The mustachioed pets captivated the ancient Egyptians with their grace and majesty, so they were revered for a long time on a par with the gods. But even now, people continue to clean out cat litter boxes and feed their pets at 6 am if they refuse to eat alone. In addition to love, the level of responsibility also increases.
The modern owner knows much more about the body of his cat than the inhabitants of Ancient Egypt, but is constantly learning something new. And this is not surprising! Some facts about anatomy are not only useful, but also so stunning that they are definitely worth sharing with your friends.
Skeleton and its parts
What a cat's body consists of can be found out through anatomy - a branch of biology that studies the structure of the body. First, you should get acquainted with the frame that holds all the important organs, that is, with the skeleton.
There are about 40 more bones in the cat skeleton than in the human skeleton, amounting to 244-250 pieces. The exact number depends on the length of the tail.
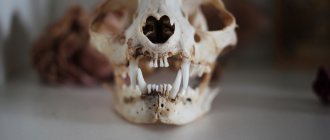
Skull and teeth
The cat's skull has 24 bones. 13 of them are on the facial part, and 11 are on the cranial part. Compared to other mammals, a cat's head is quite small in relation to its body, but it has a well-developed brain inside its skull.
The strong jaws of mustachioed pets have 30 sharp teeth. A smaller number (26) is typical only for kittens. By 7-8 months, their milk teeth are replaced by molars, and the dentition is replenished with missing molars.
Spine and tail
A cat's flexibility is due to the amazing mobility of its vertebrae. They can all be divided into 5 departments:
- cervical, consisting of the most massive bones;
- thoracic, to which 8 pairs of ribs are attached;
- lumbar, surrounded by muscles that hold the contents of the abdominal cavity;
- sacral, consisting of 3 fused vertebrae;
- caudal, including from 12 to 28 vertebrae.
Thanks to the massiveness of the cervical vertebrae, the animal can easily turn its head almost 180°, and thanks to its underdeveloped collarbones, it can easily penetrate the narrowest crevices.
The tail plays a special role. With its help, the cat maintains balance while jumping or falling from a height.
Four paws, and there are scratches on them
A cat's paw bones are not directly attached to the skeleton. They are held in place by muscles and tendons.
The hind limbs differ from the front limbs in being longer and having fewer fingers. There are as many of them in front as there are in humans, and in the back there are only 4.
Each of the fingers is equipped with a sharp claw. In a calm state, the claws are retracted into a special pouch, but when you press on the pad, they can be returned back. This is very convenient when trimming overgrown claws.
Due to the unusual location of the knee (right under the belly), cats always walk on tiptoe. This bizarre method of transportation is not only silent, but also very safe. When jumping, the paws absorb all the energy expended, so landing from a great height is soft and quiet.
History taking
Before diagnosing diseases in cats, a medical history is taken. It involves studying several factors.
Age and breed
In kittens up to one year old, itching and rashes all over the body can be caused by dermatophytosis or skin parasites. Adults under 4 years of age are most susceptible to allergies. And in older cats, sores are often associated with skin tumors.
Some cat breeds are predisposed to skin diseases. In Sphynxes these are allergies, in Persians - idiopathic dermatitis and dermatophytosis.
Lifestyle
Keeping a large number of cats, visiting exhibitions, access to the outdoors - these and other factors increase the risk of infection with skin parasites, fungal, viral diseases and other cat diseases.
Seasonality
Allergies to plants and pollen, tick and mosquito bites - these causes of itching and sores are seasonal.
Cat anatomy: structure of internal organs
The anatomical structure of a cat is close to humans and other mammals. Despite this, each animal has its own characteristics that distinguish it from other species.
Heart, blood and vessels
The heart is responsible for saturating cells with oxygen. This important muscle consists of 4 sections: 2 atria and 2 ventricles. On average, the heart rate is 130-140 beats per minute.
Calculating your pet's pulse is quite simple. To do this, you need to find the artery on the inside of the thigh.
The circulatory system includes 3 types of vessels:
- arteries saturated with oxygen;
- veins that carry carbon dioxide;
- capillaries that regulate metabolism and deliver blood directly to the organs.
The composition of any blood includes plasma and blood cells (platelets, erythrocytes, leukocytes). The uniqueness of cat blood lies in the fact that it is divided into only 3 groups: A, B and AB. They are taken into account when diluting and transfusing, since not all of them are compatible with each other.
The nervous system and its “ruler” – the brain
The nervous system regulates the animal's behavior. It consists of 2 departments:
- Central
. Includes the brain stem, spinal cord and brain. Responsible for reflexes (breathing, swallowing) that arise as a result of reactions to internal and external stimuli.
