Lice eaters in cats are insects that feed on scales that peel off from the animal’s skin during its life. Like many other ectoparasites, lice eaters cause a significant deterioration in the pet's health, prompting him to constantly scratch his skin until wounds appear. The occurrence of open wounds, in turn, can lead to more serious infections and a significant deterioration in the cat's health. We will tell you further how to determine the presence of lice eaters in your pet and fight them.
Lice eaters in cats: symptoms and treatment
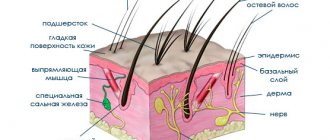
Description of the cat lice eater
The cat lice eater looks like a flat beige bug several centimeters long (usually 1-2 cm).
The structural features of the cat lice eater are as follows:
- wings are missing;
- the belly is elongated, oval-shaped, covered with bristles;
- the breast is underdeveloped, divided into three segments;
- three pairs of legs are equipped with hooks that dig into the cat’s skin;
- the head is disproportionately large, has short mustaches;
- mouth is large;
- triangular eyes are underdeveloped;
- color varies from whitish to light red.
The exoparasite feeds on the animal’s blood, dead epidermis, and particles of fur.
The female lays 100-120 eggs on the fur, attaching them to the hairs with sticky mucus.
The larvae go through 3 stages of maturation in 28 days, turning into adults. Rapid reproduction occurs in autumn and winter. Lice eaters, unlike lice and fleas, cannot survive without the host's body.
Stages of development of feline trichodectosis
In the development of trichodectosis, 3 stages can be distinguished, the duration of each of them is determined by the number of pathogens, the state of the cat’s immune system, as well as environmental conditions:
- initial stage - there are still few parasites, the cat feels satisfactory, sometimes itches with its paw, there may be occasional scratches on the skin;
- stage of the height of the disease - with an increase in the number of lice-eaters, all the symptoms typical of trichodectosis appear: thinning of the coat and areas of baldness;
- severe skin itching;
- multiple traces of scratching on the cat’s skin;
- disturbance of general well-being and behavior;
- dandruff appears;
- allergic reactions: this intensifies skin itching, which ceases to depend on the activity of parasites, as well as their number, and becomes permanent and intense;
- redness and swelling of the skin around the lesions;
- weight loss;
- viral leukemia;
How does infection occur and what are the risk factors?
Infection of a cat most often occurs during communication with infected relatives or contact with an infectious mouse caught while hunting.
You can become infected with ectoparasites while walking. At home, the pet is also not protected from the problem: people bring hundreds of lice-eater larvae on the soles of their shoes. Therefore, it is important to take care of the cleanliness of surfaces with which your pet comes into contact.
Signs of the presence of a lice eater in a cat:
- the cat itches intensely and often, trying to gnaw bugs out of its fur at the same time;
- the skin is covered with scratches and inflamed;
- the groin, neck, and abdomen areas have bald patches;
- The cat doesn't sleep well and looks apathetic.
Pets who have recently suffered an infectious disease or surgery are at risk of becoming infected with lice. Kittens, older cats with weakened immune systems and chronic diseases are also included in the risk factors for ectoparasite infection.
Rarely, lice beetle eggs are transmitted through a dirty groomer's tool.
Routes of infection
A cat becomes infected when adult lice eaters or larvae of lice eaters come into contact with its body. Routes of infection:
- Contact with other animals (cats, guinea pigs).
- Through common household items (bedding, carriers, combs).
- Cats walking outside can become infected from rodents.
- Kittens most often receive parasites from their mother.
There are a number of factors predisposing to the spread of the disease:
- High humidity in the room where the cat lives.
- Many animals are kept in a small area.
- Poor nutrition.
- Weakened immunity.
Diagnostics
Diagnosing lice in a cat at home is easy. You need to place the animal in direct sunlight or a lamp. After waiting 5 minutes, inspect the wool. Heat-loving lice eaters will come to the surface. This behavior distinguishes them from lice, fleas, and ticks, which prefer to hide.
Black dots stuck in the fur in clusters are the waste products of lice eaters. If you place such a point on a sheet of white paper and drop water on top, a bloody stain will form around it.
A cat infected with a parasite stops responding to the owner’s commands, which is due to lack of sleep from unbearable itching and pain from scratching.
How to spot lice eaters?
If desired, the owner can determine the presence of suspected parasites on the animal’s fur before going to the veterinarian. To make a diagnosis, you will need to place the cat under natural or artificial light. It is important that the animal does not go anywhere for 8-10 minutes, otherwise the experiment will not be successful.
To check for the presence of lice, the cat must be brought to a light source
As we already know, lice eaters love warmth and, as soon as they feel it, they will certainly move closer to its source, ending up in the upper layers of the animal’s fur. It is then that a person will be able to see them. It should be noted that this method also allows you to separate lice eaters from fleas or ticks, which do not experience the same attraction to heat and do not respond to lamps or sun.
