Standards of behavior - what to expect from a cat after giving birth?
Strange behavior of a cat after giving birth may be due to simple mistakes of an inexperienced owner or too active maternal instinct. In both cases, the situation needs to be monitored and gently adjusted.
Most cats that have recently given birth show a restless state, but at the same time behave confidently and know exactly what to do. In the first few weeks, the cat desperately wants to control her offspring. The young mother is constantly with the kittens, licks them, purrs loudly and protects them from annoying attention.
For his part, the owner must show maximum loyalty, but control the development of the kittens. To reduce the anxiety of a young mother, the nest with kittens must be isolated in a separate room. Place a water bowl, feeder and cat litter box next to the nest.
Important! Unless necessary, kittens should not be touched more than once a day. In the first two weeks, to monitor growth, it is recommended to weigh and examine kittens once every 1-2 days.
Try to examine the kittens and change the bedding at the same time. Talk to the cat, calm it down, and with all your appearance make it clear that you do not pretend to be a guardian. The first instinct that guides a young mother is the desire for safety. The cat will make every effort to ensure that its offspring are hidden from annoying attention and are warm and comfortable.
Only by ensuring maximum comfort and safety will the mother cat be able to relax and unwind. It is for this reason that it is important to prepare the nest for kittens several weeks before giving birth. This will give the cat time to get used to the place and make sure it is safe.
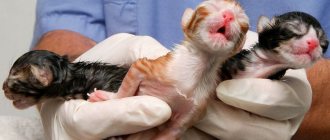
Immediately after the birth of a kitten, the cat pays maximum attention to removing mucus and fluid from the baby's respiratory tract. When the kitten starts to squeak, the cat pushes it towards the nipples. As soon as the kitten begins to suckle colostrum, the cat chews the umbilical cord and eats the afterbirth.
What to do if maternal instinct is violated?
If the cat was very exhausted from childbirth, or when the last one was frankly difficult and unsuccessful, your pet may simply not have the strength left to care for her offspring. In these cases, the role of “nanny” will have to be taken on by the owner himself.
We have already described above exactly how cats do this in natural conditions. Remember that you need to “imitate” maternal care as carefully as possible, without rushing.
So, the following is required of you:
- Gently remove the remaining membranes, wipe the kitten's nose and open the mouth, then slightly tilt the pet's head down and try to remove all the liquid and mucus from there.
- If the cat has not chewed off the umbilical cord either, measure about two centimeters from the kitten’s navel, tie the umbilical cord with silk thread, and then cut the “lace” (of course, over the knot you tied). The stump must be lubricated with alcohol tincture of iodine. Please note that you cannot simply cut the umbilical cord! We have already written that when a cat bites it, it simultaneously crushes the edges of the organ, thereby preventing the development of bleeding. If you simply cut the umbilical canal, your baby may bleed to death within minutes.
The most difficult thing is when the kitten is not breathing: perhaps he was born tail first and managed to drink in the amniotic fluid. If medical assistance is not provided immediately, the baby may die from suffocation. You can try to remove the liquid using the smallest baby syringe.
Experienced veterinarians advise using a urinary catheter connected to a regular syringe. In addition, you can massage the kitten’s throat, trying to induce a cough (if you’re lucky, the animal itself will spit out all the excess).
Rocking is another simple, but still quite effective method of resuscitation. To do this, place the kitten in your palm with its back facing down and squeeze its head (gently) between your thumb and index finger. After this, it is necessary to rock the baby for about five minutes, and at this time the hand should make movements like a rocking cradle. During motion sickness, fluids entering the respiratory tract will fluctuate and irritate the corresponding receptors. The latter stimulate coughing and, if the kitten is lucky, it will spit out all the excess.
Keep in mind that you shouldn’t pretend to be a centrifuge with your hand: you certainly won’t do anything better for the baby, but it’s quite possible to cause a hemorrhage in the cerebellum.
The cat is constantly hiding kittens
Many cats that have recently given birth behave very restlessly and constantly move their kittens from place to place. Owners become confused because they do not understand how to stop this process. A cat can carry kittens even if the nest was prepared in advance and the birth went well.
Dragging is explained by only one factor - the cat does not feel safe . If you are confident that you have provided maximum comfort for the young mother and her offspring, it is wiser to isolate the family in a separate room.
Note! Cats after their first birth are more prone to constantly dragging kittens around. Restless behavior is explained by hormonal changes in the body.
