The translucent film on the eyes of cats is called the third eyelid. This anatomical feature of the feline family performs important functions.
Let's find out which state of the nictitating membrane corresponds to the norm, and what is considered a pathology. We will also analyze situations in which urgent consultation with a specialist is necessary.
Reasons for the appearance of a white film on the eyes of cats
A similar defect in representatives of the cat family can appear for various reasons, including:
- breed, genetic predisposition;
- the presence of foreign objects in the eye that irritate the mucous membrane;
- allergies to allergens that have entered the cat’s body through nutritional, aerogenic, or contact routes;
- birth defects;
- exhaustion, sudden weight loss;
- corneal necrosis, corneal lesions (keratitis, corneal ulcer, uveitis);
- conjunctivitis of various etiologies;
- neoplasia, oncological processes;
- inflammation of the third eyelid;
- pathologies of the nervous system;
- age-related changes in the body;
- chemical effects on the mucous membranes of the eyes.
Important! The third eyelid in cats (nictitating membrane) is an important part of the visual aid, performing a protective function. It is a kind of barrier for the eyes, softening the effect of mechanical influences. Clears the eyes of small dust particles and debris.
A white, bluish film on a cat’s eye can also form due to bacterial, viral, parasitic infections, diseases such as chlamydia, immunodeficiency virus, cat flu, herpes virus infection, severe helminthic infestation.
Mycoses (fungal infections), disorders in the functioning of the digestive tract can also cause the appearance of a whitish film on the eyes of a pet.
If a cat is walking outside and a white film appears on one eye, your pet most likely suffered damage to the cornea as a result of a fight. It is possible that debris, street dust, and plant seeds may have gotten into your pet’s eye.
What to pay attention to
The formation of the film is preceded by the appearance of signs that cannot be ignored.
Tearing, white veil
Increased lacrimation can develop from infections, after injuries, or from a foreign object.
A white veil on the organ of vision appears due to weight loss, dehydration, and oncological processes. This is the third eyelid, which droops with adenoma, exophthalmos, enophthalmos .
Signs of pathology
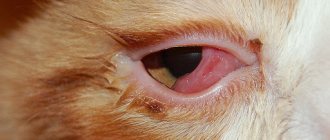
When a white veil covers the floor of the eye, they speak of prolapse of the third eyelid. In a normal state, its movement is invisible to prying eyes. The eyelid cleans the surface of the apple and produces a third of the tear fluid.
When the gland protrudes, the following symptoms are observed:
formation of a reddish clot in the inner corner of the eye;- profuse lacrimation;
- redness of the edge of the apple;
- development of conjunctivitis.
If the condition is advanced, pus is released from the corners of the eyes, the mucous membrane swells, the animal squints, and the eyelids become swollen.
Alarming symptoms
When a white-gray film appears on the eyes of a furry pet, owners should carefully examine the eyes of the pet and pay attention to the general condition and behavior of the cat.
Alarming symptoms:
- frequent blinking;
- tearfulness;
- discharge from the eyes of a different nature;
- changes in behavior (lethargy, inactivity, restlessness);
- loss of appetite, digestive problems;
- fever, chills;
- change in the shade of the mucous membrane;
- swelling of the eyelids;
- lack of pupil reaction to light;
- photophobia.
With this problem, cats prefer to retire to secluded places and are reluctant to make contact. Restless behavior gives way to apathy and depression. The pet constantly rubs its eyes with its paw, shakes its head, blinks frequently, squints its eyes, and cannot tolerate bright light. Purulent, serous exudate may accumulate in the corners of the eyes.
Why does prolapse develop?
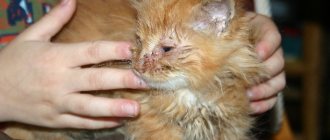
When a cat's eyes are half covered with a film, they speak of prolapse of the third eyelid. In this case, the cat feels discomfort and his vision gradually deteriorates, up to its complete loss. The reason for the development of this degree of disease may be associated with pathology of the organ of vision itself, as well as with diseases of the nervous system or gastrointestinal tract, reduced immunity of the pet, or with a fracture of the nictitating membrane as the kitten grows older.
Some cat breeds even have a genetic predisposition to third eyelid prolapse, which often occurs within the first year of life. And due to the hypertrophy of the nictitating film, it constantly rubs against the cornea, irritating the mucous membrane of the latter. At the same time, kittens with such an injury begin to rub their faces, wanting to get rid of the unpleasant sensation.
The film on the eyes of cats is often associated with inflammation, when the membrane becomes swollen, its hyperemia and prolapse develop. All this causes discomfort to the pet, and he washes himself more often.
