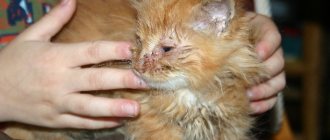
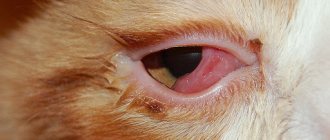
Ophthalmological diseases are common not only among people, but are also often diagnosed in pets. A cloudy eye in a cat can signal increased intraocular pressure, cataracts and other diseases of the visual organs. At the same time, the pet’s vision deteriorates, he may often bump into objects and move with caution. If there is a problem, it is worth consulting with a veterinarian in time so that the cat does not develop complications, including complete blindness.
Characteristic symptoms
Doctors distinguish several degrees of damage to the organ of vision:
- peripheral (a border is observed at the edges of the eyeball);
- central (clouding of the eye is noted in the very center);
- total (the cat’s organ of vision is completely closed).
In most cases, if a kitten has a cloudy eye, there will be accompanying symptoms.
Against the background of decreased vision, the pet begins to walk unsteadily and does not notice obstacles . He becomes irritable and overly excitable. Strabismus, pain, swelling, and the appearance of discharge are possible.
If the cornea is affected, there is clouding of the surface of the eye. It acquires a blue or white tint and loses its shine.
Sometimes the lens is affected, but the cornea continues to remain transparent, and only the pupil becomes cloudy. Under the influence of bright light, a narrowing of the turbidity is observed, and when exposed to dim light, it expands.
Complications of scleritis
Some consequences of an unfavorable outcome have already been mentioned. Sometimes the inflammation is complicated by the cornea, iris and ciliary body. Because of this, adhesions form between the lens and the pupillary edge of the iris. This leads to blurred vision and clouding of the anterior chamber of the eye. The main complications of scleritis:
- keratitis;
- iridocyclitis;
- opacity in the vitreous body;
- thinning of the sclera;
- deformation of the eyeball;
- astigmatism;
- secondary glaucoma;
- retinal detachment;
- corneal clouding;
- endophthalmitis;
- panophthalmitis.
According to medical statistics, 14% of patients have severe vision deterioration in the first year of illness. Approximately 30% of patients notice a decrease in visual function within 3 years after inflammation. 50% of patients diagnosed with necrotizing scleritis die within 10 years. Death occurs mainly from a heart attack.
The outcome depends on the form of the pathology and when treatment is started. An unfavorable prognosis is not often made. It is only important to identify the disease in time.
Cloudy eye in a cat: signs
If a cat's eye is cloudy, then at first glance he appears to be blind. However, this is not always the case. There is only one sign of cloudy eyes in an animal – a white veil.
A cat's eye can become cloudy for a variety of reasons.
But over time, other symptoms may appear, for example:
- Blepharospasm and photophobia.
- Swelling of the conjunctiva.
- Irritability.
- Protrusion of the eye from the socket.
- Enlargement of the eyeball.
- Dilatation of blood vessels in the eye.
- The presence of purulent or mucous discharge from the eyes.
- Sleep disturbance.
- Loss of appetite.
You should not wait for signs of complications to appear, and if you notice clouding of the eye, you should immediately contact a veterinarian.
Glaucoma
Glaucoma is an eye disease in cats that develops against the background of increased intraocular pressure. The cornea loses transparency during an acute attack of the disease.
Optic nerve atrophy leads to complete blindness of the animal within 2-4 days after the attack. Therefore, the animal needs urgent veterinary care.
Symptoms of an acute attack of glaucoma:
- pain when touching the eye;
- photophobia;
- corneal edema;
- high intraocular pressure.
Treatment for an acute attack of glaucoma involves urgently reducing the pressure inside the eye. Manipulations must be carried out by a veterinary specialist with monitoring of the animal’s condition.
Further treatment consists of the use of drugs that reduce intraocular pressure, diuretics and agents that help stabilize the cat's condition.
Most common reasons
Often changes in eye condition are observed due to the development of cataracts, glaucoma, and corneal damage. It is worth considering each of these conditions separately.
Cataract
At the initial stage, changes occur deep in the organ. There is clouding of the pupil. One or two eyes may be affected. With further development of the pathological process, the lens loses its transparency and becomes white.
This happens for the following reasons:
- injury;
- past infectious diseases;
- inflammatory processes;
- metabolic disorders in older animals.
Sometimes congenital cataracts are observed.
Glaucoma
As intraocular pressure increases, the eyeball increases in size. There is loss of vision.
