- The role of the liver in cats
- Visually detectable signs of liver disease in a cat
- The most dangerous liver diseases of cats by class, symptoms and treatment methods
- Cirrhosis
- Hepatosis
- Cholecystitis
The most common liver diseases in cats
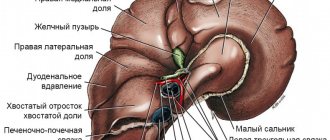
The cat's liver is a powerful biological filtering station, which is responsible for neutralizing substances harmful to the body that enter with food, air, and drink.
The role of the liver in cats
Passing through it, through the action of special cleansing enzymes, a completely healthy secretion of useful substances enters the blood and organs. This hardworking organ is also responsible for the synthesis of proteins and hormones, and is also a strong immune stimulant.
Most harmful substances - allergens, chemicals, various toxins from the air and food undergo thorough cleaning in the liver, causing more and more damage to it each time. Malfunctions in the work of the body’s main “cleaner” affect the functioning of vital organs, and at the same time a favorable atmosphere is created for the development of serious diseases:
- Gallstone disease;
- Cirrhosis;
- Hepatitis A;
- Cholecystitis;
- Neutrophilic and lymphocytic cholangitis;
- Lipidosis;
- Liver failure;
- Amyloidosis
Everyone knows that the liver has an amazing self-healing function, but it should be understood that the process is very long, labor-intensive and requires a professional approach. Therefore, it would be wiser not to delay at the first sign of a malfunction in the liver of cats and contact a veterinary clinic.
Every owner should remember that if their beloved pets refuse even a tasty morsel offered to them, most likely this is a manifestation of liver disease in cats, symptoms and treatment for which a certified veterinarian can recognize and prescribe.
For a more detailed understanding of the symptoms and consequences of the most common liver diseases, as well as possible treatment methods, owners will be given the information below.
Liver tumors
Tumors are rare in cats. However, they are most often malignant. Among liver tumors, bile duct cancer ranks first, followed by carcinoid and sarcoma.
Benign neoplasms include hepatic cell adenoma, hemangioma, hepatoma and leiomyoma. Bile duct cystadenoma is the most common tumor in cats.
Benign tumors usually do not cause any discomfort to a cat and do not cause the development of disease, however, until they grow or rupture, causing bleeding in the cat.
Visually detectable signs of liver disease in a cat
In veterinary practice, there are several main symptoms, upon detection of which the owner can be sure that this is inflammation of the liver in cats, and there is no need to hesitate:
- Failure to defecate, with frequent diarrhea or constipation;
- Vomit;
- Yellowness of the skin;
- Dark brown coloration of urine;
- Exhaustion and thinness;
- Severe bloating;
- Refusal of food;
- Increased change in liver size;
- Sharp or stabbing pain;
- Apathy and powerlessness;
- Rupture of blood capillaries, which is clearly visible on the skin;
- Poor blood clotting;
- The appearance of a feverish state
Based on the above signs, the owner can independently suspect liver disease in cats, the treatment of which should be entrusted to the hands of qualified specialists.
How to prepare your cat for research
At home, it is important to follow a fasting diet for 10-12 hours (if there are no contraindications to its implementation, if in doubt, consult your doctor).
When performing an ultrasound procedure, owners place the cat on a special table flat on its back (if there are no contraindications to this) and hold its front and hind legs. The doctor shaves the cat’s fur in the area of the anatomical location of the organ to ensure good visualization, treats the skin with alcohol and applies a special acoustic gel. If the animal is not hungry and there is food or gas in the stomach, or the animal is overweight, the test will be difficult. The transverse colon, which is filled with feces, may also complicate visualization.
Video - interview with a visual diagnostics doctor about performing an ultrasound of the liver in a cat:
Ultrasound results are not a diagnosis! Many pathologies look the same when performing an ultrasound examination of the liver, and vice versa - the liver may be structurally normal, but there are functional disorders, they will not be visible on ultrasound. The final diagnosis is made by the attending physician, based on the clinical picture, blood tests, cytological and histological studies.
(c) Veterinary center for the treatment and rehabilitation of animals “Zoostatus”. Varshavskoe highway, 125 building 1. tel.