Treatment
If you find a lice eater in your pet, you should immediately seek help from a doctor. The veterinarian will take a skin scraping, determine the degree of infestation by the parasite, and prescribe appropriate insecticide treatment.
All pets living in the apartment must be treated for the parasite, despite the fact that only one was found to have the lice eater. There is a high probability of larvae getting on the fur of other cats.
Sprays for lice
Using such products is an easy way to combat lice.
How to treat a cat against lice with a spray:
- place the animal in front of you, holding it tightly;
- spray the entire body with an aerosol, except the muzzle, paying attention to the stomach, groin areas, and neck;
- put on a special collar;
- after 2 hours, wash the cat with zoo shampoo;
- repeat treatment after 10 days.
The spray is not used for pregnant and lactating cats, kittens under 3 months.
Effective sprays against lice: Greenfort , Bayer , Rosagroservice .
Drops from lice
Drops against lice will help get rid of the problem, protecting against the invasion of the parasite for a whole month. The drug is applied in places that the cat cannot reach and lick: on the withers, behind the ears, along the spine.
The product is used every 30 days. It is important to apply the number of drops recommended in the instructions, taking into account the weight and age of the cat. An overdose of the drug is fraught with acute poisoning of the animal.
Drops “Bars” , “Advantage” , “Stronghold” .
Shampoos for lice
Anti-ectoparasite shampoo is a safe repellent for cats. It moisturizes the skin, reduces itching, and disinfects wounds. The shampoo is ineffective without the use of an antiparasitic collar. This remedy works well as a preventive measure.
Using anti-hairworm shampoo for cats:
- wet the cat's fur;
- apply shampoo with massage movements to all areas of the body;
- leave the foam for five to seven minutes;
- Rinse thoroughly with warm water.
After bathing the cat, be sure to disinfect the bath or pour boiling water over it.
The advantage of the shampoo is that, together with the collar, it can be used for pregnant females and kittens. However, it is worth remembering that hair mites in cats are not completely washed out with shampoo.
Acaricidal shampoos: Ms Kiss , Rolf Club , BioVax , BIO-GROOM , Celandine .
Emulsions against lice
Emulsion insecticides are diluted with water (5-10 liters of liquid depending on the preparation) and rubbed into the skin of the animal along the spine. The procedure is repeated after 14 days, and then the cat is washed with zoo shampoo. It is important to follow the instructions on the package and correctly calculate the dose of the drug.
For short-haired cat breeds, it is enough to spray with an aqueous emulsion solution, avoiding fine splashes getting into the eyes, nose, and mouth of the animal. It is more effective to treat long-haired pets with a diluted Delcid , blotting the skin with a cotton pad soaked in the emulsion solution, spreading the fur using a single-row comb.
Deltsid is diluted at the rate of 1 ampoule (2 ml) of the drug per 1.6 liters of water. For medicinal purposes, double treatment is carried out with an interval of 10 days. It is recommended to spray the same emulsion in a room where animals are often present. After two hours, ventilate the room, wash the floors and wipe the surfaces using detergents. Spray the room in the absence of pets and children.
The emulsions used are Deltsid , Merial , Agrovetzaschita , Pfizer , and Bionix .
Folk remedies for lice
The initial form of liceworm infection in cats is treated with folk recipes:
- Brew 3 tablespoons of string in 0.5 liters of boiling water. Let it brew for several hours. Cool, strain, rub into the cat’s skin after bathing.
- Boil 3 teaspoons of chamomile flowers in 200 ml of water. Strain through cheesecloth. Pour into a bathtub at the rate of 5 liters of water per glass of broth. Bathe the cat in the solution.
- A tablespoon of dry celandine (2 tablespoons of fresh) is poured into a glass of cold water. Boil the mixture over low heat. Leave the decoction for an hour. Dilute in 5 liters of bathing water.
An important point: the pet must be bathed in these decoctions every day until the lice eaters are eliminated and the scratching disappears. It is worth closely monitoring whether there will be an allergic reaction to medicinal herbs.
Symptoms of lice infestation in cats
The main symptoms of trichodectosis are:
- the cat itches with its paws, tries to catch parasites in its fur with its teeth;
- Due to constant itching, the cat becomes irritable and even aggressive, and may experience insomnia;
- multiple scratches and abrasions from scratching are visible on the skin; with the addition of secondary bacterial or fungal flora, dermatitis develops;
- small crawling insects, as well as their metabolic products, are noticeable in the wool;
- the coat becomes dull and sparse;
- in places of greatest concentration of lice-eaters, areas of baldness appear;
- dandruff appears.
With trichodectosis, areas of baldness form
Diagnosis of trichodectosis
The diagnosis is established based on an examination of the cat, a questioning of its owner about the development of the disease, as well as when lice eaters and their eggs are found on the cat’s skin and fur. To verify the diagnosis, parasites are combed out of the fur and examined under a microscope to clarify their species.