The following symptoms are observed:
- the cornea becomes cloudy, acquires a white tint, and loses sensitivity;
- the pupil dilates;
- the animal suffers from problems with coordination of movements.
The cat bumps into various objects not because of vestibular disorders, but because of blindness. As the disease progresses, the mucous membranes harden.
Glaucoma can be congenital and acute. Among the reasons for its development are lens dislocation, a complication of keratitis.
Corneal lesion
The color deep within the organ remains unchanged. The surface of the eye becomes cloudy. Pathological changes are caused by inflammation of the corneal tissue due to injury or infection.
The disease is called keratitis. Often, as it develops, a dense film of gray, white or pink color appears.
With metabolic disorders and the development of infections, excessive accumulation of lipids is observed in the cornea. Associated symptoms appear, characteristic of specific pathologies.
Cloudiness is sometimes caused by swelling of the cornea. Such problems occur with premature tissue degradation.
When acids and other aggressive substances penetrate the mucous membranes, corneal ulcers appear and clouding develops.
Eye pathologies
The main pathologies of the eye that cause clouding of the lens or cornea. Of these, the following should be highlighted:
Keratitis
or the occurrence of inflammatory processes in the corneal tissues. In this case, the eye becomes cloudy only on the outside, while no dangerous changes occur inside. But why do inflammatory processes occur? Inflammation often occurs due to injury or infection in the visual organ. The described disorders are often the cause of the development of a disease such as keratitis. Any form of this disease causes significant harm to the health of the pet. This can be explained by the fact that the inflammatory process in the cornea in most cases leads to its death.
Glaucoma
With this disease, intraocular pressure increases, as a result of which the organ of visual perception increases in size. At the same time, the ability to see clearly is lost. If such a disease occurs, you can observe poor coordination of movements in the cat and dilated pupils. As for the cornea of the eye, it completely whitens and becomes less sensitive. Due to the sudden loss of vision, the animal runs the risk of bumping into various objects, which can lead to additional damage. The risk of negative consequences increases if the second eye is also infected. Due to such a serious illness, the tissues of the sensory organ harden, and the eye lens dislocates. It is also worth noting that in some cases this pathology is congenital and often occurs in an acute form.
Cataract
As this disease progresses, predominantly the central part of the eye, in the area of the pupil, becomes cloudy. One or both eyes can become infected with cataracts. As the disease progresses, the lens becomes less transparent, almost white. The disease can occur due to infection, as well as as a result of traumatic exposure or an inflammatory process.
Conjunctivitis
It is characterized by copious transparent discharge from the eyes, which in the most severe stages can become purulent. At the same time, the pet’s general health worsens, body temperature rises, redness and swelling of the eye occurs, and the pupil area often becomes cloudy. If eye pathologies occur, you must immediately contact a veterinarian with many years of experience. Based on the tests, it will help to correctly determine the severity of the disease and prescribe the necessary treatment to prevent negative consequences.
We recommend the article: What causes red spots in a cat's ears?
Common causes of cloudy eyes in cats
The most common causes of cloudy eyes are glaucoma, cataracts or keratitis. These problems are increasingly being identified in cats of different breeds and ages.
Glaucoma
When a cat has glaucoma, the intraocular pressure increases, the size of the eyes changes, and vision begins to disappear.
The cat owner may also notice the following changes:
- the pupil is dilated;
- the cornea is almost white;
- coordination is impaired.
But the cat mostly bumps into surrounding objects only because it doesn’t see well. Moreover, the disease can affect both eyes at once. The cause of glaucoma, which can be congenital or acute, can be a severe form of keratitis or lens luxation.
Cataract
A cataract is a clouding of the eye that begins at the pupil. The lens may completely lose its transparency. The disease can be caused by an inflammatory disease of the eye, trauma, or a previous infection. Most often, this problem occurs in older cats due to metabolic disorders.
Cloudiness of the eye can occur due to cataracts.
Corneal lesions (keratitis)
In this case, clouding of the surface of the eye is observed. It can begin to grow from any area of the eye, resembling the gradual stretching of a dense film. Keratitis in cats occurs due to an inflammatory process in the tissues of the cornea, or due to an infection in the eye. It is not uncommon for the eye to become cloudy after an injury. In any form, keratitis is a serious problem.
Keratitis is also a consequence of age-related disorders, untreated conjunctivitis, and the formation of ulcers on the corneas.
