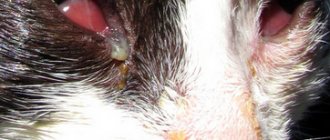
Every pet owner must monitor the health of their pet. It is necessary not only to feed the cat well, but also to carry out hygiene procedures - bathe in a timely manner, clean the ears and wipe the eyes.
In the absence of hygiene, the pet often develops pathological processes in the eye area, causing the appearance of purulent exudate.
The main reason for the appearance of pus from the eyes of cats is inflammatory processes in the area of the conjunctival membrane, which were not eliminated in a timely manner.
The factor that provoked the development of the disease must be established in a veterinary clinic, where the animal will undergo all the necessary diagnostic procedures and be prescribed adequate treatment.
Causes
Festering eyes are not an independent disease, but only a symptom, and veterinarians identify many causes.
One of the most common is ophthalmological pathologies:
- Conjunctivitis is a harmless disease that is an inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes.
- Keratitis is damage to the cornea due to trauma, burns with chemicals, infections, and allergies.
- Blepharitis is an inflammation of the edges of the eyelids caused by bacteria.
- Injuries to the mucous membrane. Minor damage heals on its own. In large wounds caused by sharp objects (claws, branches), an inflammatory process with suppuration of the eyes may occur.
Often kittens are born with pathologies of the organ of vision. The defects cause watery eyes and discharge of pus. So, the baby may lack a lacrimal punctum, the lower eyelid may turn inward, eyelashes may grow in several rows, etc. Other causes of suppuration include:
- poor quality care, lack of hygiene;
- unbalanced diet;
- decreased immunity;
- colds caused by drafts and hypothermia;
- allergy;
- atopic dermatitis;
- chlamydia;
- heredity.
The eyes can fester in any animal, regardless of gender and age. Breeds such as Scottish, British, and Persian are especially susceptible to this pathology. This is explained by the anatomical features of the skull.
What diseases can cause your eyes to fester?
Purulent discharge from the eyes is a symptom of both eye diseases and general diseases.
Common diseases accompanied by purulent discharge from the eyes
Common diseases that cause cat eyes to fester:
- Allergy - at the beginning of the disease, the discharge is mucous in nature, bilateral in nature, which changes to purulent with the addition of secondary microbial flora. Additionally observed: sneezing;
- nasal discharge;
- redness of the conjunctiva;
- skin rash.
- instability of appetite;
- panleukopenia: sudden fever up to 40–41 ° C;
- fever;
- fever;
- periodic fever;
- at the very beginning of the disease, the purulent discharge is unilateral, later the second eye is affected;
Chemosis is the predominant symptom when the conjunctiva is affected by chlamydia
- fever;
- sneezing, coughing;
Photo gallery: systemic diseases in which purulent discharge from the eyes is observed
Panleukopenia causes profuse purulent discharge from the eyes and nose.
With herpetic conjunctivitis, the discharge from the eyes is purulent in nature
With chlamydia, purulent discharge from the eyes is typical, as well as chemosis - swelling of the conjunctiva
Measures to improve the condition of the conjunctiva
In case of general diseases, purulent discharge from the eyes is treated only together with the underlying pathology of which they are a symptom. To improve the condition of the eyes in case of general diseases, the following are used as part of complex therapy:
- Regular toilet of the eyes to remove pus and microbial accumulations using hygienic eye lotions: Klini;
- Veda;
- Dewdrop.
- Tsiprovet;
- tetracycline ophthalmic;
- Forvet;
Anandin is a drug that has anti-inflammatory, antiviral and immunomodulatory effects.
Table: eye diseases with purulent discharge
| Type of disease | Symptoms | Treatment |
| Eye injury |
|
|
| Conjunctivitis is an inflammation of the conjunctiva and eyelids, which is unilateral or bilateral. |
|
|
| Keratitis - inflammation of the cornea |
|
|
| Blepharitis - inflammation of the eyelids |
|
|
| Uveitis - inflammation of the choroid of the eye |
|
|
| Entropion is a chronic injury to the surface of the eye by the edge of the deformed eyelid, as well as by its eyelashes. |
| Surgical restoration of the correct position of the eyelid |
| Dacryocystitis - inflammation of the lacrimal sac |
|
|
Thus, purulent discharge from a cat’s eyes may indicate both the presence of a systemic disease and the development of eye disease. Moreover, purulent inflammation can mask the primary nature of the process and return after the use of antibiotics without treating the underlying cause of the disease.
Photo gallery: eye diseases that cause purulent discharge from the eyes
Purulent discharge from the eyes in cats most often occurs due to conjunctivitis.
Keratitis is characterized by clouding of the cornea. Dacryocystitis is characterized by swelling at the inner corner of the eye.