If you notice that your cat is constantly carrying kittens, this process needs to be monitored. Restless behavior is not a reason to endanger children. It happens that after the next move of the offspring, the cat forgets to move one of the kittens and it freezes. Also, against the background of increased anxiety, it is important to ensure that the cat does not have access to the street.
Moving kittens once after birth is a normal occurrence due to the desire to protect the offspring. After birth, traces of amniotic fluid and secretions remain on the litter, the smell of which can attract other animals. If this happens in the wild, the kittens will most likely die.
Prevention of complications
With the onset of the postpartum period, it is important to provide first aid to the animal in case of deviations from the norm or disturbances in the cat’s well-being. It is important to make sure that all babies have been born and to gently palpate the abdomen to diagnose a remaining placenta or an unborn kitten. It is necessary to pay attention to all the changes that occur with your pet, monitor the emotional state, body temperature, and the presence of discharge.
Note! You should not pick up kittens again. This causes stress for the mother.
Near the nest with kittens you need to place all the attributes necessary for a new mother - a toilet, a bowl of food, clean drinking water.
How to prevent pregnancy in a nursing cat
If the cat does not participate in breeding, and its offspring are not of particular financial interest to the owner, it is advisable to sterilize the animal. The best time for this is after 6 months - 1 year. Theoretically, it is possible to perform surgery on a nursing mother cat to prevent her from becoming pregnant again. If sterilization is undesirable, you can give your pet sedative medications based on medicinal herbs (such as “Cat Bayun”, “Fitex”). You also need to monitor your nursing cat, especially if she goes into heat soon after pregnancy. That is, it is necessary to exclude contacts between the female pet and cats.
You should not use alcohol tincture or valerian tablets as a natural sedative. This remedy for pets is a drug that puts them in a state of extreme excitement. That is, a cat who has started to heat, after a small amount of valerian solution or tablets, will have one goal - to quickly connect with the cat. The existing kittens will naturally go to the side.
Also, hormonal drugs that suppress sexual desire are also extremely undesirable for calming a nursing pet. Products of this type (“Sex barrier”, “Contrasex”, etc.) have a lot of contraindications, and they cannot be used by cats during lactation.
Vaginitis
A very common postpartum pathology. This is the name for inflammation of the vaginal tissue . The reasons are varied, but they are not particularly “cunning”: during childbirth, it often happens that the mucous membrane of the genital organs is damaged, as a result of which the likelihood of pathogenic and conditionally pathogenic microflora penetrating there sharply increases. This is almost always how cases of inept obstetric care end.
If you do not have the appropriate experience and knowledge, do not try to help your pet in labor (most likely, she does not need it). You are unlikely to be able to help, but you can do a lot of harm!
The clinical picture is not very specific, which is why vaginitis is often confused with endometritis. The cat becomes lethargic, does not want to take care of the kittens, and a large amount of exudate (often very odorous) is released from its external genitalia. In addition, upon external examination, swelling of the genital organs and pain when attempting to palpate them may be detected.
Therapy is also not particularly rich in options - broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed in loading doses. Preferably intravenously. Ringer's and glucose solutions are administered in the same way, as they help relieve intoxication (and in case of severe inflammation, it will certainly appear).
Reproductive health recovery time
During the entire period of gestation, during childbirth and during feeding, the body of the expectant mother undergoes serious changes that have a far unfavorable effect on her health. After lambing, many cats lose weight, shed rapidly, and suffer from various viral and infectious diseases due to decreased immunity. The thing is that during pregnancy, for the normal formation and development of fetuses, the body of the expectant mother loses many vital vitamins, minerals and other substances. Most of all calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus are lost. If a pregnant cat does not receive enough of these substances, after the birth of babies, the likelihood of developing dangerous degenerative and destructive diseases of the musculoskeletal system increases.
In addition, a cat’s estrus, the subsequent period of gestation and childbirth are accompanied by severe hormonal disturbances. When the rut begins and the cat asks for a cat, the body intensively produces estrogen, under the influence of which follicles grow rapidly and ovulation occurs. Immediately after conception, the hormone progesterone is produced, which is responsible for the normal course of pregnancy itself. A week before the birth itself, the hormone oxytocin increases sharply. It is under its influence that labor develops, and the mammary glands are prepared for feeding newborn babies. The entire period while the cat is feeding the kittens, prolactin is produced, which is responsible for milk production. All these processes lead to severe exhaustion and immunodeficiency.