- Peripheral
. Includes cranial and spinal nerves. Connects the central nervous system with the organs of the body and is responsible for conducting nerve impulses. Thanks to the work of this department, conscious actions are carried out: releasing claws, licking and moving in space.
Each part of the brain performs a specific function. The occipital lobe is responsible for vision and touch, the olfactory bulb is responsible for smell perception, and the temporal lobe is responsible for memory.
The gastrointestinal tract is the main system, according to the cats themselves
The digestion process begins immediately after swallowing food. In the mouth, pieces of eaten food are softened by saliva and teeth. This makes it easier for them to pass through the pharynx and esophagus.
The environment in a cat's stomach is more acidic than a human's, so it easily processes the coarse fibers of raw meat. Problems arise only with carbohydrates, so your furry pet’s diet should not contain a lot of cereals.
Products broken down into water, proteins, fats and carbohydrates move to the duodenum and small intestine. Some of the nutrients are absorbed into their walls, and unprocessed residues are compacted into the feces and exited through the rectum.
Breathe and purr
The cat's body is supplied with oxygen through the respiratory system. It includes:
- nasal cavity, which cleans the inhaled air of dust and bacteria;
- pharynx, which provides additional filtration, warming and humidification of the air;
- the larynx, which regulates the volume of incoming oxygen and protects the trachea from food ingress;
- trachea - a special tube that regulates the flow of oxygen and the removal of carbon dioxide;
- the lungs are the main respiratory organ responsible for the process of gas exchange;
- the diaphragm, which controls the process of contraction and expansion of the lungs.
Whiskered pets breathe more frequently than humans and dogs. At rest, they take 20-30 breaths per minute.
In addition to the respiratory function, the larynx is responsible for the production of sounds. Thanks to her, animals meow.
With purring everything is more complicated. The mechanism of its appearance is explained by several theories, but most scientists are inclined to vibration of the hyoid bones.
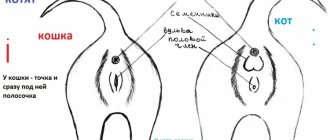
How is a cat different from a cat?
The internal structure of a cat and a female cat are largely the same, but their genitals are different from each other. The male reproductive system consists of:
- testes;
- vas deferens;
- prostate;
- scrotum;
- penis.
The testes are responsible for the production of testosterone and sperm maturation. Through the ducts, sperm enters the penis and exits, allowing you to conceive offspring. With age, its quality deteriorates, but only castration can stop its production.
Bearing kittens is carried out exclusively by females, whose reproductive system is represented by:
- bicornuate uterus;
- cervix;
- vagina;
- ovaries;
- fallopian tubes;
- vulva.
The ovaries are an analogue of the testes. They are responsible for the production of female hormones and the maturation of eggs. Fertilization is possible only during estrus, so the most effective way to protect against unwanted pregnancy is timely sterilization.
Cats also go to the toilet...
The cat's urinary system consists of 4 organs: the urethra, bladder, ureters and kidneys. Urine enters the urethra only after careful filtration in all other sections. At the exit, it becomes secondary, as it loses some of its impurities.
Cats go to the toilet 2-3 times a day. The color of their urine is light yellow, and any change in shade indicates pathology. Due to the narrow urethra, males often suffer from blockage of the urethra by hard formations. As a result of injury to the walls of the bladder, the shade of urine changes to bright orange, brown or red.
Endocrine system
The endocrine system is primarily responsible for hormones and their production in the corresponding organs. Thus, the cat’s brain produces antidiuretic hormone, oxytocin, corticotropic hormone, adrenocorticotropic hormone, cortisol and growth hormone.
The adrenal glands produce a lot of other hormones, the main purpose of which is to regulate metabolism, and are also responsible for behavioral characteristics. The adrenal glands also produce cortisol, a small portion of testosterone, as well as epinephrine and norepinephrine.
What shapes an animal's appearance
Having figured out what the cat’s skeleton and its internal organs are made of, you can consider the external features and sensory organs. Unlike dogs, the appearance of these cats is practically no different from their wild counterparts. Exceptions include only decorative species obtained artificially.
Strong muscles
A cat's body has 517 muscles, which is 133 less than a human's. Despite this, the muscular system is very elastic. That is why mustachioed pets easily curl up into a ball and take other bizarre poses, surprising their owners with their flexibility.
Cat muscles are divided into 2 types:
- striated
, regulating the mobility of body parts and controlled by the central part of the nervous system;
- smooth
, controlling the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract, respiratory system and all internal organs with the help of impulses received from the peripheral nervous system.
Each muscle consists of 3 sections. The first ones are responsible for jumping over long distances, the second ones for running short distances, and the third ones for soft and quiet sneaking up during the hunt.
Beautiful skin
The skin covers the entire body of the animal, protecting it from temperature changes, germs and injuries. It consists of 2 layers:
- epidermis
, formed as a result of cell death and keratinization;
- dermis
containing capillaries, sebaceous glands and hair follicles.
