What will you learn from the article?
- Causes of papillomas in cats
- Symptoms of warts in cats
- Diagnosis of papillomas in cats
- Treatment of papillomas in cats Treatment of papillomas with novocaine
- Folk remedies for treating warts in cats
Papillomas, or warts in cats, are benign skin formations similar to cauliflower inflorescences that are found not only in humans. These new growths can be different in shape, and the size ranges from the size of a millet grain to a pea or more. The color of warts can also vary, from flesh-colored to gray or yellowish. The tumor may have a small stalk or, conversely, fit tightly to the animal’s body.
Papillomas in cats are found in the ears, paws, head, neck, as well as on the mucous membranes of the mouth, eyelids and lips.
Causes of papillomas in cats
It is believed that the formation of warts is caused by the papilloma virus. Cats can contract this virus during periods of weakened immunity, for example, after a long illness, use of medications, or after giving birth. Also, kittens are especially susceptible to the papilloma virus due to immature immunity and older cats due to weakened body defenses. To become infected with the virus, contact with an animal carrying the papilloma virus is necessary.
I would like to note that the feline papillomavirus is not dangerous to human health. Just like a person with the papilloma virus is not dangerous for an animal.
Diagnostics
The diagnosis is made comprehensively based on clinical signs, analysis of medical history and laboratory diagnostic methods. If you find a wart in a cat, it is very important not to self-medicate and immediately contact a veterinary clinic: any seemingly harmless skin tumor can turn out to be a fast-growing malignant tumor (for example, mastocytoma). In the presence of a malignant tumor, the start of treatment plays an important role in the prognosis of the disease and the life expectancy of the pet.
Source - otvet.mail.ru
For a preliminary diagnosis, routine diagnostic methods can be performed - blood tests, cytology from the affected area (a so-called fine-needle biopsy is performed). But to confirm the diagnosis, a full biopsy is necessary: for this analysis, a piece of the formation is taken (or the entire wart, if it is small) and submitted to the laboratory for histology. To identify papillomavirus, it is necessary to perform histology with immunohistochemical staining of the material.
Source - otvet.mail.ru
Also, the PCR diagnostic method is currently used to detect the papillomatosis virus in a cat and to determine the type of virus. However, it is worth noting that this test can show a positive result in a clinically healthy cat, which can be explained by the carriage of the virus and the pet’s strong immunity.
In any case, if you notice a mole on a cat, be sure to show it to a veterinarian!
Symptoms of warts in cats
Warts can appear on a cat's body 1-2 months after infection with the papilloma virus.
- decreased appetite;
- lethargy;
- the appearance on the body of an animal of formations of different sizes, either a single appearance or a group of interconnected tumors;
- Some warts can cause itching and discomfort for your pet, and small bleeding wounds appear as a result of scratching.
Provoking factors
The following factors can trigger the activation of the virus:
- chronic illness;
- pregnancy and feeding of kittens;
- long-term use of medications;
- stress;
- avitaminosis;
- hypothermia;
- advanced age of the animal.
Small kittens often suffer from papillomatosis. Their immunity is still poorly developed.
It is important to remember that if papillomavirus has entered an animal’s body, it remains in the cells forever. Treatment can only reduce its pathogenicity and lead to the disappearance of external manifestations of papillomatosis. After therapy, the virus will be in a “dormant” state. It can be reactivated at any time as soon as the animal’s immunity decreases.
Treatment of papillomas in cats
Attention, the author of the article is not responsible for self-medicating your pet for warts with medications or folk remedies. All information below is provided for informational purposes only.
To stimulate the body's immune defense, immunostimulants (Gamavit, Canina Immunoprotect, Maksidin, Roncoleukin) and vitamin complexes are used.
If the wart itches and the cat scratches it, then to prevent infection the neoplasm is treated with antiseptic ointments or solutions, for example, alcohol iodine solution, chlorhexidine, decasan, hydrogen peroxide, betadine ointment, pantestine, etc.
It should be noted that treating mucous membranes with the above drugs without a doctor’s prescription is contraindicated!
Drug therapy
To eliminate cutaneous horn in cats, the necessary treatment is selected only after conducting research, studying tests, and establishing the cause of the pathology.
In some cases, when there is no need for surgical intervention, it is permissible to treat your pet at home. You can treat yourself using medications that are prescribed by a veterinarian. For a certain form of the disease, the most suitable drugs are used.
When the disease is viral in nature, various immunomodulators are used. Such drugs include Aldara cream. When the cream comes into contact with the skin, the substances included in its composition stimulate the body’s immune response and increase the production of interferon.
Rules for using the drug:
- it is applied directly to the affected area, rubbed until completely absorbed;
- treatment is carried out no more than 3 times a week, every other day;
- It is necessary to ensure that the cat does not lick the medicine.