Prolapse also develops during burns with aggressive chemicals or thermal burns, which injure not only the conjunctiva, but also the cornea of the eye. The affected tissues are swollen, reddened, lacrimation is observed and the cat feels a burning sensation and severe pain in the eyes. He begins to behave restlessly, shaking his head and rubbing his muzzle. The most dangerous burns are those of chemical origin, since they often injure deep-lying tissues and are complicated by bacterial infection.
The peculiarity of burns is that the severity of the injury can be assessed only on the second or third day from the moment it was received . Most often only one eye is affected.
If a kitten's cartilage tissue develops incorrectly, a fracture of the nictitating membrane may occur that cannot be restored. In this case, the third eyelid loses its functional abilities.
© shutterstock
Prolapse of the third eyelid is also possible with rhinotracheitis, when the disease is in its initial stage or in a mild form. In this case, the kitten experiences rhinitis and a rise in body temperature, it becomes apathetic, eats poorly or refuses to eat at all.
Sometimes the cause of the pathology is a membrane adenoma, which looks like a pink or red growth in the corner of the eye, which gradually grows, covering the eye . In this case, the cat experiences lacrimation, a rise in temperature, a worsening general condition, it becomes aggressive and cannot completely close the affected eye.
What to do if your cat has a white film on his eyes
It is impossible to independently determine what caused the appearance of a whitish film on a cat’s eye, so if you notice such a defect, take the animal to the veterinary clinic for examination as quickly as possible.
Important! If a white, bluish film appears on both eyes at once, this is a very alarming signal, which, if ignored by the owner, can lead not only to deterioration of visual function, partial or complete blindness, but also seriously affect the health of the cat.
The veterinarian will determine the root cause, make a diagnosis based on anemnesis, clinical picture, instrumental and laboratory studies, special tests, and then select the appropriate therapy. Treatment methods (drug therapy, surgery) are selected on an individual basis.
If the cause of the defect is viral-bacterial diseases, the animal is prescribed a course of antibiotic therapy (complex antibiotics, antiviral drugs in injections, tablets), symptomatic drugs to normalize the general condition, vitamin and mineral complexes.
It is mandatory to use ophthalmic agents in the treatment in the form of medicinal drops (Lacrimide, Colbiotsin, Tsiprobid), ointments, gels (Zovirax), as well as eye washes, which have a pronounced anti-inflammatory and antibacterial effect.
Surgery is used for adenoma, pathological formations in the eye, prolapse, protrusion of the third eyelid, as well as in the case of correction of congenital defects and developmental anomalies.
If foreign bodies get into the cat's eye, they are removed and the eyes are washed with special solutions.
How does drinking alcohol affect eye health?
Table of contents
Negative effects of alcohol on vision Short-term effects of alcohol on eyes Long-term consequences Gilan solution to eliminate dry eyes
Negative effects of alcohol on vision
The eyes are a very sensitive organ, so it is not surprising that alcohol consumption does not go unnoticed on them. The mechanism of action of ethyl alcohol is known to everyone: first, it dilates blood vessels for a short time, then constricts them, which leads to oxygen starvation. In this case, it does not matter at all how much and what kind of drink a person drank. The reaction to alcohol is always the same, it just manifests itself with different strength.
Short-term effects of alcohol on the eyes
Alcohol and its breakdown products have a poisonous effect on nerve endings, reducing their sensitivity. They relax the eye muscles, as a result of which the quality of visual perception decreases: a split image effect (diplopia) appears, visual acuity, color perception, the ability to distinguish between light and dark, follow moving objects, and see the whole picture deteriorate.
With severe intoxication, so-called tunnel vision occurs: central vision works, but peripheral vision is completely turned off. It feels as if a person is looking through a telescope. As a rule, all of these disorders disappear without treatment in about a day.
Effect on color perception
Studies have shown the dependence of color perception on blood alcohol levels. Thus, at a concentration of 1.2 ‰, about 50% of subjects are mistaken when identifying colors, at a level of 1.2-2.0 ‰ - 98%, and at levels above 2 ppm, 100% of people cannot correctly name colors. This effect occurs due to swelling of the optic nerve.
Effect on adaptation to lighting
Alcohol intoxication slows down recovery from exposure to bright light. In sober people, when there is a sudden change in lighting, their vision quickly adapts to new conditions, so they continue to see well. For a drunk person, this process takes much longer. This is why so many drunk drivers get into accidents after being blinded by headlights on the road at night.
