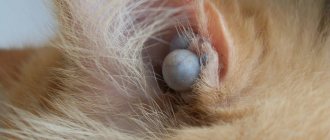
If the owner discovers a ball under the skin of a cat, he should consult a veterinarian. The appearance of tumors on an animal’s body can be associated with benign or malignant tumors.
Some formations under the skin do not require medical intervention and do not pose a serious threat to the pet. But there are a number of diseases that require immediate conservative treatment or surgical intervention.
Any bumps on a cat’s body are a reason to contact a veterinarian and you should not self-medicate. Particular attention should be paid to those neoplasms under the pet’s skin that are prone to rapid growth and their number is increasing.
Subcutaneous bumps may bleed or cause significant discomfort to your pet. Only in a veterinary hospital will a competent doctor be able to prescribe a full examination (biopsy, blood biochemistry, urine analysis, ultrasound or x-ray) and make an accurate diagnosis, as well as prescribe adequate treatment.
Signs
The cause of the appearance of a lump under the skin of a cat can be cancerous tumors, lymphadenitis, hernias, benign tumors (lipomas, wen, papillomas, fibromas).
Cats are often diagnosed with lumps under the skin that develop as a result of inflammatory processes of the skin - furunculosis, folliculitis, carbuncles, abscesses, and phlegmon. The cause of a cone in a cat can also be the bite of a poisonous insect - a wasp, bee or bumblebee.
Depending on what type of tumor the animal has under the skin, the symptoms will be different. If a ball is found under the skin of a cat's neck, the cause may be a benign or malignant tumor. The main signs of benign neoplasms are:
- long-term development;
- a clear boundary between healthy and modified tissue structures;
- presence of encapsulation;
- absence of metastases;
- roundness of shape and smoothness of surface.
Malignant neoplasms are characterized, on the contrary, by rapid growth, the presence of sites of stasis and the occurrence of ulcerations. Balls under the skin associated with malignant tumors have a bumpy surface with areas of necrosis of tissue structures.
A tumor diagnosed under the skin on the cat’s abdomen may well turn out to be a benign formation – a lipoma. The main differences between this neoplasm and a malignant one are the absence of rapid growth, soft structure, and roundness of shape.
A characteristic feature of a lipoma is its ease of movement, as if a ball were rolling under the skin of a cat. Lipoma does not require immediate removal. In the vast majority of clinical cases, the neoplasm is systematically monitored by specialists.
Surgical intervention is prescribed only if the location of the lipoma begins to cause discomfort to the animal - it itches, greatly increases in size, and in every possible way interferes with the cat’s usual activities.
To differentiate a lipoma from a possible malignant neoplasm, it is advisable to perform a biopsy, as well as laboratory tests of the animal’s blood and urine.
Diagnosis of the disease
Fats that tend to grow into blood vessels and deep tissues (infiltrative lipomas) are often confused with cancer, so they must be examined carefully.
To determine the nature of the neoplasm, a biopsy (tissue sampling) is performed. In case of infiltrative compaction, computed tomography (CT) is prescribed to determine the extent of tumor damage to blood vessels and muscles.
Histological analysis
Lipoma consists of lobules of adipose tissue separated by connective tissue septa. If there are few blood vessels, then it is dense and damage does not lead to heavy bleeding.
Any neoplasm on the animal’s body must be examined, since there is a risk of degeneration of a benign tumor into a malignant one (liposarcoma).
Types and reasons
The appearance of a lump on a cat’s neck under the skin, abdomen, head or paws may be associated with a malignant or benign neoplasm. The main reasons for the appearance of balls under the skin of a pet are:
- Abscess. A purulent formation that occurs as a result of a pet being bitten by another animal. As a result of a specific reaction of the body, leukocytes are sent to the site of damage to further combat pathogenic microflora. As a result, pus is formed, containing dead bacterial microorganisms along with dead leukocytes. An abscess can be large and located in a variety of places on the body. Thus, the appearance of a lump on a cat’s neck caused by an abscess leads to painful sensations in the animal, and there is a significant increase in body temperature in the affected area. Hair loss may also occur at the site of the injury.
- Skin cancer. Not all malignant skin tumors lead to the appearance of bumps on the cat’s stomach or other parts of the body. But some types of cancer, such as melanoma, sarcoma, sebaceous tumor, mastocytoma or basal cell carcinoma, can cause lumps to appear under the skin.
- Contact type dermatitis. A disease that occurs as a result of pet contact with potential allergens - household chemicals, hazardous chemicals or poisonous plants.
- Acne. Having felt a ball under the skin of a cat’s neck, the owner may be very afraid for the health of his pet. But it may just be acne, which is a pimple that forms in the chin and neck area, as well as the tail. The development of pathology is associated with blockage of the sebaceous glands. There are cat breeds that have a genetic predisposition to the disease.
- Hematoma. As a result of damage and injury, a hematoma (subcutaneous hemorrhage) may form under the cat’s skin. Hematomas are most often diagnosed on the hind legs (results of jumping from a height), the head (after fights with other cats).
- Injection granuloma. A lump that appears in the neck area at the injection site may be a granuloma. This pathological change occurs quite often after vaccination of cats. The bumps are capable of self-resorption and go away on their own without medical help a few days after the injection. But in some cases, the lump under the skin may grow and in this case it is important to consult a veterinarian.