You can make the diagnosis yourself, since lice eaters have a peculiarity - they are very heat-loving. If you bring a cat to a heat source, for example, to a radiator, then after 5–10 minutes small moving insects will appear on the surface of its fur. This trait is characteristic only of lice eaters; fleas, lice, and skin mites do not show it.
Near a heat source, lice eaters, trying to get closer to it, rise to the surface of the fur - this is their distinctive feature
Hygiene and care during treatment
A pet suffering from trichodectosis must wear an Elizabethan collar, which helps avoid licking off insecticidal preparations before they are absorbed.
Hygiene requirements when treating a cat for lice:
- do wet cleaning of premises daily with Ecocide and Ectomin ;
- wash in hot water, steam treat toys, beds, rugs, scratching posts;
- treat wounds and scratches with antiseptics;
- after treatment, worm the cat;
- Extensive scratching, cover wounds with a sterile bandage.
When feeding your pet naturally, be sure to include vitamin and mineral complexes as recommended by your veterinarian. A cat eating ready-made industrial food is switched to the “Skin and Wool” or “Sensitive Skin” .
The danger of lice-eating cats for human health
There is no need to be afraid of lice-eaters parasitizing humans, but accidental parasite bites are possible in close contact with an infected cat, which can result in:
- development of an allergic reaction;
- cucumber tapeworm infection;
- infection with bacteria or fungi.
Children are especially vulnerable, so they are not allowed to interact with an infected cat until it is treated.
Lice eaters are carriers of dipylidia
Precautions when caring for a sick cat
Precautionary measures are simple, since modern means quickly destroy lice eaters:
- it is necessary to treat the cat with the drug (spray or drops) as quickly as possible;
- carry out processing with gloves and a disposable cape to avoid contact with parasites;
- the cat must be isolated until the parasites are destroyed;
- To destroy lice eaters, as well as their eggs, wet cleaning is carried out in the apartment with wiping of surfaces with solutions: Neostomazan 2%;
- Ecocide;
- Ectomina;
Can humans and other pets become infected with lice from a cat?
The hair-eating tick cannot survive on the human body: it dies from hypothermia on bare skin without fur. However, these parasites are carriers of worm eggs. If a lice eater is accidentally swallowed, a cat, and from it a person, becomes infected with a common tapeworm - the cucumber tapeworm, reaching a length of 70 cm.
It is important to observe hygiene standards: wash your hands with soap after handling animals, clean rooms with chlorine-containing substances, handle trays more thoroughly using rubber gloves, and regularly change the filler.
How dangerous are lice eaters?
These pests can be dangerous to your pet's health because they can cause serious illnesses. Lice eaters can transfer endoparasite eggs to the pet's skin, which leads to helminthiasis. This disease leads to depletion of the cat's body.
A disease such as trichodectosis may also occur, the symptoms of which are not only itching, but also severe hair loss. Due to the damage to the pet's skin by lice eaters, wounds remain on it through which bacteria can enter the cat's blood.
The cat hair eater is not dangerous for people, because the human body temperature is too low for them, and they die from the cold. Lice-eaters are not transmitted to humans, even through direct contact with an infected cat.
Preventive measures
To avoid infecting a cat with a lice eater, the following preventive measures must be observed:
- every week inspect the animal’s fur and skin for the presence of parasites;
- use an insecticidal collar when walking;
- do not allow the cat to communicate with stray cats;
- feed with balanced food;
- Wash the tray in a timely manner;
- monitor the cleanliness of beds, toys, rugs used by the pet;
- deworm your cat quarterly;
- bathe your cat regularly using special anti-parasitic shampoos;
- When purchasing a second pet, carefully examine its fur for the presence of lice;
- Visit the veterinarian regularly and get vaccinations to prevent skin diseases.
Proper care and the owner's attentive attention to detail are the key to healthy skin and fur of a cat. If the problem is noticed in time, it will allow you to get rid of parasites as soon as possible and prevent the pet’s condition from worsening.
The danger of trichodectosis for cats
The danger of trichodectosis for cats is:
- possibility of helminth infection; lice eaters are carriers of helminth infections, for example, dipilidia caused by cucumber tapeworm;
- the possibility of allergic skin reactions, especially miliary dermatitis;
- the possibility of the emergence or aggravation of an existing immunodeficiency state and exacerbation of chronic diseases, including viral infections;
- development of anemia;
- weight loss;
- thinning of the coat, the appearance of foci of alopecia (baldness), and a decrease in the attractiveness of the appearance of the coat.
Waste products of parasites visible in a cat’s fur are one of the symptoms of lice-eater infestation
Prevention
- Limit contact with sick animals.
- Monitor your pet's walk; the best solution would be not to let the animal walk on its own.
- Bathe your pet when you notice dirt. Cats are quite clean, so these actions are quite rare.
- The cat must be examined by a specialist at least once a year.
- Buy an insect repellent collar. Other preventive methods can be used.
Monitor your pet's condition; if the disease develops, the animal faces severe baldness and lethargy. Take care of the safety and comfort of your pet.