Redness of the eyes
Hyperemia or redness of the sclera is one of the common consequences of drinking alcohol. Due to intracranial pressure, the blood vessels burst and the eyeball becomes reddish. If hemorrhages occur frequently, then accumulations of blood appear in the corners of the eyes. This condition is usually painless.
Long-term consequences
The toxic effects experienced by those who abuse alcohol increase over time. The risk of thrombosis increases because ethanol in the blood causes red blood cells to clump together and clog capillaries. This is why a few hours after drinking alcohol, a person’s eyes turn red. If at first hemorrhages are noticeable only on the sclera, then they spread to the eyelids and the area around the eyes.
The degree of impairment largely depends on the individual characteristics of the organism. In some people, even after several doses of alcohol, the process of malnutrition of the optic nerve begins, in others it takes several years: first, retinal thrombosis develops, then ruptures or detachment and hemorrhage. In the presence of retinal pathologies, for example, myopia, alcohol intoxication can cause an immediate reaction.
Let's highlight some of the most dangerous conditions that alcohol consumption causes.
Macular degeneration
A disease that develops closer to old age in non-drinkers. In alcohol drinkers, retinal destruction occurs much faster. The pathology is characterized by loss of central vision and contrast sensitivity, so a person cannot distinguish small details and faces, it is difficult for him to read and drive a car.
The following symptoms indicate macular degeneration:
- blind spots in the field of view;
- fog in the eyes;
- optical aberrations (distortions);
- increased photosensitivity.
If you contact a specialist late, it is extremely difficult to restore visual function.
Cataract
A disease in which the lens becomes cloudy and ceases to perform its functions. It is known that cataracts are more often diagnosed in people who drink, and women who drink alcohol have a higher risk of having a child with congenital lens opacity. Alcohol oxidizes the proteins that make up the lens, causing it to lose transparency.
Alcohol not only provokes the development of cataracts, but also negates the positive results of surgery to remove them. It slows down the restoration of eye tissue, causes hemorrhages, and reduces the effectiveness of medications.
Alcohol as a cause of dry eye syndrome
Research into the effect of alcohol on the development of dry eyes is being conducted by scientists from different countries. Their results allow us to conclude that alcoholic drinks negatively affect the mechanism of tear production, change the composition of tear fluid, and reduce the time it takes for the tear film to break.
Alcohol impairs blood circulation, so after some time after drinking an alcoholic drink, the eyes experience a lack of oxygen. The cornea begins to absorb it from the tear fluid, which causes the tear film to dry out faster. When the surface of the eye is not wetted in time, microcracks appear on it, which become a target for various infections.
In people who drink, the development of dry eye syndrome occurs faster, since the protective functions of the body are reduced against the background of intoxication. Experiencing discomfort in the eyes, a person more often touches them with his hands, thereby contributing to their infection.
Since alcohol has a detrimental effect on the entire body, treating dry eye syndrome becomes more difficult. It is important to contact a specialist as soon as possible. The main medication that can alleviate the patient’s condition is artificial tears.
Gilan solution to eliminate dry eyes
Gilan ophthalmic solution based on hyaluronic acid is suitable for people of any age and is compatible with all types of contact lenses. It quickly and effectively eliminates the symptoms of dry eyes, moisturizes the cornea, and has a preventive effect.
Before using Gilan solution, consult a specialist. Depending on the condition of the eyes, you can choose a solution with different concentrations of hyaluronic acid - 0.18% and 0.3%.
Recommendations for owners
After treatment, the veterinarian will provide recommendations to cat owners on care and nutrition, which owners must strictly follow, constantly monitoring the condition of the eyes and health until the animal is completely healed.
For eye rinsing and hygiene, medicinal decoctions of medicinal herbs and ophthalmic solutions (boric acid, warm water, decoction of chamomile, sage) are prescribed. Potassium permanganate lotions, tricylan powder, and furatsilin solution (the tablet is diluted in water) also help well.
Advice! After therapeutic therapy, even if the cat’s white film has disappeared from his eyes, his condition has improved, do not be lazy to take your pet to the clinic for a second scheduled examination!
Prevention
Each pet needs to be provided with proper care: a balanced diet, regular hygiene procedures. Timely vaccination is important to keep your pet healthy.
It is not recommended to let your domestic cat outside; contact with stray animals is undesirable.
Timely deworming is the key to good health for your pet. The procedure is performed on kittens and adult animals.
How can mycetoma be cured?
Is it possible to do without surgery? It is impossible to get rid of fungus in the maxillary sinus without surgical intervention, I will say this right away. No pills, no drops of “dancing with a tambourine” and everything else will give the desired therapeutic effect. First of all, it is necessary to surgically remove the fungal body, remove this mycelium, remove all the fungus from the maxillary sinus.