For the body to recover, at least 12 months must pass after the last lambing. Therefore, if after 2-3 weeks the cat goes on a spree again, the owner is strictly forbidden to allow re-breeding.
Sections
In most cases, labor, childbirth and the period after it are not a threat to the mother.
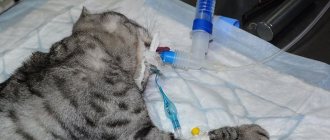
But not everything goes smoothly. During the postpartum period, sometimes dangerous situations arise that pose a danger to the cat's health. The mother rarely experiences vaginal bleeding. They stop spontaneously. In some cases this does not happen. Blood clotting tests may show abnormalities. The administration of oxytocin on the first day accelerates recovery of the uterus and separation of the placenta. The cat is sensitive to the drug 24-48 hours after birth. Therefore, oxytocin must be administered without delay.
Reasons to call a doctor after childbirth
Temperature below 36.5 ᵒС or above 40 ᵒС.
Purulent discharge with an unpleasant odor from the vagina.
Lethargy, depression and loss of appetite for 24 hours.
Shortness of breath, anxiety, tremors and tension.
Kittens scream too much.
Problem with lactation. Bloody and purulent discharge from the mammary glands. There is no milk, the glands are painful, hot, swollen.
Vomiting or diarrhea in the mother. Strong.
The pushing continues after all the babies are born.
Eclampsia
Eclampsia - postpartum hypocalcemia and tetany. The reason for this condition is low calcium levels. This syndrome is less common in cats than in dogs. Eclampsia often affects animals that have previously given birth to at least five kittens. The first birth is also a risk factor. Calcium deficiency is rarely observed in mothers with a small number of children. But that doesn't mean it doesn't happen.
The first symptoms of hypocalcemia are irritability and restlessness. As the disease progresses, coordination of movement is impaired, vomiting and muscle tremors appear. In serious cases, death can occur. Diagnosis is made based on complex characteristics. Sometimes hypoglycemia is added to hypocalcemia - a lack of glucose.
The causes of calcium deficiency have not been studied. Probably, most of it is spent on the formation of milk and the laying of bone tissue for future offspring. The reason may be poor absorption of calcium from food, which occurs due to loss of appetite. Treatment consists of administering the mineral intravenously. It is recommended that kittens be separated from their mother as soon as possible.
Taking calcium during pregnancy may increase the risk of developing eclampsia. Therefore, injections are not a panacea. If you use a nutritious diet and mineral supplements, calcium injections are not needed.
A pregnant mother should receive high-quality food. During lactation, the diet of a cat with a history of hypocalcemia should be supplemented with calcium supplements. They cannot be used during pregnancy.
Insufficient milk production
The pituitary gland produces prolactin, a hormone that stimulates the development of mammary glands during pregnancy. Thanks to it, lactation is supported. Prolactin acts together with oxytocin.
Some young or nervous cats produce insufficient milk or too late. Kittens should start feeding within the first two days of life. The hungry offspring constantly screams and sucks the mother to no avail. A cat who has given birth for the first time begins to carefully feed the kittens when they are brought to her for a long time.
Sucking stimulates lactation, so that milk may appear after it. If this does not happen, use oxytocin injections.
Sometimes cerucal or metoclopramide are used. These drugs stimulate the production of prolactin. They can be given orally or by injection every eight hours. Sometimes plant substances are included in food: dill, marshmallow, alfalfa, thistle and others. How safe this is is still unknown.
Mastitis
Bacterial infection of one or more mammary glands. They become hot and hard. Seals appear inside. The cat becomes depressed and refuses to feed the kittens. The causative agents of mastitis are streptococci and staphylococci.
The veterinarian prescribes a course of antibiotics. Milk and scrapings from the damaged area are taken for analysis. Hot compresses are applied to the affected area. If the treatment works, the kittens can be left with their mother to learn how to feed. Serious damage leads to the development of abscesses. Their treatment requires surgery. In such cases, the milk becomes toxic, and the kittens must be separated from the mother.
Metritis
Inflammation of the uterus with penetration of infection. Metritis is often confused with pyometra, a hormonal disease.
