What causes bones to get stuck in the throat?
There are several common reasons as a result of which the phraseological phrase “like a bone in the throat” turns into a real dangerous situation:
- Prolonged hunger . If a cat has not received food for a long time, it can literally attack the food, swallowing large pieces without chewing. In this case, there is a high risk that the animal will choke.
- Eating from someone else's bowl . Almost all mustachioed striped animals have a reputation for being very arrogant and unprincipled individuals who are not averse to eating from dog cups. Moreover, particularly shameless individuals may not even allow the owner to approach the bowl until they themselves “taste the dishes.” And if dogs can eat large bones without any problems, then cats may not be able to handle such food.
- Eating a whole fish . Responsible and experienced cat owners know that these pets can only be given boiled fish, previously deboned. But often whole fish, raw, are included in the diet of domestic cats. Not only can such a “delicacy” be infected with helminths, but also sharp fish bones often dig into the delicate mucous membrane of the throat, getting stuck in it or penetrating further into the esophagus and fixing there.
- Picking up street trash. This is a common problem for cats accustomed to free-ranging outside. Here they can eat any, including dangerous, objects that are not always edible.
How to keep your cat safe. The owner should monitor his pet more closely and avoid the presence of:
- duck bones;
- bones of large fish of fatty varieties: silver carp, pike, Siberian roach;
- fish tail bones, heads, as well as gills and gill covers.
If, despite all the preventive measures, a bone still gets stuck in the cat’s throat, then the owner will definitely notice warning signs.
Removing foreign bodies from the eyes
During active walks, debris, dust and other contaminants get on the mucous membranes of the eyes, causing discomfort. The mucous membrane becomes irritated, and the cat or dog feels pain or stinging in the eyes. This can be understood by several characteristic features. First of all, the pet begins to constantly rub its eyes with its paws, and they also turn red and profuse tearing appears.
As first aid, you can rinse your eyes with saline solution or at least boiled water. Removing a foreign object from the eye yourself can be a dangerous task, so it is better to bring your pet to our clinic.
The specialist will carefully pull back the eyelid, and then use a syringe to pour in a special liquid for disinfection. The foreign body can be removed with a swab or a piece of bandage, and sometimes even tweezers are used. The main thing is not to put off a visit to the veterinarian, because if the animal rubs the eye for a long time, the speck will damage the mucous membrane. The damage may be irreversible.
By contacting Irina Onyshchuk’s veterinary clinic, you can be sure that experienced veterinarians will take care of your pet. You can check the exact cost of a hospital with an intensive care unit from the administrator by calling +7. We work around the clock!
How does a cat behave with a bone in its respiratory tract?
The behavior of a cat caught in such a situation will definitely change. The owner should be alarmed if:
- There is a lack of appetite - if your pet refuses even treats, then perhaps he has a bone stuck in his esophagus.
- There are signs of suffocation, and the cat is breathing frequently and heavily.
- The cat itself makes attempts to get rid of the foreign object, clears its throat, makes appropriate movements and helps itself with its paws.
- Salivation (salivation) increases.
- Exhausting, suffocating spasms of the larynx occur, as with a sore throat.
- The cat is vomiting; there may be a urge to vomit, accompanied by characteristic sounds.
Some cats get scared, begin to avoid people, hide from view and let out a plaintive meow. Prolonged restlessness of a pet is an alarming sign for the owner. If this happens, it means that the animal was unable to cope with the problem on its own and needs human help.
conclusions
If it was not possible to remove the object, you must urgently take the cat to the clinic.
If the efforts made do not bring results, and it was not possible to remove the foreign object, you must urgently call a veterinarian or take the animal to the clinic , having first reported the problem to the doctor. It is necessary to transport your pet in the most comfortable conditions. Provide adequate access to fresh air. In a hospital setting, the doctor may inject the cat with an anesthetic for a more thorough examination and procedure.
False symptoms
If a cat has dyspnea (feeling of lack of air), it is recommended to examine its mucous membranes. With hypoxia, that is, lack of oxygen, it acquires a rich red tint or becomes bluish. With obvious symptoms of suffocation, the pet can quickly die if emergency assistance is not provided.
But in some situations, a prolonged, obsessive cough that causes gagging has nothing to do with foreign objects in the respiratory tract. These may be other conditions:
- The cat swallowed fur - his behavior makes it seem like he is choking. A little later, you will notice how he regurgitates hairballs, as a result of which the signs of the disorder disappear.
- “False suffocation” - experiencing severe hunger, the cat inhales air so forcefully that its larynx is pulled into the soft palate. In this state, it is advisable to give him food, drink or stroke his chin.