Entropion of the eyelid is treated surgically
Table: drugs that are used to treat eyes in cats with purulent discharge
| A drug | Compound | Operating principle | Application | Price, rubles |
| Ophthalmosan, eye drops |
| Bactericidal, anti-inflammatory, decongestant |
| 185 |
| Leopard, eye drops |
| Antibacterial agent |
Instill 1-2 drops 3-4 times a day for a course of 1-2 weeks. | 159 |
| Ciprovet, eye drops | Ciprofloxacin | Antibacterial agent |
Instill 1 drop 4 times a day for 1–2 weeks. | 196 |
| Tetracycline eye ointment | Tetracycline | Antibacterial agent | Infectious eye diseases caused by pathogens sensitive to tetracycline. Apply 3–5 times a day. | from 44 |
| Maksidin 0.15, eye drops | Germanium bis(pyridine-2,6-dicarboxylate) |
| Treatment of conjunctivitis and keratoconjunctivitis. Apply 1 drop 2-3 times a day for a course of no more than 2 weeks. | 52 per bottle |
Photo gallery for the treatment of eye diseases with purulent discharge
Sinulox is used for systemic antibacterial therapy for infectious eye diseases.
Tetracycline ointment has a broad spectrum of action and is used to treat both bacterial conjunctivitis and chlamydia
Bars eye drops are a combined antibacterial drug with an extended spectrum of action.
Korneregel promotes corneal healing
Maxidin is a veterinary drug that is used for immunocorrection in the fight against diseases of viral origin.
Dekta-2 eye drops are intended for the treatment and prevention of ophthalmic diseases of bacterial origin in pets
Ciprovet for cats is an effective antibacterial drug with a complex spectrum of action.
How to treat a cat's eyes
To carry out treatment procedures, it is better to use the help of an assistant who would hold the cat. If there is no assistant, the cat is immobilized, swaddled in a towel.
The following treatment procedures are carried out at home:
- Eye rinsing: a napkin is moistened with eye lotion or an antiseptic solution and passed over closed eyelids, removing secretions;
- if the eyelids are stuck together, a napkin richly moistened with an antiseptic solution is applied to them and lightly pressed, after which the eye will open, you cannot use force to open the eye, you can damage the eyelids;
- You cannot touch the surface of the eye with a napkin; it is washed with an antiseptic solution from a syringe, after removing the needle.
Since ointments and drops are irritating, it makes sense to wear a protective (Elizabethan) collar on the cat to prevent scratching of the eyes with its paws.
Protective collar prevents paws from scratching your eyes
Video: how to care for your pet's eyes
Symptoms
It is impossible not to notice that a cat’s eyes are festering. As a rule, suppuration is accompanied by other signs. Cats are very clean, so discharge causes them great discomfort. The animal blinks frequently and constantly rubs its muzzle, trying to get rid of dried crusts.
The eyes become red, swollen, watery, and yellow, green or brown pus is released from them. The fur near the eyelids darkens and a dense crust forms around it, preventing the cat from opening them completely.
A previously active and cheerful pet becomes lethargic, apathetic, refuses to eat, and tries to hide in a dark place, away from the light. In some cases, the temperature rises.
If you notice purulent discharge from your four-legged pet, you should immediately contact a veterinarian. If this is not possible, then you need to rinse the eyes, but still show the animal to a specialist.
Prevention
In order to keep your cat’s eyes healthy, it is necessary to follow preventive measures:
- First of all, while walking, you need to avoid injury. If your pet has received minor wounds, it is necessary to treat them as quickly as possible.
- A small kitten needs daily rinsing; for this you can use plain boiled water or a herbal decoction.
- Timely vaccinations will help keep your cat healthy and protect him from infectious diseases and colds.
- Regular use of anthelmintic drugs will help avoid infection with parasites and prevent the occurrence of an allergic reaction to the products of their excretion.
- Scratching wounds located near the eyelids should not be allowed, as this can lead to suppuration of the eye. It is better to trim the hair growing near the organ of vision a little, especially for long-haired breeds.
In other words, this is caring care from the owner, timely preventive vaccinations, and regular medical examinations. If you promptly treat small wounds received while walking, you can avoid health problems, the symptoms of which may be purulent discharge from the eyes.
Diagnostics
First, the doctor examines the animal for injuries, collects information about its state of health, and finds out what chronic diseases it has. Next, to make a diagnosis, the veterinarian needs to conduct a number of diagnostic tests, including studying the frequency and consistency of discharge.
In some cases, it is necessary to conduct an ultrasound examination of the affected eye and x-ray of the skull.
What can you do before visiting a doctor?
If there is heavy discharge, do not put off going to the veterinarian. Before going to the veterinary clinic, you can relieve your pet's condition by rinsing the eyes yourself.
Until the causes of the disease are determined and adequate therapy is prescribed, the following should be used:
- weak solution of potassium permanganate,
- herbal infusion,
- decoction of tea leaves.
Any of the above products must be cooled to room temperature.