Signs by which you can determine clouding of the lens of the eye
Visually, at the first stage of cataract development, it is impossible to notice changes in your pet. This is due to the fact that the deterioration of visual function is compensated by well-developed hearing and sense of smell. Therefore, the symptoms of the disease are noticeable when the surface of the lens is already severely damaged.
Symptoms that may indicate the development of cataracts in an animal:
- the appearance of a small cloudy spot or film on the surface of the eye;
- the cat ceases to navigate indoors (especially in the unknown);
- the animal moves poorly;
- constantly bumps into furniture and objects;
- He practically doesn’t play because he doesn’t orient himself in space.
Diagnostics
To choose the right treatment, it is necessary to make an accurate diagnosis. To do this, the following diagnostic measures are carried out:
- Schirmer's test. During the procedure, special paper is used. It is applied to the corner of the organ and the degree of wetting is observed. In this way, it is possible to determine the level of tear fluid.
- Use of ultraviolet lamps. The technique makes it possible to identify erosions and ulcers.
- Tonometry. By measuring intraocular pressure, it is possible to detect glaucoma already at the initial stage of development.
- Complete serological blood test. The study is carried out to identify infections.
- Activities aimed at identifying leukemia, toxoplasmosis, infectious peritonitis, immunodeficiency.
Additionally, the following studies are performed:
- corneal scraping;
- serology;
- Ultrasound;
- vitreous sample;
- tests to determine sensitivity to medications;
- detection of herpesvirus;
- electroretinography.
Causes of clouding and damage to the lens
The pupil of the eye itself does not lose transparency, since it is a hole in the iris. The transparent biolens of the organ of vision, called the lens, becomes cloudy. It is located behind the pupil.
The main cause of clouding is considered to be cataracts. This pathology manifests itself for several reasons:
- changes in metabolism associated with the age of the animal (old individuals);
- endocrine diseases - lipid metabolism disorders, diabetes mellitus;
- pupil injuries;
- infectious pathologies in a pregnant individual can cause pathology of the eye lens in a kitten;
- Certain breeds of cats have a genetic predisposition to this disease: Persians, Burmese, Siamese.
Treatment of cataracts, carried out with the help of medications, can only temporarily slow down the development of the disease.
Corneal erosions and ulcers
These corneal defects of varying depths can occur due to mechanical, chemical and thermal injuries, chlamydia, inflammatory pathologies of the eye, glaucoma and other pathologies. The eye acquires characteristic features:
- redness of the cornea of the eye;
- photophobia;
- corneal clouding.
Treatment consists of eliminating the underlying cause of the disease and symptomatic local therapy. Complex treatment includes antibacterial, corneoprotective and immunostimulating drugs.
Therapy methods
Treatment at home is carried out as prescribed by a veterinarian.
For infectious pathologies, antibiotics are used, and antibacterial agents can be used.
Identified corneal ulcers and glaucoma require surgical intervention. Often, for glaucoma, complete removal of the eye is performed.
Excision of corneal ulcers is a less painful procedure. During this procedure, only the affected tissue is removed. After the procedure, scars remain that prevent full restoration of vision.
Therapy is carried out using non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. The drugs have an impressive list of contraindications and, with prolonged treatment, can negatively affect the general condition of the animal .
For any pathologies, it is recommended for the cat to drip antiseptic drugs and apply medicinal ointments. At the same time, the affected organ is moisturized.
With timely treatment, it is possible to prevent the penetration of pathogenic microorganisms.
The cat needs to create comfortable conditions. He needs rest and diet.
Sometimes complex therapy is used:
- use of Gamavit and Tetracycline ointment;
- washing the organ with Metrogyl solution;
- use of drugs containing Actovegin;
- prescription of antiviral drugs.
Traditional methods of treatment
Traditional medicine should be used carefully. It is advisable to consult a veterinarian before starting therapy.
The following remedies will help alleviate your pet's condition:
- Tea. 1 tbsp is poured into a glass. dry tea leaves, pour boiling water. Use after completely cooled.
- Elder. To prepare the medicine, 1 tsp. elderberries are poured with boiling water (0.5 cups). Let the liquid infuse for about an hour and filter.
- Celandine. Five leaves pour 2 tbsp. boiling water The liquid is infused for half an hour, then filtered.
- Calendula: 2 tbsp. raw materials are poured with a glass of boiling water, left for a quarter of an hour, filtered.
- Aloe. Three leaves are crushed in a blender, the juice is filtered using gauze.
Medicines are used as follows:
- moisten a cotton pad in the liquid and move it from the outer corner to the inner one;
- change the cotton pad after each wipe;
- both eyelids are treated.