The product "Acitretin" is classified as dermatotropic and has the following properties:
- stimulates tissue regeneration;
- promotes the resorption of scars;
- normalizes the processes of skin keratinization;
The drug must be used strictly under the supervision of a veterinarian, since its mechanism of action remains unknown.
You should know that such remedies only eliminate skin keratinization, affecting only the symptoms of the disease, but not its cause.
To act directly on the causative agents of skin infections, antibiotics should be used. Azithromycin is an antimicrobial drug that is effective against a wide variety of microorganisms. They are usually treated with antibiotics for 10 to 14 days.
Are there other causes of warts?
There is an assumption that in some cases viruses may not be related to the wart that appears in a cat. In particular, in old animals with a severely weakened immune system that can no longer perform its functions normally, tumors of a different nature may appear. In some cases, they are initially malignant in nature. In addition, it may be due to some autoimmune diseases that are inherited. This version is indirectly confirmed by experienced breeders: if the parent animals had papillomas, then their descendants will have them with a very high degree of probability.
Symptoms and types of papillomas
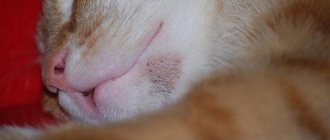
What do papillomas look like in cats? Warts are growths on the skin. They can fit tightly to the epidermis or rest on a stalk. The color of the growths can vary from flesh-colored to yellow or dark brown. The size of warts can range from 4 mm to 1 cm. In severe cases, papillomas merge and form growths similar to a head of cauliflower. A photo of papilloma in a cat can be seen below.
This viral infection is accompanied not only by the appearance of warts. Other signs of the disease are also noted:
- loss of appetite;
- lethargy, apathy;
- skin itching in the area of the rash;
- ulcers at the site of torn warts.
A general deterioration in health occurs more often in small kittens. Papillomatosis can be difficult for pups to tolerate.
Rashes can be localized in different areas of the skin and mucous membranes. Papilloma on the ear in cats most often occurs due to tick-borne infestation - otodectosis. In this case, the appearance of warts is accompanied by severe inflammation and itching in the ear. This combined disease requires persistent and long-term treatment.
Papilloma in a cat's nose can cause pain. After all, the animal’s nostrils are very sensitive. A large wart in the nasal passage can significantly complicate breathing.
Pathogenesis of papillomatosis
The mammalian epithelium is designed in such a way that the skin cells at the surface are highly differentiated, but at the same time multiply slowly. In the depths of the skin layer, on the contrary, cells quickly divide, but are poorly specialized. As the cell moves upward, it loses the ability to divide, but it differentiates.
The peculiarity of the papillomavirus is that it can only infect the lower basal undifferentiated cells. Then, together with the affected cell, it enters the periphery, where it begins to produce offspring. The degenerated cells become rounded and begin to produce daughter virions.
In a cell, the virus exists in 2 variants:
- Episomal. That is, in the nucleus of the cell, but outside the chromosomes
- Introsomal. When the virion integrates into the cell genome.
Cells infected with papillomavirus form epithelial neoplasms that are superior in size and layering. At the same time, cells transformed by viral proteins, despite differentiation, continue to divide. In addition, they accelerate metabolism, especially glycolysis, and there is no reaction to serum growth suppression factors.
The prognosis of the pathology is favorable. Often there is no need to resort to treatment, as the disease goes away on its own.
Traditional methods
Is it possible to treat papilloma in cats at home? You should not rely completely on folk remedies. After all, papillomatosis is a viral infection, and it is impossible to do without drug therapy. Folk remedies can be used only after consulting a specialist. They are used only in combination with veterinary drugs and sometimes with surgical treatment.
For small papillomas, the following remedies are effective:
- Iodine. This antiseptic should be applied to a cotton swab and cauterized the stem of the wart.
- Rowan. Ripe fruits are crushed to a paste and applied to papillomas twice a day.
- Celandine. You need to squeeze the juice out of the plant and treat the new growths with it.
- Acetic acid. The product is applied to a cotton swab and the papilloma is cauterized.
- Garlic. You need to squeeze the liquid out of the garlic clove and lubricate the wart.
Folk remedies are effective only for single tumors. If papillomas affect large areas of the skin, then only drug and surgical treatment can help.
Possible complications
As already mentioned, warts in animals can lead to serious consequences. Papillomatosis is often accompanied by itching. Animals scratch the affected areas and tear off tumors. Bleeding ulcers appear on the skin. This can lead to malignant cell degeneration and skin cancer.
Oncological diseases are the most dangerous, but far from the only complication of papillomatosis. When large warts are injured, severe bleeding may occur, leading to anemia. Also, sores and scratches can become infected and fester.