This can be done either through a nasal surgical approach or an intraoral approach.
How to remove fungus from the maxillary sinus
With intraoral access, a perforation is made in the vestibular wall of the maxillary sinus - access, and evacuation occurs through this hole, i.e. removal of the fungal body, mushroom mycelium. Then the maxillary sinus is well washed, treated with antifungal and antimicrobial drugs and sutured. Subsequently, the patient is prescribed antifungal therapy.
Surgical removal of mycetoma shows good results today, relapses are extremely rare.
Symptoms during the formation of mycetoma
In the early stages, a patient with mycetoma feels absolutely nothing, because there are no symptoms of the disease yet.
And as the fungal growth increases in size, it will become more difficult for the patient to breathe due to nasal congestion on one side, while the nose will be clean, without discharge. But sometimes the discharge can be in the form of crumbly masses of a gray-dirty color. In addition to the symptoms listed earlier, the patient may experience dizziness, headaches, when the mycetoma grows strongly, it occupies the entire volume of the maxillary sinus, creating excess pressure, including in the orbital area. And, of course, with a large growth of mycetoma of the maxillary sinus, sinusitis is possible. The patient may have pain in the upper teeth in the lateral part from the side of the mycetoma. And, as I said earlier - difficulty breathing, the patient switches to mouth breathing as a result of acquired chronic sinusitis.
How extensive can a mycetoma be?
Molds can grow until the maxillary sinus is completely filled. And when the mold ball occupies the entire maxillary sinus (it usually takes 5-7 years to grow), the diameter of the ball reaches an average of 3-5 centimeters.
For example, here is a photo of a mycetoma of the maxillary sinus, when the growth of fungi has almost completely “captured” it. The cause of the formation of mycetoma in this case was a part of the root filling of the tooth that was removed into the maxillary sinus:
We describe in detail how the root filling got into the maxillary sinus in this clinical case.
Tumor
All of the previously listed diseases are, for the most part, treatable if the causes are identified in time. But there is a disease in which swelling in the eye area may indicate the presence of a neoplasm. If, in addition to the tumor, your pet begins to have difficulty oriented in space, or there is a noticeable disturbance in the coordination of movements, then conduct an independent examination.
If the swelling is hard and there is an increase in body temperature, this is a reason to sound the alarm and immediately take the animal to a veterinary clinic, this will increase the chances of a positive outcome and possible avoidance of surgical intervention.
If, during a self-examination, you notice that the swelling has a dense structure, then the best solution is to contact a veterinary clinic.
Why is the formation of fungus in the maxillary sinus dangerous?
How can the growth of a fungal colony be dangerous? In any case, it’s not very pleasant when some kind of parasite, mold, or fungus lives in you. This is really a parasite that lives in the cavity of the maxillary sinus and feels great there. In addition, mycetoma is dangerous because the blood supply and oxygen supply to the brain deteriorates, since the function of nasal breathing is disrupted. A person simply begins to experience partial oxygen starvation due to mycetoma.
Plus, the waste products of the fungus in the maxillary sinus flow into the nasopharynx, which can additionally lead to additional complications, including the development of allergies and provoking respiratory diseases. And, of course, chronic sinusitis.
The role of CT in the study of mycetoma
Of course, a good computed tomogram gives a complete picture of the maxillary sinuses and is the main tool in diagnosing “mycetoma” when examining a patient. A CT scan of the maxillary sinus shows the location, size, and volume of mycetoma damage (local volume or total fungal infection of the cavity).
In fact, computed tomography is the gold standard for diagnosing mycetoma today.
Eye damage by helminths
It is believed that worms in the eyes of a cat is a myth, but you should know that theoretically these parasites can live in any organ. It is important to remember that helminths of this type are very dangerous and your pet may simply lose his sight if treatment is not started in time.
How do these parasites get into a cat's eyes? They require an intermediate carrier – fruit flies. They sit on the animal’s eyelids, lay eggs close to the mucous membrane, and when the pet washes itself, they inseminate it. After the development stage, the egg develops into a larva, which moves into the eyeball and begins to grow.
Symptoms that indicate that the eye is affected by helminths:
- Loss of eyelashes;
- Itching in the eye area;
- lacrimation;
- Inflammation of the mucous membrane and cornea
- Cloudiness
- Increased body temperature
- Deterioration of vision (blindness)
This symptomatology is well known to us and is very similar to other ophthalmological diseases that we have already listed. A definitive diagnosis can only be made in a clinical setting.