Scar (thorn) of the cornea
A scar or cataract of the cornea causes it to become cloudy after injury, burns or ulcers. There are several types of pathology:
- peripheral cataract, it is located away from the pupil and does not have a significant harmful effect on vision;
- a total cataract that covers the pupil and cornea. Vision deteriorates significantly;
- central thorn. It is located on the pupil, covering it partially or completely. The field of view becomes limited.
INTERESTING TO KNOW: Deworming cats at home
Partial or complete restoration of the cornea in this pathology is possible only with timely professional treatment.
Prevention
Preventing cloudy eyes in a cat consists of following a few simple rules for keeping the animal:
- timely vaccination against infectious diseases;
- regular examinations of the animal and timely contact with a specialist at the slightest inflammation of the pet’s eyes;
- if you suspect clouding of the eyes, urgently contact a veterinary ophthalmologist.
It should be remembered that any eye disease can lead to vision loss in a cat. Therefore, you should not ignore even the slightest eye inflammation in a cat and promptly contact a veterinary clinic.
Keratitis
With this disease, vision always deteriorates or is completely lost. Keratitis is a consequence of toxic liver damage due to poisoning and intoxication, acute infectious eye diseases caused by bacteria, viruses, fungi, or neurogenic pathologies.
To prevent your cat from going completely blind, immediate professional help is required.
The first symptoms of keratitis are redness of the eye and the presence of serous or purulent discharge. After some time, the cat’s eye becomes cloudy and the cornea loses its transparency. With prolonged development of the pathology, ulcers and necrosis of the cornea develop.
To select adequate treatment, reliable diagnosis is necessary. It is carried out using a special fluorescent liquid. In the light, damage to the cornea becomes visible. Diagnosis is carried out in a veterinary clinic.
Self-treatment is strictly contraindicated, since keratitis is a polyetiological disease, and without a clearly established cause, treatment can cause additional harm.
The prescribed treatment after diagnosis should be aimed at combating the consequences of the identified eye infection and maintaining the animal’s immune status.
INTERESTING TO KNOW: Plasmacytic pododermatitis of cats
Antiseptic solutions for washing the eyes, antibacterial or antiviral drops and ointments are required. A complete diet with sufficient vitamins and microelements is also necessary.
Treatment
First of all, it is worth noting that everything depends on the nature of the identified disease. In some cases, surgery may be required.
You need to remember the following:
- If the cloudy eye appears as a result of an infectious disease, then the pet will need treatment with antibiotics that have a wide spectrum of action. Antibacterial agents can also help, and their dosage should be much higher. Only an experienced veterinarian can give accurate recommendations;
- If there are corneal ulcers or glaucoma develops, then surgical intervention will be required. Therefore, you should not delay treatment with medications. This is explained by the fact that in the case of surgery, complete removal of the eye may be required (in case of developing glaucoma). Corneal ulcers are eliminated less problematically, and only damaged tissue is excised. You should be prepared for the fact that after surgery, scars often remain, which makes it almost impossible to fully restore vision. However, the pet will still be able to see and distinguish objects;
- In some cases, the veterinarian may prescribe non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs. They should be used only as prescribed by a doctor, since such medications have a number of contraindications. Over a long period of use, they can even have a negative effect on the animal’s body;
- For almost any type of disease, the veterinarian will prescribe antiseptic eye drops, which should be applied to the conjunctival cavity. You can also add various ointments (tetracycline, gamavit, etc.). This will help moisturize the damaged organ and protect against the penetration of various microbes into the eye, which will prevent the occurrence of pathogenic microflora;
- Metrogyl solution can have an effective effect. They should rinse the cat's eye to relieve symptoms of diseases;
- The use of medications based on Actovegin;
- Use of antiviral drugs. In addition to medications and procedures, you should also provide your pet with comfortable living conditions. The animal requires complete rest and a special diet (food must contain vitamins A and E). Vitamins will allow you to restore damaged areas of the eye in a shorter period and even restore vision. However, pet treatment must be comprehensive. Otherwise, when using any one method, it is unlikely that it will be possible to see an improvement in the animal’s condition.
Popular What can cause a cat to develop a rash on its stomach?
Clinical manifestations of eye injuries
With traumatic injuries to the eyeballs, sharp pain, automatic spasm of the eyelids, lacrimation and photophobia occur.
Small foreign bodies, lingering in the cavity of the conjunctiva, cause a feeling of pain and acute burning, aggravated by blinking, with profuse lacrimation.
