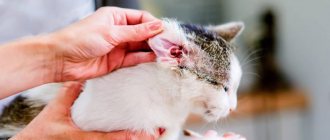
Cats are very graceful and flexible animals. Their ability to deftly overcome even very high obstacles is admirable. But sometimes the owner may notice that the cat has a limp and a swollen paw, and there is no trace of grace left. This is a reason to carefully assess your pet’s health status and, if necessary, consult a doctor.
Causes
Swelling of the limb (edema) occurs because fluid accumulates in the tissues, in their intercellular space: lymph, blood or pus.
The cause of swollen paws can be various circumstances. To determine them, you need to carefully observe your pet. Swelling does not occur on its own. Additional signs and symptoms will certainly be present.
- Limb injuries (fracture, bruise, dislocation, sprain, cut, laceration) are one of the common causes of edema. In these cases, you can additionally notice the following symptoms: the animal limps and does not lean on its paw; violation of the integrity of the skin - when soft tissues are damaged to the point of bleeding by sharp objects; suppuration, redness at the site of injury; increase in body temperature. The pad on a cat's paw is covered with delicate skin. Therefore, it is often she who can get injured and swell.
- Allergy in its severe manifestation is another reason why a paw may swell. Basically, an acute allergic reaction occurs when poison enters the body from an insect bite or after contact with chemicals. As a rule, there is no pain or it is not too noticeable, the area of edema is cold. Allergy is not accompanied by swelling alone. May appear: itching; lacrimation, excessive salivation; runny nose.
- Fungal infection (mycosis) can also cause the paw to swell. Associated symptoms can help diagnose a fungal infection, such as: peeling of the skin, for example, on the pad; unpleasant odor; cat dandruff. The fungus develops when the animal’s immune system is weakened. Basically, those pets that often walk outside are susceptible to this.
- Inflammation of the joints (arthritis) is accompanied by local asymmetrical swelling in the limbs. Joint diseases usually develop in older cats, limit their mobility, and cause pain.
- A recently born kitten may develop a disease such as hyperparathyroidism due to disruption of hormone production. Symptoms may include swelling of the limbs, lameness in the front or back legs due to muscle pain.
- In case of venous insufficiency and diseases accompanied by blockage of blood vessels (thrombosis, thrombophlebitis), a distinctive feature is the regular occurrence of asymmetrical edema.
- Kidney diseases and accompanying renal failure, as well as diseases of other internal organs (heart, liver) also provoke the formation of edema. A characteristic sign is swelling of only the hind limbs. Such swelling begins from the tips of the paws, gradually spreading upward. There is no fever or pain.
- Lymphadenitis is inflammation of the lymph nodes. It occurs with pain and severe swelling of the paws if the axillary lymph nodes are inflamed.
- The most serious reason that a cat has a swollen paw is mammary cancer. Swelling of the limb in this case occurs because the malignant formation blocks the circulation of lymph in the vessel, causing it to stagnate. Only the paw on the side of which the mammary gland lesion has developed becomes swollen.
What to do if you notice swelling in your cat?
In any case, it is worth showing the animal to a veterinarian as soon as possible. Edema can develop rapidly, within a few minutes, and threaten the life of the animal. Your first aid in this case can significantly alleviate the cat’s condition and improve the prognosis.
- If your swelling is hot and red, you can try applying cold and go to an appointment;
- If there is swelling of the muzzle or lips, try to give the animal an antihistamine (if you have one at home) and go to a veterinary clinic in Krasnoyarsk as soon as possible. It is better to clarify the dosage of the drug by calling our clinic;
- If you see your cat's breathing deteriorating due to swelling in the face or any other part of the body, try to provide air flow. See your doctor as soon as possible. If breathing stops, it is necessary to perform artificial respiration through a napkin, carefully opening your mouth with it.
At the clinic, the doctor will urgently examine the animal and provide symptomatic therapy aimed at stabilizing the condition, and then conduct additional diagnostics to make a diagnosis.
Allergic reactions
Allergic reactions most often manifest themselves as skin lesions. Allergies can have many causes - from food intolerance to complications after fungal or parasitic infestation.
Atopic dermatitis
Occurs due to exposure to external irritants - pollen, dust, detergents, powders, food. Characterized by profuse hair loss on the head, ears, belly or inner thigh. Sometimes the disease is complicated by purulent wounds and severe itching. In a cat, the sore usually appears on the neck with blood scabs or on the back.
Treatment consists of broad-spectrum antimicrobial drugs and taking antiallergic drugs (Clemastin, Sanoderm and others).
Miliary dermatitis
Miliary dermatitis occurs as a complication of fungal infections, autoimmune diseases, or as a reaction to an external irritant. Characteristic symptoms include severe itching, irritation, excessive hair loss and a rash in the form of small nodules.
Treatment consists of eliminating the cause of dermatitis, and after that, residual symptoms are relieved and vitamin and mineral complexes are prescribed.
Allergy to food
The most common type of allergic reaction is intolerance to a certain type of food or its components. Such a reaction can also be observed during a sudden transition from one type or type of nutrition to another. Also, the cause of an allergy to food can be the use of low-quality economy-class food in the diet of cats.
The main symptoms of an allergic reaction to food:
- disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system;
- vomit;
- rash similar to hives;
- nausea, weakness and lethargy;
- sneezing, runny nose;
- cough;
- severe itching and skin irritation.
In cases where the disease has progressed, it gives complications in the form of nodes around the mouth. The most severe allergic reaction is characterized by angioedema and, as a consequence, anaphylactic shock.