The constant desire to rub against a person and surrounding objects is explained by the release of a specific secretion with which the cat marks its territory. It is formed from the sebaceous glands on the face, between the fingers and in the anus area.
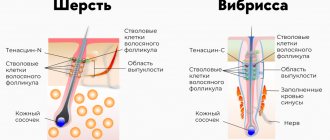
The coat consists of undercoat and guard hairs. Each hair is capable of reflecting light, giving the coat a beautiful shine. That is why the appearance of dullness is a symptom of internal pathologies.
Thanks to the erector muscle, the hairs of a mustachioed pet can stand on end. The characteristic stripe on the back and fluffy tail can be seen in moments of fright or extreme cold.
Whiskers, paws and tail like cat documents
Differences can be seen not only in animals of different sexes, but also in animals of different breeds. The British cat's body parts are not similar to the Siamese's body parts. In the first case, the pet will be more massive and densely built, and in the second, thin and graceful.
Belonging to a particular breed is determined by the shape of the ears, the shape of the eyes, the length of the tails and paws, as well as the color of the coat and even its presence. Only short-haired breeds are divided into 3 large groups: American, European and Oriental. But there are also long-haired and bald ones.
There is even a separate classification based on body type. Thanks to such diversity, you can easily choose a pet based on your preferences and capabilities.
Diagnostic methods
Identifying the exact cause of a cat’s sores is an important stage of treatment, since only a competent diagnosis will allow us to identify the source of the problem and prescribe adequate therapy:
- Combing the fur determines the presence of fleas, ticks and lice. Based on the results of the study, remedies are prescribed to get rid of parasites.
- Examination of earwax under a microscope reveals ear mites.
- Skin scraping. Used to detect fungus and ectoparasites if there are itchy sores.
- A Wood's lamp will help diagnose the presence of fungus.
- Cytological examination reveals secondary infections and allergic reactions.
- Trichogramma determines the presence of spores and parasites on a cat’s body.
- Fungal culture. A time-consuming but most effective method of identifying fungus.
- Elimination diet. Recommended for suspected food allergies.
Navigating in space
Finally, it is worth mentioning what a cat’s sense organs are made of. This includes not only the eyes, ears and nose, but also the tongue and whiskers.
The vision of a genius
Whiskered pets see perfectly in the dark, distinguish 3 colors (red, blue, green) and as many as 25 shades of gray. The mysterious glow of their huge eyes at night is explained by the tapetum - a special vascular layer located behind the retina.
Thanks to the convex cornea, the viewing angle of these animals is almost 270°, so with the help of their necks they are able to assess the situation at all 360°.
Whiskers
The tactile function is performed by vibrissae, that is, cat whiskers. In fact, they also belong to hairs, but their follicles lie much deeper than the guard coat and undercoat. They actively interact with nerve impulses, determining the surrounding temperature, perceiving signals of pain and pleasant touches.
These tactile hairs are found not only on the face, but also on the hind legs. Because of this, mustachioed pets actively shake them when they step in the mud or enter the water.
Pulling or cutting mustaches is strictly prohibited. In addition to acute pain, the animal may permanently lose its tactile function, which will affect orientation in space and mental health.
Nose-sniffer
The cat's nose contains 80 million olfactory receptors, so its sensitivity is 2 times higher than that of humans. Additionally, the Jacobson's organ, a small tube located on the upper palate, is responsible for the perception of odors.
Another interesting fact is that the imprint of a wet cat’s nose, like the pads of human fingers, is unique. Thanks to this, it can easily be classified as biometric data.
Ears-on-top
The developed hearing of furry pets even detects ultrasound. Its ears, consisting of an outer, middle and inner part, are responsible for this. The task of the first is to collect sound, the second is to transmit a sound signal, and the third is to convert sound vibrations into nerve impulses.
Thanks to this feature, animals moving to the dacha in the summer can easily find their way back during their walks. Having moved away 3 km, they perfectly hear the voices of their owners and other sounds associated with a country house.
Tongue - lover of food
Despite night vision, an excellent sense of smell and acute hearing, cats are inferior to us in some ways. The tongue has only 473 taste buds, while the human tongue has as many as 9,000.
Whiskered pets are good at distinguishing sour, salty and bitter foods, but almost unable to detect sweet ones. The love for ice cream is explained by its similarity to milk, familiar from childhood. For this reason, treats should be avoided as animals become lactose intolerant as adults.
Separately, it is worth noting 2 special receptors that are not typical for humans. One recognizes the taste of umami, that is, monosodium glutamate, and the second recognizes the taste of water. This is why cats often steal sausages and have a special love for unstagnant tap water.