Many people are familiar with the phenomenon of gumboil - when the cheek next to a sore tooth swells literally before our eyes and painkillers do not relieve acute pain. This is the periosteum of the tooth becoming inflamed, or, as doctors say, odontogenic periostitis of the jaws has developed. This disease in itself is a complication of dental problems (periodontitis, periodontitis), but in the absence of proper treatment, such inflammation can also cause the development of even more serious complications.
Why can the periosteum of a tooth become inflamed?
The most common is odontogenic periostitis of the jaws, that is, an inflammatory process provoked by diseases of the teeth or periodontal tissues. Deep caries, pulpitis, periodontitis (inflammatory process at the apex of the tooth root), periodontitis - all these diseases, if not treated in time, lead to the appearance of gumboil. Also, one of the reasons for the development of the inflammatory process may be alveolitis - inflammation of the tooth socket, which in some cases occurs after tooth extraction. Inflammation of the periosteum after tooth extraction usually develops in those patients who do not rush to see a dentist when the first signs of complications appear in the postoperative period.
Much less common is toxic periostitis, caused by infection through the blood or lymph (usually due to some general infectious disease). The disease can also be caused by injuries to the jaw bone or surrounding soft tissue.
How to help your pet
An attentive owner manages to notice problems in time and take action. But if it’s not entirely clear why a cat’s teeth fall out before the age of 6, try to independently determine the direction of the search:
- With age-related tooth loss, they fall out in a strict order: first the incisors, then the canines, then the premolars and molars. The loss is extended over time. If this order is broken, then you need to look for another reason.
- If you find wounds on the gums or chipped enamel, take measures to neutralize the consequences of the injury.
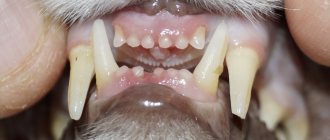
- Pay attention to the presence of tartar and caries, a specific (sweet, putrid, sour) odor from the mouth. If the gums have changed color, the crowns wobble or look transparent, gray, or black, this is a direct indication of disease. If you notice these signs, contact your veterinarian for treatment.
Something else interesting: How to determine the age of a cat
Inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth: symptoms
Depending on the form and localization of the process, symptoms may be as follows:
- General symptoms: severe pain in the area of inflammation, swelling, noticeable swelling, discoloration of the gums, mobility of the dental unit, which served as a source of spread of the pathological process. Depending on the location of the source of infection, facial swelling will look different: when inflammation develops near the front teeth, the upper lip or middle third of the face swells; when inflammation occurs near the chewing teeth, the cheek, sometimes the lower eyelid, and parotid area swell. You can evaluate what different types of edema look like during inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth using a photo.
- Acute serous periostitis of the lower or upper jaw is accompanied by severe redness of the mucous membranes, rapid development of edema, and increased body temperature. The general symptoms of this form of inflammation are especially pronounced.
- In the acute purulent form of the disease, severe sharp pain is characteristic, and the pain subsides under the influence of cold and becomes stronger when exposed to heat. Sleep and appetite are disturbed, the temperature rises noticeably, and the patient’s general condition worsens. Pain in most cases radiates along the branches of the corresponding nerves. For example, acute purulent periostitis of the lower jaw can make itself felt by pain in the neck, chin, ear and temporomandibular joint. Purulent periostitis of the upper jaw most often provokes pain in the orbital area, temporal bone, and ear.
- The chronic form of the disease is quite rare, and chronic periostitis of the lower jaw usually develops. The symptoms are mild, the swelling is almost unnoticeable and can gradually develop over a very long time. Pain and discomfort appear from time to time (periods of exacerbation).
At the initial stage of the inflammatory process, it usually has a serous form, later, without treatment, it becomes purulent. With a large accumulation of pus, the formed abscess can burst with the flow of purulent contents into the oral cavity. At the same time, the swelling decreases and the pain subsides. In this case, some patients calm down, believing that the problem has been solved, and are in no hurry to see a dentist. In fact, this is only temporary relief, since the pathological process can resume at any minute.