8 (499) 372-27-37
Cirrhosis
This disease can be easily detected by lightly stroking the pet's belly. If there is growth in the abdominal cavity, this is a signal of a serious liver disease - cirrhosis, leading to changes in the organ up to its decomposition in the future. Symptoms of the development of the disease manifest themselves in certain signs:
- Conjunctiva with red spots;
- Diarrhea;
- Refusal of food;
- Yellowness of the skin;
- Organ enlargement;
- Rapid breathing;
- Arrhythmia
The development of cirrhosis in cats can be facilitated by a sedentary lifestyle, lack of vitamin B and protein, infestations, and the consequences of a previous disease. In addition, a stimulator for the development of cirrhosis can be the ingestion of various toxins into the body, for example, from low-quality food.
Only a doctor can correctly prescribe medications for liver treatment in cats, which are selected according to the established diagnosis. In this case, the veterinarian will determine drug therapy followed by a rehabilitation period.
Prevention
Monitor your pet's diet. Do not feed your dog or cat food from the table. Buy only high-quality, proven food. If your pet is on a natural diet, give raw lean meat, boiled fish, fresh vegetables and fruits. Wipe or steam the greens for better absorption. Avoid sausages, sausages, do not give rotten, bad food.
Other recommendations:
- Remove toxins that may harm the liver. This means that you need to avoid unnecessary pesticides and medications. Avoid frequent cleaning using household chemicals.
- Synthetic vitamins and minerals can be given strictly according to the instructions, without exceeding the course duration and dose.
- Supplement with the antioxidants glutathione, the amino acids N-acetylcysteine (NAC) and S-adenosylmethionine (SAMe). They bind to toxins in the liver before the poisons can damage the gland. Be sure to consider the dosage.
- Get vaccinated against deadly diseases on time.
Hepatosis
The second most severe disease is hepatosis in cats, symptoms and treatment, which is determined strictly after a thorough examination. According to symptoms, there are several main signs:
- When the eyelid is pulled upward, the visible yellowness of the membrane is smoothed;
- What is typical for the skin of the lower lip and gums
The cause of the disease is determined by the ingestion of toxinogenic substances into the body - drugs, poisons, allergens - the accumulation of which in the blood ensures the development of hepatosis.
When a veterinarian makes such a diagnosis, they are prescribed comprehensive treatment. If the cat’s condition is mild, then it is possible to undergo treatment at home, but with strict adherence to all doctor’s instructions.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of liver failure in cats involves a wide range of tests, but the first step is to obtain a detailed history. To confirm the diagnosis, a general examination of the animal and palpation is used. A study is carried out of general clinical and biochemical blood tests, ultrasound of the abdominal cavity. If ascites is present, the fluid is diagnosed, its cytological composition, biochemical examination, and, if necessary, culture.
Cholecystitis
If a veterinarian identifies cholecystitis in cats, treatment will also be required for the inflamed gallbladder, the normal functioning of which directly depends on a healthy liver. The symptoms of the disease are acute and debilitating and manifest as:
- Alternating frequent diarrhea with constipation;
- Severe pain;
- Increased body temperature
The main stimulators of the development of cholecystitis are liver damage by lamblia and cholelithiasis. When contacting a veterinary clinic, drug treatment for the liver in cats will be prescribed, medications and a course of physiotherapy.
These are the most common liver diseases in cats, symptoms and treatment, which will help owners promptly recognize the disease and take their pet to a veterinary clinic. Remember, delay can cost your pet’s life and it’s not worth the risk.
What is hepatic encephalopathy
Hepatic encephalopathy in cats develops quite quickly - within several hours or days from the moment of exposure to the pathological factor. The cause of hepatoencephalopathy is severe damage to the liver parenchyma caused by toxic substances, infectious processes, and blood poisoning.
Against the background of damage, acute organ failure develops. The basis for the development of liver failure is the death of hepatocytes (cellular structures of the liver), as well as diffuse fatty degeneration. Multiple vascular collaterals arise in the area of the vena cava and vorna, provoking the passage of toxic metabolic products past the liver itself.
