is intended for humans. Before using it on animals, you should consult your veterinarian. Only a specialist can take into account the indications and contraindications for the use of an aerosol.