If anxiety does not disappear after such events, and the cat refuses food, then it needs urgent help.
The difference between a normal physiological process and the presence of a foreign object
You need to be aware of the differences between the signs of a foreign object and a normal physiological process.
- A cat may experience rapid or difficult breathing when trying to regurgitate a hairball stuck in the esophagus or stomach.
- At the same time, the cat tenses up, may arch over, and cough forcefully.
- Such symptoms can easily be confused with vomiting and asthma attacks.
A cat may experience difficulty breathing when trying to regurgitate a hairball.
False suffocation
The problem of false suffocation is eliminated by gentle stroking.
It is also necessary to remember what your pet ate. It is quite possible that false asphyxiation could occur.
This happens if your pet inhales too deeply and can pull the soft palate into the larynx.
The convulsive breaths that the cat makes only move the palate closer to the windpipe. The problem can be eliminated by gentle stroking or it is necessary to give the cat something to eat so that the swallowing reflex removes the dangerous symptom.
First aid
It is important that the owner immediately pays attention to the condition of the pet. You need to act according to the algorithm:
- Wrap the animal in a diaper or blanket to limit physical activity. Leave only your head free.
- Conduct a thorough examination of your pet's oral cavity. To look into his mouth, you need to carefully move the lower jaw down with the pressure of one finger.
- If a foreign object is visible, then you should try to pull it out using tweezers. It is not recommended to use your fingers in the cat's mouth. It is unlikely that you will be able to remove the bone in this way, but driving it much deeper and aggravating the situation is as easy as shelling pears.
To make the procedure more effective, it is better to involve an assistant in it.
Together, it is easier to fix the resisting “patient” and avoid possible injuries.
The bone is not in the throat. If a foreign object is not found in the pharynx, then further examination of the mouth should be abandoned. In this case, other actions are necessary to push it out:
- You need to confidently slap your pet on the back, choosing the area between the shoulder blades. The movement should be careful, but clear.
- You can quickly squeeze the cat's chest from the sides. The person needs to sit on the floor with the animal's croup facing him. The hind limbs should be raised and clamped with the knees. Place your hands on the cat's sides and squeeze the sternum to about 1/3 of its volume. You can’t fuss and push hard.
Such actions are aimed at provoking a cough, during which the cat itself can push out the bone that causes discomfort.
Tonsil plugs: causes
To find out the etiology of the occurrence of purulent accumulations in the tonsils, you need to understand what role the palatine tonsils play in the body.
The tonsils are an important organ of the human immune system, which is the first to stand in the way of bacteria and viruses that enter the body through the mouth. As soon as “strangers” reach the surface of the tonsils, they begin to intensify the production of leukocytes, which enter into battle with pathogenic microorganisms. As a result of such “battle actions”, dead leukocytes, bacteria, and epithelial remains accumulate in the lacunae of the tonsils. Over time, minerals accumulate here, and the contents of the lacunae begin to harden, forming caseous plugs.
The main cause of traffic jams is chronic tonsillitis. But they can also form in the palatine tonsils for various reasons:
- accumulation of staphylococci, streptococci, pneumococci and other bacteria;
- in people who have a weak immune system;
- frequent sore throats;
- the presence of herpes virus and fungi in the body;
- dental problems (caries);
- viral infections (flu, ARVI).
Each of the above reasons can provoke inflammation of the tonsils. The risk of accumulation of caseous masses in the lacunae of the tonsils is increased by unhealthy diet, smoking, and alcohol consumption.
Traffic jams do not form just like that, for no reason. They are a consequence of another disease and signal that an inflammatory process is underway in the body.
Pet lost consciousness
If the bone has blocked the cat's airway and he has fallen into an unconscious state, then you cannot waste a second:
- The animal's mouth must be opened as wide as possible.
- After examining the oral cavity, remove the bone or other object using tweezers.
- In an extreme situation, you can use your hands if the owner is confident that he can remove the obstacle.
- When the item is removed, you need to remove the accumulated liquid from the animal’s mouth with a cloth or other clean material. The victim should lie so that the back of the body is higher than the head. This will prevent salivary fluid from flowing into the throat.
- After removing the cat's bone, perform artificial respiration - blow air from the victim's mouth into the nostrils.
The faster and more competently the owner reacts, the higher the pet’s chances of survival.
Removing splinters after a walk
During walks, especially in parks or in the forest, as well as in littered areas, the animal can drive splinters into itself - wood or metal, and can even get glass deep under the skin.
Usually in such situations the pads are damaged. Splinters cause pain or discomfort, and if nothing is done in a timely manner, the onset of suppuration is possible. A cat or dog with a splinter begins to lick the sore spot, limps and tries to remove the foreign object with its teeth, but usually nothing works.