Severe intoxication of the body resulting from metabolic disorders leads to the development of a coma. The most dangerous breakdown product during metabolism is ammonia. In addition, the cause of acute intoxication and, as a consequence, hepatic coma, are phenols, which under normal conditions are neutralized by hepatocytes.
Acute liver failure provokes disturbances in water and electrolyte balance, reduced levels of potassium and sodium in the body, as well as metabolic acidosis. The main factors provoking hepatic encephalopathy are:
- use of medications;
- intoxication of the body with organophosphorus compounds, nitrates and salts of heavy metals;
- infectious lesions by bacterial microorganisms and viruses (adenoviral infection, hepatitis);
- malignant and benign neoplasms in the liver;
- cerebral edema;
- necrotic changes in the liver.
The mechanism of development of hepatoencephalopathy is provoked by necrotic-type changes in the liver and hepatic coma. Coma itself occurs as a result of swelling of the cerebral cortex. Against this background, an increase in the capacity of the blood-brain barrier and the passage of fluids develops. Toxic substances (ammonia, octonoate, phenolic acids) penetrate into the brain tissue, provoke oxygen starvation of the brain tissue, combined with disruption of the pulmonary structures, provoked in turn by low pressure.
Edema in the lungs is one of the signs of hepatic encephalopathy, provoked by increased capillary conductivity. In an attempt to neutralize oxygen starvation of tissues, hyperventilation of the lungs develops and thrombocytopenia develops, expressed in the form of hemorrhagic diathesis.
Two types of deficiency
Acute form.
In addition to the listed symptoms, the pet may have mental disorders. The cat is constantly tormented by bouts of vomiting and is disoriented. This is a sad picture, and if you do not seek veterinary help in time, the animal will go into shock. In most cases, the acute form of liver failure is easily treatable, but this requires hospitalization.
Chronic form.
In this case, the process lasts several months and it is more difficult to save it.
What can I advise you, dear friends?
Causes of diseases
What could cause harm to this most patient, hardworking, and therefore precious organ? Perhaps, just because of two circumstances that... are completely avoidable:
- poor quality nutrition (fatty and smoked foods, mold);
- the presence of parasites and infections in the body.
A malfunction occurs in the circulatory system if the liver eventually becomes ill with these ailments:
- hepatitis;
- cirrhosis;
- cholangitis;
- lipidosis;
- poisoning;
- oncology;
- liver failure.
A scary list, isn't it?
Ask your veterinarian:
- What foods should I not give my cat due to her health condition?
- How can human food affect a cat's health, you ask?
- Would you recommend Hill's Prescription Diet for my cat?
- Ask about special foods for your cat.
- How much and how many times per day should you feed your cat the recommended food?
- Discuss what treats you can give your cat with the recommended food.
- How quickly will my cat show signs of improvement?
- Can you provide me with written instructions or a brochure with information about the liver disease my cat has been diagnosed with?
- What is the best way to contact you or your veterinary practice if I have questions (email/phone)?
- Ask if your cat needs follow-up care.
- Please confirm whether you will be sent a reminder letter or an email notification.
Importance of Nutrition
If your cat has been diagnosed with liver disease, you're probably wondering, "How to care for her?" Treatment of any liver disease is aimed at giving the liver “rest” and minimizing its load, which is associated with the processing of fats, proteins, carbohydrates and medications. It is especially important to feed the cat correctly. Give her a diet with easily digestible carbohydrates, high-quality fats, and limited salt to control existing liver damage and improve liver function.
For an accurate diagnosis and proper treatment, always consult your veterinarian and ask for recommendations on the best food for your pet's liver health.
Etiology
According to modern concepts, the development of primary liver tumors in dogs and cats is associated with the action of various etiological agents. The role of physical, chemical, bacterial, viral, parasitic, age-related, genetic and other factors is noted. A special role in the occurrence of a tumor is played by the action of mutagens, which, acting on the genetic apparatus of the cell, cause mutation and transformation of a normal cell into a tumor cell.
Tumors of the mammary glands, ovaries, and all organs drained by the portal vein of the liver most often metastasize to the liver. Metastases to the liver occur very rarely in cancer of the oral cavity, pharynx, prostate, and bladder, and practically never occur in skin cancer.
Treatment
The surgical method is the most effective in treating liver tumors.