- Wen. A lipoma, or in other words a wen, is a benign neoplasm that occurs as a result of pathological changes in adipose tissue. The appearance of lipomas is observed, as a rule, in animals after 7 years of age.
- Eosinophilic granuloma. Damage of an inflammatory nature, more often occurring on the upper lip than on the lower lip and other parts of the muzzle. Eosinophilic granuloma appears as an ulcerative lesion, and the causes are still not clearly defined.
- Mastitis. Lumps on a cat's nipples, which occur more often in cats that have not been sterilized, are called mastitis. The occurrence of mastitis has also been noted in cats during active lactation. The pathology is characterized by an inflammatory process in the mammary glands, leading to discomfort in the animal and an increase in body temperature to high levels. Without the intervention of a veterinary specialist, coping with the disease is quite problematic.
- Tumors of the mammary glands. New growths of the mammary glands look like multiple nodules localized on milk bags, closer to the groin area. Breast cancer is characterized by the appearance of nodular neoplasms on milk bags, hot to the touch, over time acquiring a red tint, and begin to bleed. In addition, purulent exudate may be released from the nipples, which indicates the last stages of cancer.
Mechanical causes of bumps
Harmless swellings on the head most often appear in cats that are free-range. They tend to find themselves in various risky situations, ranging from falling from heights to collisions with dangerous insects. The main causes of bumps on the head are:
- Insect bite . Curious furry pets often love to catch butterflies, dragonflies and other insects. Sometimes during the game they may encounter wasps, bees, and ticks. And the result of such a meeting can be disastrous for the pet. Also, the appearance of a bump can be caused by flea or midge bites. In this case, you need to remove the remaining insect particles and relieve the swelling if it is very strong. For this, drugs such as Suprastin, Claritin, Zyrtec are suitable.
- Fight . Bully cats often get bruises in street fights. The reason could be anything, but the result is the same. A bright red, painful swelling that turns blue over time can indicate internal hemorrhage and even a fracture of the skull bones.
- Splinter . Foreign bodies under the scalp are common in cats. Splinters can include wood chips, thorns from various plants, cactus needles, and even metal shavings. Some time after a splinter enters the skin, a cavity filled with pus forms under the skin, and a soft tubercle appears. If detected, you need to remove the splinter, rinse the cavity with an antiseptic and apply a bandage to the wound.
Malignant neoplasms
Oral cancer is not common, but in three out of a hundred cats it causes growths in the area where the whiskers grow. Therefore, if your cat has a bump on its cheek, contact your veterinarian.
The cause of this serious disease is frequent smoking by the owner in the presence of the pet, and unnatural nutrition based on canned cat food. The most common diagnosis is squamous cell carcinoma or fibrosarcoma.
Treatment of such diseases is not carried out at home; surgical removal of the bump on the cheek is prescribed. Chemotherapy is used to prevent metastases. However, with a progressive tumor and advanced disease, the cat cannot be cured.
© shutterstock
How are atheromas removed?
No amount of burdock, plantain or compresses with alcohol help with atheroma. It needs to be treated surgically. You should visit a doctor as early as possible. If the atheroma has festered, you need to run to the surgeon.
The most senseless way to remove scalp atheroma is puncture, when a needle is inserted into the cyst and its contents are pumped out with a syringe. No normal doctor does this (except perhaps to obtain the contents of the cyst and send it for a biopsy). As long as the walls of the atheroma are preserved, it will fill up again and again. In order to rid the patient of a cyst, its walls must be completely removed. The classic operation looks like this:
- Two bordering incisions are made on the skin in the area of atheroma.
- A blunt instrument (most often closed scissors) is placed under the atheroma.
- The atheroma is peeled off, and stitches are placed on the wound.
The intervention is performed under local anesthesia. Usually the operation is performed on an outpatient basis, but if the atheroma is large, hospitalization in a hospital may be required. However, scalpels are becoming a thing of the past. Surgeons now have more efficient tools. For example, lasers. With their help, atheroma on the head less than 5 mm in size can be evaporated without a trace; for larger ones, additional small incisions will have to be made.
An even more advanced way to remove atheromas of the scalp is radio wave and laser surgery. These are the methods that doctors at the ProfMedLab clinic use. Laser or high frequency radio waves work instead of a scalpel. They cause little tissue damage, healing occurs faster, and the cosmetic effect is better.
The cat has a lump on his neck
The presence of a lump under the skin on a cat's neck may not always indicate a tumor. Of course, if you discovered bumps some time ago and they do not disappear, but on the contrary, they only increase, the reason is most likely related to a tumor.
But often a cat can suffer from a less dangerous disease - subcutaneous mites, which can also manifest themselves in the form of small bumps and lumps on the neck.
In any case, only a doctor can make a correct diagnosis for your cat. Therefore, if, when feeling your cat, you notice lumps, lumps, sores or bald patches, do not waste time and take the animal to the doctor. Early diagnosis is the key to successful treatment!
Prices for appointments in our network of veterinary clinics
| Name of veterinary services | Unit | Price, rub |
| ⭐ Initial appointment | 1 animal | 400 |
| ⭐ Repeated appointment | 1 animal | 250 |
| Initial appointment with a specialist | 1 animal | 1100 |
| Consultation without an animal | — | 550 |
| Consultation with a doctor based on test results | 1 PC. | 400 |
| Weighing animals | 1 animal | For free |
| Additional fixation for aggressive animal behavior | 1 animal | 700 |
All our Veterinary Clinics:
For any suggestions regarding the site: [email protected]
|