Treatment in dentistry
To eliminate pathological abrasion of hard dental tissues, you need to establish its cause and then get rid of it. The next step is to restore the configuration of the dentition. In the early stages, treatment with medications may be sufficient. If the symptoms are pronounced, only an orthopedist will help.
Medicines
The techniques used are based on the process of remineralization of the enamel layer. In this way, compensatory reactions are activated and mineral metabolism in hard tissues is normalized. Experts prescribe vitamin and mineral supplements with a high content of calcium and phosphorus. Additionally, pastes are used to reduce sensitivity. If the destruction has just begun and the dentin has not been damaged, this option for treating tooth wear can be very effective.
Orthopedic methods
If the defect is serious, medication alone is not enough; more radical correction is required. Most often, doctors use inlays and artificial crowns. If some units fall out, a bridge structure, clasp prosthesis or other types are installed. This therapy allows you to completely restore the functioning of the rows and evenly distribute the chewing load.
Periostitis in children
In children, the inflammatory process usually develops as a result of untreated caries of baby teeth, infectious diseases or injuries. Due to the peculiarities of the physiology and anatomy of the child’s body, as well as due to the immaturity of the child’s immune system, the pathology develops quickly and rapidly, and the infection quickly spreads through the bloodstream and lymph flow, so multiple lesions can form.
Periostitis of the upper jaw in a child requires special attention, which, when localized in the palate, may not change facial features - swelling forms inside the oral cavity and can only be noticed by the characteristic convex swelling on the palate. The abscess gradually grows, capturing the mucous areas of the pharynx and tongue, which causes pain when swallowing and chewing. If a child develops symptoms such as fever, loss of appetite, or painful swallowing, it is imperative to check whether such a condition is caused by developing gumboil.
Prevention
To prevent pathology, it is necessary to regularly visit the dentist for preventive examinations at least once every six months. It is also important to promptly replace dental defects. In addition, all experts advise correcting malocclusion pathologies in a timely manner already in childhood or adolescence. Orthodontic therapy will help cope with the abnormal position of the teeth and prevent wear of the crown part.
You won’t have to decide what to do when the hard tissues of your teeth are worn away if you treat all the diseases that lead to it. For example, this includes bruxism, mineral metabolism disorders, thyroid pathologies, and problems with the digestive organs.
If the patient is at risk due to professional activities, it is necessary:
- use personal protective equipment;
- take a responsible approach to regular hygienic oral care;
- take courses of vitamins and minerals prescribed by your doctor.
The most important point remains the qualitative diagnosis of the transitional stage between physiological and pathological erasure. For this purpose, regular examinations and timely treatment of identified disorders are indicated.
Possible complications and diagnosis
If the disease is not treated properly, very serious complications soon develop: osteomyelitis (purulent inflammation of bone tissue, provoking its necrosis), phlegmon (a diffuse purulent process that affects nearby tissues and requires immediate surgical intervention), sepsis (a general infection of the body, often ending in the death of the patient ). Each of these conditions requires emergency medical care and long, painstaking treatment. Therefore, it is better not to let the situation lead to complications and contact a dentist at the first signs of an inflammatory process.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, the doctor will need to conduct a differential diagnosis using instrumental diagnostic methods (radiography, CT). This disease is similar in symptoms to acute periodontitis, acute inflammation of the salivary glands, lymphadenitis, and osteomyelitis. Therefore, in order to prescribe adequate treatment, it will be necessary to exclude these conditions and accurately determine the cause of the patient’s poor health.
Treatment: what the doctor prescribes
Therapy is selected individually, taking into account the reasons that led to such changes. The main goal of its implementation is to eliminate the provoking factor and normalize the animal’s condition.
Nutrition correction
The first thing to do is to adjust the animal’s diet.
It is extremely important that the menu is balanced . It should contain a sufficient amount of vitamins and microelements.
Tartar removal
If necessary, remove hard plaque under anesthesia. The pet is conscious, but cannot offer resistance.