How to carry out the procedure:
- Calm the animal, secure the paws with a towel, wrap the entire body, and lay it on its side.
- Use a pipette or syringe without a needle to drip warm boiled water onto your eyes to soften dried discharge, and gently wipe your eyelids with a swab.
- Moisten 2 cosmetic discs generously in the solution, wipe each eye with a separate disc.
On a note! To avoid infection in a healthy organ of vision, you should take a new cotton pad after each wiping; repeated use is unacceptable.
During treatment, do not bring the syringe or pipette close to the eyes; the kitten may twitch, which will lead to mechanical injury. Processing is carried out from the outer corner towards the inner.
Treatment, prognosis
There is no single treatment for purulent eyes in a cat. The veterinarian develops an individual regimen depending on the disease, with the elimination of which the problem of purulent discharge will disappear.
Eye drops and ointments are required, which are divided into three groups:
- Antiseptic (bactericidal). The composition includes polysept, anesthesin and other components that help eliminate pain. The most effective are drugs such as Oftalmosan, Lakrikan.
- Antibacterial. Indicated for bacterial infections. Tsiprovet, Dekta-2, Lacrimin aseptic have proven themselves well. They relieve inflammation and successfully treat chronic diseases of the organs of vision.
- Immunomodulatory. Prescribed for inflammatory processes and viral infections. As a rule, the veterinarian prescribes Anandin and Maxidin. They strengthen the immune system, accelerate wound healing and suppress the activity of viruses.
The medicine and dosage are determined by the veterinarian. Before applying ointment or instilling drops, the eyes must be cleaned of pus and crusts using a special disinfectant solution.
Congenital anomalies are corrected surgically.
Rinse the cat's eyes: useful tips
If a kitten's eye is swollen and festering, rinsing should be done carefully, having first taken care of your safety. During the procedure, the pet will be nervous and struggle, so it should be well secured (or use the help of a second person who will hold the animal). The best option is to swaddle the cat with a towel or diaper so that only the head remains outside. Please also adhere to the following recommendations .
- Rinse each eye with solution from a separate container.
- Twist the cotton wool into a tight rope, dip it in a warm broth (medicinal solution), and squeeze it onto the animal’s festering eye.
- When the pet's eyes are completely cleared of purulent discharge, apply tetracycline ointment (1%) under the cat's eyelid. To do this, pull back the animal’s lower eyelid and, using a special spatula, place the composition on its inner surface. Then close your cat's eye completely and massage it lightly. This will help the product to be distributed evenly. To further enhance the effect of using the ointment, preheat the tube with it in your hands. But if the cat is very nervous, then you should not apply the ointment under the eyelid (this can lead to injury to the organ of vision).
© shutterstock
What to do at home
The owner must follow the veterinarian's instructions. Self-medication is dangerous and can make the situation worse.
You can wash your cat's eyes with chamomile decoction, boric acid solution, or furatsilin. The pet is unlikely to accept this manipulation with delight, so it is advisable to perform the procedure together: one person holds the cat, the second treats its eyes, and then instills the drug.
The solution used must be warm. Rinsing is carried out with a cotton pad, twisted into a tourniquet, until the pus from the eye is completely removed. Only after this the drug is used.
You cannot use a dry pad or cotton swabs, as they can injure your eyesight.
Types of discharge from the eyes
For a more accurate diagnosis, the owner needs to determine the nature of the discharge from the eyes: this will help distinguish dangerous eye diseases from less serious ones. The type of discharge will also help determine the involvement of pathogenic microflora in inflammatory phenomena.
The following types of discharge from a cat's eyes are distinguished:
| Type of discharge | Consistency | Possible reasons |
| Serous | Watery discharge of yellow, pink shades | The presence of an allergic reaction, including to chemicals or cigarette smoke or a viral infection |
| Mucous | Light viscous discharge without odor of protein structure | Chronic influence of various allergens, pathological conditions of the cornea, tear ducts |
| Purulent | Thick pus with a characteristic odor ranging from dark yellow to green | Bacterial, fungal infections |
Serous discharge may indicate the initial stage of development of pathologies of the visual organs. Often serous discharges turn into mucous discharges, and mucous discharges develop into mucopurulent discharges.
Basic recommendations
We've figured out what to do if a cat's eye is seriously festering. But you should not lose sight of the basic recommendations regarding treatment and prevention, aimed at reducing the likelihood of complications. And if complications have already begun, these recommendations will help you cope with them with minimal damage to your cat’s health:
- If more than three months have passed since the last deworming, it is time to repeat the procedure. If this does not help, you should go to the doctor.
- At home, you can help your pet by making lotions with chamomile infusion or green tea before instilling the medicine.
- Do not treat cats for pus in the eyes with medications intended for humans. There is a high probability that the drug will only worsen the situation to a critical state. Only a veterinarian can prescribe “human” medications.