To relieve symptoms of itching and irritation, antihistamines are used in the form of drops, ointments or tablets (Suprastin, Stop-itch, Tavegil, Loratadine, etc.). Further treatment depends on the severity and the reason that caused the body’s response to the stimulus. Hormonal drugs, sorbents, probiotics, complexes of vitamins and minerals, antibacterial ointments and drugs that protect and restore immunity are prescribed.
Therapy
Treatment methods and techniques are selected based on the characteristics and type of pathogen, or negative environmental factor, under the influence of which inflammation occurred in each specific case. Thus, antibiotics are used for bacterial infections, acaricidal drugs are prescribed if pododermatitis occurs due to the action of parasitic mites. A therapeutic dose of prednisolone will help combat some of the inflammation caused by the autoimmune disease. In all cases, it is useful to wash the animal’s paws using antiseptic agents.
What is it and what causes it?
This is the name of the pathology in which the paw pads become inflamed. This prevents the animal from moving and playing; due to the strong pain reaction, the cat becomes restless, nervous and even aggressive. Unfortunately, not all owners notice the true cause of what is happening to the cat right away, and therefore the pathological process enters an advanced stage.
The causes of the disease in this case are quite varied. Firstly, many types of pathogenic and opportunistic bacteria can lead to such an outcome. For example, Staphylococcus aureus, some streptococci, and the ubiquitous E. coli (in the form of individual strains) can cause the disease. If your cat has injured its paws, then this outcome is quite likely.
Secondly, pathogenic fungi are often involved in the development of the disease. These are quite common and extremely dangerous pathogens. They can be difficult to identify, and to prescribe correct and effective treatment in this case is even more difficult. In addition, this type of pododermatitis causes frequent relapses, since complete recovery is not achieved in all cases. Fungal inflammation almost always becomes chronic.
How to treat cats?
Adult cats with almost all types of skin diseases require careful care and supervision. In case of scabies and microsporia, the cat should be isolated from healthy animals, but try not to keep it indoors, since stress will only worsen the situation.
A pet should always be treated with prescribed medications and vaccinated; they help completely kill the virus from the inside. We must not forget that any vaccine or drug must be prescribed only by a veterinarian. Trying to cure an animal yourself will only cause harm.
Additional recommendations regarding lifestyle changes and dietary nutrition should not be ignored. also need to give the animal vitamins . They will restore the immune system to its former resistance to disease and health.
A sick cat should not be allowed outside. So, you endanger other animals and children who will certainly want to stroke and caress your pet.
Parasitic
The most common skin diseases are parasite infestations. These include fungal, tick-borne and flea infestations.
Flea infestation
Of all the parasites, fleas most often infect all animals, including cats. Not only strays, but also pets can become infected with them. Fleas, flea larvae and flea eggs can enter indoors on a person's clothing or shoes. It is easy to remove fleas; it is important to start fighting them in a timely manner.
Symptoms of a flea infestation include severe swelling and irritation, which can be localized to specific areas or throughout the body. In its advanced form, the disease is complicated by anemia. The flea feeds on the blood of the animal, biting through the skin and leaving wounds. Through these wounds, the infection enters the body and as a result, inflammation or an allergic reaction develops.
To control fleas, you must first destroy all larvae, eggs and live fleas directly on the animal. To do this, use shampoos, gels, ointments and antihistamines to reduce itching and irritation. After this, the premises are treated with anti-parasitics.
You can see the signs of cat disease in more detail in the photo below:
Fungal
Fungal infections trichophytosis and microsporia provoke a disease such as ringworm. It is easily transmitted to humans, and children are especially susceptible to this infection. The fungus can penetrate indoors on clothing or shoes.
Symptoms of ringworm include:
- baldness of some areas of the body;
- peeling of the skin and the acquisition of a gray color of the skin;
- pain and discomfort.
It is important to start treatment promptly because for larger lesions, treatment will take longer and be more difficult.
It is necessary to treat with the use of antiseptics, antifungal shampoos, ointments or aerosols. Sometimes your doctor may prescribe 2-3 shingles vaccinations every 14 days.
Tick-borne
Notoedrosis, scabies, cheyletiosis, demodicosis and sarcoptic mange are tick-borne diseases.
Notoedrosis is a sore on the cat's neck under the fur. It is characterized by severe itching and irritation; in advanced form, purulent dermatitis may appear. Treatment consists of using anti-tick ointments - sulfur ointment, Amitrazine.
Scabies is characterized by severe itching and inflammation; the animal constantly itches and scratches the affected areas. In these places, a secondary bacterial infection forms. Scabies affects animals with weak immunity or with severe symptoms of vitamin deficiency. Treatment consists of the use of anti-tick drops (Bars, Inspector), ointments (Aversectin) and subcutaneous injections (Ivermectin). Antihistamine ointments or drops are used to relieve itching and inflammation.
Cheyletiosis is a sore on a cat's back. Dandruff appears along the ridge and causes severe itching and irritation. Treatment is carried out with injections (Fipronil, Pyrethrin) and antiseborrheic shampoos.
Demodicosis most actively affects cats and people in the warm season - the period of tick activity. It is characterized by severe baldness, itching, redness and the formation of ulcers. If left untreated, it can be fatal. For treatment, injections (Amitrazine, Ivermectin) and antihistamines are used to relieve itching and inflammation.
Sarcoptic mange is similar in symptoms to scabies and is very dangerous for people. Therapy is carried out using Stronghold drops.