If the splinter is visible, you can try to remove it yourself with clean tweezers, but you will need an assistant to hold the cat or dog. After extraction, the wound is treated with iodine and bandaged. Our clinic’s veterinarians act in a similar way, but if necessary, they put the animal under anesthesia and use more complex instruments.
Nuances to consider
Unfortunately, not every person who does not have a medical education and certain training is capable of providing emergency care. It’s even worse when a panicking owner, trying to help the pet, makes mistake after mistake, not giving it the opportunity to get out. What should you pay attention to if such a situation arises? First of all this:
- It is not recommended to remove a sharp bone located deep in the throat on your own unless the cat has lost consciousness. This can lead to damage to mucous tissues and subsequent suppuration.
- If the animal's efforts to get rid of the bone lead to vomiting, then most likely the object will come out along with the vomit. You shouldn’t interfere with your pet’s “getting rid of the excess.”
- When time passes, and the problem with the bone is not solved and the owner is unable to help the animal, you need to seek advice from a veterinarian. It will not be difficult for a specialist to assess the cat’s condition, determine the cause of the deterioration of the condition and remove the foreign body.
- Sometimes it is impossible to provoke vomiting in animals, for example, if he has swallowed a chemical substance.
- If your pet’s life is not in danger, then you can help get rid of the bone in a simple way by pouring 2-3 tablespoons of vegetable oil into its mouth.
The tissues of the larynx in animals are quite sensitive and can be seriously injured if sharp objects penetrate deeply.
The veterinarian will remove the bone as carefully as possible, using painkillers and disinfectants if necessary.
Also watch the video on what to do if your cat chokes on a bone or other food:
Our advantages
Around the clock
Experienced doctors
Modern equipment
Hospital
Regardless of the situation, it is important not to hesitate, but to urgently take the necessary measures. It is not always possible to provide qualified assistance to your pet on your own, so it is better to contact an experienced veterinarian. Our clinic is located in the Babushkinskaya and Medvedkovo metro areas, so many Muscovites come to us, bringing cats, dogs and other pets for an appointment.
Foreign bodies of the esophagus
Causes.
Hasty eating, missing teeth, inadequate dentures, decreased pharyngeal reflex, alcohol intoxication, cicatricial narrowing of the esophagus. Foreign bodies usually get stuck in the area of physiological narrowings, most often at the level of the first thoracic vertebra.
Symptoms.
The onset of the disease is sudden and associated with food intake. Characterized by pain in the throat or behind the sternum with irradiation to the back, interscapular area, dysphagia, aphagia, drooling, general weakness, malaise, pain on palpation of the neck (on the left), aggravated by tapping on the spine, possibly forced positioning of the head.
When a foreign body is localized in the area of the first physiological narrowing of the esophagus, the head is tilted forward, down, the patient holds it motionless, and turns the whole body. When a foreign body is localized in the thoracic esophagus, the patient is in a semi-bent position (“carrying posture”).
Indirect laryngoscopy reveals swelling, hyperemia of the mucous membrane in the area of the aryepiglottic folds, arytenoid cartilages, and accumulation of saliva in the pyriform pouch (usually the left one). Vomiting and coughing are possible. A large foreign body can cause difficulty breathing through the larynx.
Complications.
Perforation of the esophagus, periesophagitis, mediastinitis, bleeding from the great vessels.
First medical aid.
. Immediate evacuation to hospital. Attempts to push a foreign body by swallowing bread crusts or using bougies are prohibited.
Specialized assistance
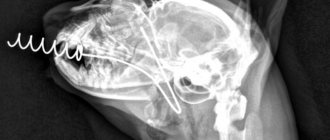
provided by otorhinolaryngologists together with endoscopists. To do this, indirect laryngoscopy and x-ray examination of the cervical spine in two projections (according to G.M. Zemtsov) are performed, which makes it possible to detect the shadow of a foreign body, indirect signs of a non-contrast foreign body of the esophagus or damage to its walls.
These symptoms are:
- straightening of the cervical spine due to tension in the scalene muscles;
- expansion of the prevertebral space;
- the presence of a symptom of an air “arrow” - an accumulation of air released from the stomach below the level of a foreign body, the pointed end of the “arrow” indicating the location of the foreign body;
- striped clearings in the prevertebral space are a sign of air penetration into the retroesophageal tissue or the development of putrefactive inflammation with the formation of gas.
Fibroesophagoscopy is also performed for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. If it is impossible to remove a strangulated foreign body of the esophagus during esophagoscopy, an esophagotomy is performed. Anti-inflammatory therapy is prescribed.