The use of chemotherapy for primary liver tumors in medicine has not led to the expected results and has also proven poorly in veterinary medicine. Chemotherapy is used to treat systemic diseases such as lymphosarcoma. According to various authors (Weis et al., 2005), lymphosarcoma accounts for 7% of all liver cancers. It uses the SOP (vincristine and cyclophosphamide) and ASOP (vincristine, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin) regimens. Chemotherapy in combination with surgery is also used for metastatic liver disease with tumors sensitive to chemotherapy. In a metastatic process, for example, from breast cancer, one of the possible regimens includes several drugs: 5-fluorouracil, cyclophosphamide and doxorubicin. The choice of regimens and doses of chemotherapy drugs depends on the morphogenesis of the tumor, the general condition of the sick animal, the results of blood tests, and the degree of dehydration.
The evaluation of the use of radiotherapy in animals with hepato-biliary tumors has not been well studied.
If the general condition of the animals is unsatisfactory, it is necessary to begin surgical treatment only after stabilization of the condition with the help of infusion therapy using antibacterial drugs, hepatoprotectors, etc.
In case of a single liver lesion, regardless of its morphological origin, a lobectomy or marginal resection of the affected lobe was performed. For a primary tumor, treatment is only surgical; for a metastatic process, the issue of using chemotherapy was decided in the postoperative period.
To perform a lobectomy, it is recommended to perform a combined approach to the abdominal cavity, which includes a median laparotomy, a lateral incision parallel to the caudal edge of the last rib, and resection of the falciform ligament. According to our data, 80% of tumors were localized in the left half of the liver.
After the above access, the affected lobe was isolated and two twisting ligatures were applied to its base. When applying the knot, the thread cut through the liver parenchyma and ligated the main vascular lines.
In case of multiple liver lesions, the extent of liver resection should be minimized and combined with local treatment methods, such as sclerotherapy and cryodestruction. In this case, it is more convenient to combine access with a Segal retractor.
Cryodestruction
Cryodestruction is based on rapid freezing of the tumor with liquid nitrogen followed by thawing, which leads to cell damage and death. This method can be used as monotherapy, and it is also used as an addition to lobectomy when ablastic tumor removal is not possible.
Alcoholization (sclerotherapy)
96* alcohol causes thrombosis of the arteries feeding the tumor, its ischemia and necrosis. The size of the tumor should not exceed 5 cm. The number of foci should not be more than 3-5, and the maximum dose should not be higher than 0.5 ml per kilogram of body weight. The introduction of alcohol must be done along the edge of the tumor until the color of the lesion changes.
As a rule, with multiple liver tumors, re-intervention by laparoscopy, performed 30 days after surgery, allows you to evaluate the effect of the treatment and, if necessary, repeat the local effect.
Histological picture
Hemangioma is a thin-walled vascular canal of various sizes, often large, with a sharply developed course. The lining endothelial cells are flattened and desquamated in some places. The vascular channels are supported by fibrous stroma.
Hepatocellular cancer - the cellular elements of the tumor tissue are large, polygonal, with an average nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio, cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm, having central vesicular nuclei with clearly defined nucleoli. The cells are arranged in the form of trabeculae or in a disorderly manner. Between the trabeculae and clusters of cells are sinusoids lined with epithelium. Mitotic figures can be determined.
Fibrosarcoma of the liver - tumor tissue is built from medium-sized monomorphic spindle-shaped and oval cells, forming cords, ribbons and swirls. The stroma is presented evenly in the form of thin collagen fibers. The growth is invasive.
Metastasis of tubular breast cancer to the liver - the tumor is built from glandular epithelium, forming tubular and pseudocystic structures. The cellular elements of the tumor are round in shape, moderately polymorphic with an average nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio. The nuclei are round, large, and contain hyperchromic chromatin. Signs of proliferation of mitoses, including atypical ones, are revealed.
Metastasis of ovarian adenocarcinoma - the tumor is often built from glandular structures separated by septa; the cells have a cubic or oval shape with an average nuclear-cytoplasmic ratio and are located on thin stromal septa. The nuclei are round, hyperchromic, contain coarse chromatin, and the cytoplasm is eosinophilic.