Injuries to the uterus and remaining fetal tissue lead to the development of this disease. Sick animals are depressed and vaginal discharge becomes an unusual color. Cats often stop paying attention to their offspring, so they should be separated from the female and bottle-fed. You can give it to another mother with enough milk.
Can a pet become pregnant while nursing?
Feeding offspring is not an obstacle to pregnancy in an animal.
Often a nursing cat begins to walk within a month after giving birth. Some owners believe that due to an excess of the hormone prolactin, ovulation does not occur, but this opinion is erroneous. Already from the first months after the cat was able to give birth, the eggs mature and the animal can go on a spree and become pregnant again without any problems. However, if there is no postpartum rehabilitation period, the next conception negatively affects the cat’s health, leading to the development of such dangerous diseases as:
- metritis;
- eclampsia;
- congestive mastitis;
- osteoporosis;
- arthritis, arthrosis.
Diagnostic measures
The veterinarian will need a complete medical history of the birth (how it went, whether the animal received obstetric care, etc.). A thorough medical examination is required to confirm/refute acute metritis based on clinical signs.
Timely diagnostic tests play a huge role in diagnosis. These include: complete blood count, blood chemistry profile, serology and urinalysis.
The most revealing may be a complete microscopic blood test : by the number of leukocytes, you can determine how intense the inflammatory process is in the animal’s body. In addition, a microscopic examination can show whether pathogenic microflora has appeared in the general bloodstream (i.e., whether sepsis has developed).
A urine test will allow the veterinarian to know how well the animal's kidneys are working and whether the cat has become severely dehydrated.
Ultrasound and fluoroscopic examination of the uterus itself is also indicated . This helps to visually assess the condition of the organ, the presence or absence of retained placenta, dead fetuses, blood or exudate. If there is discharge from the external genitalia, a specialist will definitely take a sample of the exudate for microscopic examination and sowing of the pathological material onto nutrient media. This will help, firstly, to identify the specific pathogen. Secondly, this way the specialist will find out which drug should be used to eliminate this particular case of infection.
Therapeutic techniques
- To help the animal's body cope with the consequences of dehydration, as well as intoxication, Ringer's and glucose solutions . This is an important part of the treatment of any severe case of postpartum endometritis. In addition, timely administration of intravenous infusions helps protect the kidneys.
- Antibiotics . Ideally, drugs are prescribed only based on the results of growing a culture of pathogens on nutrient media. If for some reason this cannot be done, broad-spectrum antibiotics are prescribed. But it is still better to identify a specific pathogen. It is possible that an inexpensive and “light” drug will be suitable for its destruction.
- The most difficult treatment will be in cases where it comes to the development of a septic process. In such situations, the cat urgently needs competent veterinary care, since the likelihood of death is very high. Loading doses of broad-spectrum antibiotics intravenously, drugs that support cardiac and respiratory activity, and intravenous infusions are required
- Surgical intervention . If the uterus is greatly enlarged and there is a suspicion of pyometra, the uterus must be urgently removed. In the event that the owners or veterinarians did not inspect it, and there is an afterbirth or dead fruits left in the organ cavity, it must be removed immediately, since any delay guarantees the development of a severe septic process. Spaying is also recommended. In some cases (when the cat has a certain breeding value) they resort to surgical cleansing of the uterine cavity. Please note that no one can give any guarantee of the success of this operation. Most likely, the cat will still develop severe metritis, after which bearing full-fledged kittens may be impossible.
Please note that after antibiotic therapy, the animal will most likely develop dysbiosis due to the death of the symbiotic intestinal microflora.
As a consequence, constipation and all other problems arising from the fact of constant intoxication of the body by deposits of feces. It wouldn't hurt to give her probiotics.
You also need to remember the need to isolate newborn kittens from their mother: antibacterial drugs or pathogens can enter their digestive tract. In any case, this will not lead to anything good. And further. Even in cases where the pet received quality veterinary care on time, it is far from certain that its reproductive function will be fully restored.
Be healthy, kitty!
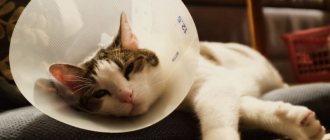
The unsatisfactory physical condition of the mother in labor is also one of the reasons leading to her rejection of kittens. It is important to determine what is bothering the cat and what is sick. Mastitis, eclampsia (milk fever), acute metritis and other complications, as well as various postpartum infections - this is not a complete list of possible ailments. Kittens in such a difficult situation are artificially fed, and their mother is treated.