With contusions (bruises) of the eyes and injuries from blunt objects of a non-penetrating nature, the manifestations can be different - hemorrhages in the eye, ruptures of the choroid and retina, retinal detachment, traumatic cataracts.
The most dangerous are penetrating injuries, when a foreign body can remain in the anterior chamber, vitreous body, lens or membranes of the eye. In this case, severe pain occurs, vision deteriorates sharply against the background of severe lacrimation and photophobia. Penetrating injuries can lead to complete destruction of the eyeball and loss of vision.
Injury or bruising of the muscles and bones surrounding the eyes often leads to eye damage. Moreover, such injuries can lead to the most serious and irreversible complications - compression, rupture or separation of the optic nerve from the eyeball.
Almost always, with traumatic eye defects, the eyelids are also damaged.
Most often, injuries manifest as swelling and bruising, but more serious injuries can occur if injured by sharp objects.
Diagnosis and treatment
An ophthalmologist can assess the severity of the injury and the possibility of preserving vision. Using an ophthalmoscopic examination and auxiliary diagnostic methods: ultrasound, radiography, the doctor will determine the depth and nature of eye damage, the degree of damage to the optic nerve. Depending on the type and severity of the injury, treatment is carried out in an ophthalmological hospital.
Eye restoration methods
Unfortunately, in some cases, eye injuries lead to the need for surgical enucleation - removal of the eyeball. Extensive wounds and burns can also cause loss of an eye and be accompanied by a defect in the soft tissues and orbit. Modern methods of eye restoration using anaplastology make it possible to completely close the defect of the eye and orbit using silicone prostheses. At the same time, the ectoprosthetic eye looks very realistic and allows patients to lead a socially active life and not experience an inferiority complex. The cost of an orbital ectoprosthesis is determined in each specific case and depends on the size of the prosthesis, methods of fastening, the amount of material used, etc. On average, the price of an orbital ectoprosthesis in European countries ranges from 1,700 to 2,000 euros. In the ProtezStudio laboratory, with world-class quality standards, prices for an ectoprosthetic eye are developed for a specific patient and are significantly lower than the European average.
Care and maintenance
Treatment for your cat requires both professional veterinary care and home care. The above studies will help keep your pet healthy. If you put off visiting the veterinarian if your pet's eye is cloudy, this can lead to vision loss in the shortest possible time.
- Examine your eye at least twice a day. Signs that may indicate that your pet's eye condition is deteriorating include inflammation, enlargement of the eye, discharge from the eye, pain (usually causing the pet to squint), or loss of vision.
- If your cat's vision is impaired, you need to minimize stress and risk of injury and place your pet in a safe place until the cause is determined.
- Don't let your pet touch the eye. If necessary, use a special collar (Elizabethan collar)
- Do not instill medications for animals intended for treating humans (“Vizin” or other medications intended to “reduce redness of the eye,” “dry eye,” etc.)
- Follow your veterinarian's recommendations and contact your veterinarian if you have any problems.
Preventive procedures
- Keep in mind that if a cat already has inflammatory processes in the eyes, the animal must be carefully monitored. Examine your pet at least 2 times a day. If you notice a sudden appearance of redness in the mucous membrane of the eye, go to the vet immediately.
- This is direct evidence of an inflammatory response. In addition, an increase in the volume of discharge may be observed. The animal may experience pain and deterioration in visual acuity. Do not hesitate under any circumstances. Things could get much worse.
- To prevent this from happening, it is necessary on your part to reduce all stress factors to a minimum. It is precisely such circumstances that can provoke a deterioration in the animal’s condition. Keep in mind that if your pet’s eyesight is severely damaged, furniture and chairs should be removed from the room where the cat is located. The problem is that the animal can get hit and get hurt.
If you see cloudy eyes in an animal, you should not treat it yourself. Don't wait, hoping that everything will pass. Call a veterinarian to your home immediately. The faster you react, the greater the chance of saving the animal’s vision.
External signs of the disease
The loss of the third eyelid is evidenced not only by the appearance of a white film on the eyes.
Signs of the disease can also be changes in the behavior of the animal, which:
- hides from bright light;
- rubs his face and eyes with his paws;
- blinks and squints frequently.
Sometimes you can notice profuse lacrimation, redness of the mucous membrane and the formation of pus. If the animal is not given timely assistance, there is a risk of vision loss.
A cat's eyes may also become covered with a white film due to age-related changes. This is typical for older animals. This phenomenon is not life-threatening for the pet, but in order to exclude pathology, it is recommended to show the animal to a veterinarian.