Upon completion of the process, the cat needs to be provided with complete care. The procedure is very stressful for him.
Treatment of the underlying disease
The main emphasis is on eliminating the pathology that provoked tooth loss. For this purpose, immunostimulating, anti-inflammatory drugs and antibiotics can be prescribed. The therapy is aimed at strengthening the gums, eliminating bleeding and pain.
Inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth: treatment
Periostitis of the lower and upper jaw requires almost the same treatment, despite some differences in symptoms and localization of lesions. Moreover, complex therapy will be required, which will quickly eliminate the infectious-inflammatory focus and prevent relapses:
- Surgery. Opening the purulent sac with removal of the contents and thorough cleaning of residual pus is a mandatory procedure in this case. The intervention is performed under local anesthesia. At the initial stage of the disease (with its serous form), it is possible to do without surgical intervention. In this case, the doctor carries out endodontic treatment (depulpation, cleaning and treatment of root canals, antibacterial therapy).
- Drug therapy. Prescribing antibacterial and anti-inflammatory drugs to eliminate inflammatory phenomena (swelling, hyperemia, fever, pain) and infection.
- Physiotherapeutic procedures. Iontophoresis, ultrasound or laser therapy, electrophoresis, paraffin therapy - all these procedures are usually aimed at resolving compactions formed as a result of the pathological process. As a rule, physiotherapy is used for chronic forms of the disease, but in some cases it can be used in the complex treatment of acute purulent forms.
Antibiotics for inflammation of the periosteum of the tooth are prescribed during the treatment process; they are necessary to eliminate the bacterial infection, which is one of the causes of the development of the purulent-inflammatory process. The doctor selects medications based on the severity of the disease, the general condition of the patient’s body and the possible presence of concomitant diseases. Along with antibiotics for periostitis of the jaw, antihistamines (antiallergic) are also prescribed as treatment, which can reduce the drug load on the immune system, as well as calcium supplements.
The success of treatment largely depends on the patient’s timely visit to the doctor and the effectiveness of the therapy itself. And if in the first case everything depends on the patient - his conscious attitude towards his own health, then in the second the success of treatment is completely determined by the qualifications and experience of the dentist to whom the patient turned. A competent specialist with extensive clinical experience will quickly and successfully cope with even such a complex disease, while an amateur can further aggravate the problem. Therefore, choosing a good specialist is important here - these are the specialists who work at the 32 Dent clinic. Our doctors have extensive experience in successfully treating any purulent-inflammatory diseases of the oral cavity, including periostitis.
How can you tell if a kitten's teeth are changing?
Kittens change teeth quite quickly, but most often do not cause them severe pain. Here are the main signs of teeth changing:
- Your gums may hurt. In this case, the kitten will experience slight discomfort when eating. Because of this, the baby may eat less than usual.
- The kitten becomes less active and plays less.
- The kitten feels uncomfortable when their face is touched.
- The pet may try to force out a loose tooth, so sometimes it shakes its head or touches its face with its paws.
- The kitten actively chews: this way it eases the pain.
- You may find baby teeth on the floor or on your pet's bed. Don't worry if you can't find your missing teeth. Very often, baby teeth fall out while eating and the kitten swallows them along with food.
During this period, you need to pay close attention to the kitten. Don't insist on playing if he doesn't want to. If the kitten is still playing, do not pull the toy when he has it in his teeth - you can hurt the pet. If you brush your kitten's teeth, it is better to skip this procedure when changing teeth. You can cause your pet additional discomfort.
During the change of teeth, it is best to feed the kitten soft food. SUPERPET food from the Minced meat line is perfect for this period. The food is soft and does not cause discomfort to kittens when feeding.
How to treat inflammation of the periosteum of a tooth before visiting a doctor?
Self-medication for any purulent processes is very dangerous, so it is recommended to consult a dentist at the first symptoms of the disease. However, before visiting a doctor, the patient can alleviate his condition somewhat by applying cold to the cheek on the affected side and rinsing his mouth with an antiseptic solution at room temperature (chlorhexidine soda-saline solution, chamomile or sage decoctions). Here's what you absolutely can't do:
- Apply warm compresses and drink hot drinks.