Separately, we note that eclampsia can be triggered by poor nutrition of a pregnant cat and insufficient intake of vitamins and microelements into its body. To avoid unpleasant postpartum moments, you should take care of your pet’s health in advance, in particular the composition of food and its quality.
How often is it safe for a cat to give birth?
If the female who gave birth does not have serious health problems and after giving birth the disturbed hormonal levels return to normal, then after 1.5-2 months the animal may begin to go into estrus. However, the owner, in order to avoid dangerous complications, is prohibited from organizing re-breeding. It will take at least 9-12 months to restore the body. Therefore, veterinarians advise breeding females no more than once a year.
If the female starts asking for a cat immediately after the babies appear, then she is even capable of abandoning them.
With hormonal dysfunction, sexual heat can occur almost immediately after lambing. In this situation, not only the cat suffers, but also her cubs. The animal refuses its litter, perceiving it as someone else's kittens, runs away, rushes around the house in search of the cat, screams, and leaves marks on the floor. Such symptoms cannot be ignored; the pet must be taken to the veterinarian as soon as possible. After a diagnostic study, the doctor will prescribe a comprehensive treatment regimen that will help normalize the animal’s hormonal levels.
Treatment
To prescribe the necessary treatment, the veterinarian conducts an examination using palpation, ultrasound, and x-rays and consists of the following:
- For minor bleeding caused by Oxytocin, veterinarians prescribe hemostatic agents; if significant blood loss is observed, then surgical intervention will have to be performed on the animal.
- If a cat gets sick, her temperature rises, then the kittens need to be isolated from their mother and transferred to artificial feeding.
- When a veterinarian prescribes gentle treatment, the owner may not have to face the question of separating the mother from the kittens.
- If a cat is diagnosed with inflammation of the uterus, then in addition to antibiotic therapy, the veterinarian prescribes medications that lead to an increase in tone. As a result, the remaining tissue is removed from the uterus. In addition to medications, you can massage your tummy. With timely treatment, a complete cure occurs in your pet after 2 weeks.
- Immunostimulants and vitamins will help the animal recover after a difficult period.
- In case of inflammatory processes in a cat, it is necessary to conduct a milk test. If it turns out to be infected, the kittens must be separated from their mother.
If your cat has bloody discharge, the situation needs to be assessed immediately. If complications occur, you should contact your veterinarian for medical help as soon as possible. It is very important that assistance is provided in a timely manner, because the life of a young mother depends on it.
Natural food products
Products are chosen fresh, rich in proteins, calcium, carbohydrates and beneficial elements.
Among them:
- boiled lean meat: chicken, beef, rabbit, turkey, veal;
- vegetables: beets, pumpkin, cauliflower, carrots, zucchini;
- cottage cheese, curdled milk, natural yoghurts, biokefir;
- cereals: buckwheat, oatmeal, sprouted wheat grains.
To reduce the risk of developing constipation due to intestinal problems, add to the main diet:
- low-fat broths in which meat was cooked;
- warm milk (in small quantities);
- 3 – 4 drops of flaxseed, olive, sesame oil (added to food);
- boiled beets or puree from them;
- young shoots of oats, wheat, barley.
Approximate diet
In the second week of pregnancy, the cat’s appetite increases, therefore the amount of food is increased by 10% of the previous volume, from the second month - by 50%. In the last weeks before childbirth, appetite decreases, it is recommended to reduce portions, and the number of feedings is calculated based on the needs of the expectant mother. An adult animal needs 180-200 grams per day to be satisfied.
Predisposing factors
Regardless of the form of endometritis, its development is caused by the entry of pathogenic or conditionally pathogenic microflora into the uterine cavity.
Of course, above we have already mentioned cases of pathology, the appearance of which was caused by hormonal imbalances... But in any situation, all this only contributes to the “rooting” of microbes, and the following negative factors lead directly to endometritis:
- Sexually transmitted diseases (yes, they occur in cats too).
- Prolonged, difficult labor.
- Large births, as well as congenital anatomical pathologies of kittens.
- Rough or inept obstetric care, poorly sterilized obstetric instruments.
- Natural or medical abortion.
- Retention of placenta, or the presence of dead fetuses in the uterine cavity. For cats, this pathology is extremely dangerous, and it leads not only to endometritis, but also to the development of septic processes (and they are already fraught with death).