- Apply any bandages yourself or use medications without a doctor’s prescription.
- It is better not to take analgesics before visiting the dentist.
- If you are undergoing surgery (opening an abscess), you should not take aspirin, since it changes the rheological properties of the blood and can cause bleeding.
When is a tooth root 100% subject to extraction?
Tooth root removal is performed if:
- the root is softened below the gum level,
- the root of the tooth is below the level of the surrounding bone tissue,
- the root of the tooth has cracks
:
- the root of the tooth is chipped
:
- the root of the tooth is severely damaged, for example as a result of canal treatment with resorcinol
:
- There are various inflammatory processes around the root and under the root of the tooth - cyst, cystogranuloma
:
- the root of the tooth is mobile,
- there is a deep dental pocket.
An alternative to implantation is autotransplantation of wisdom teeth
Don't rush to remove your wisdom teeth. Firstly
, there must be clear indicators for their removal.
Secondly
, you don’t need to follow fashion, trends and delete eights just because “a girlfriend or friend deleted them and that’s cool.” There are a number of moments in life when wisdom teeth come to our aid.
It is not for nothing that nature has created a number of organs that duplicate each other in our body, for example, we have two lungs, two kidneys, which in case of problems with one lung/kidney come to our aid. Also with wisdom teeth: if a person (for some reason) has problems with the chewing group of teeth, for example, caries has destroyed the sixth or seventh tooth, then eights can come to the rescue. How so? After all, wisdom teeth are not involved in the chewing process. Yes, you are right here. But a wisdom tooth can serve as a donor, and it can be transplanted into place of a tooth with destroyed roots. Fantastic? No, advanced technologies in dentistry. This is called autotransplantation.
In the following video we show in detail the dental transplant surgery. The roots of two sixths of the patient's teeth had just been destroyed, and they were replaced by the patient's own wisdom teeth. And, by the way, this patient at the end of the video gives a detailed review after 1 year after the operation. Look, this is useful:
Loss of teeth in cats in old age
Cats that have crossed the seven-year mark are considered elderly. Manufacturers of ready-made food make special food for cats over 7 years old. By this age, pets are excluded from breeding and are recommended to be neutered.
The process of teeth abrasion begins. However, everything is individual. There are fifteen-year-old pets. retaining all the dents.
The first incisors fall out at the age of 9; the pet loses its fangs after the thirteenth birthday.
Kitten behavior when replacing teeth
You may not notice tooth loss if you don’t look into the mouth, or until a kitten’s fang falls out in front of the owner’s eyes. But the behavior of all kittens changes at this time: they become restless and chew on everything. This is normal because the gums where the permanent teeth erupt are itchy.
© shutterstock
It is important not to forget about raising a kitten and to monitor what exactly it chews. Items such as wires, plastic, anything that he can bite off but his stomach will not digest must be removed or else a blockage in the stomach or intestines may occur. There is no need to train an animal to gnaw the hands and feet of its owner. This bad habit becomes ingrained during the change of teeth, and it will not be easy to wean it off. The harmless and almost painless biting of a kitten will later be replaced by the bite of strong and sharp incisors and fangs of an adult cat.
Is implantation possible after tooth root removal?
Yes, of course it is possible. And we at the clinics of the German Implantology Center widely use implantation after tooth root removal. Our conditions allow us to carry out implantation in such cases. And if we can achieve primary stability of the implant, then in 90% of cases
After removal, we immediately install the implant. We have rolled out the technology to perfection and gives excellent results.
Of course, with the exception of wisdom teeth, no implant is placed after their removal. But, by the way, wisdom teeth in this situation can be extremely useful, since they... can be transplanted to the place of the problem tooth being removed! Dental transplantation has been practiced in the clinics of the German Implantology Center since 2017, and our specialists have accumulated a wealth of clinical experience. Let's talk about this a little more.