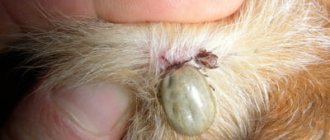
Removing a tick is not always easy. If you followed our step-by-step guide to removing a tick and your cat is left with a stuck tick head, you need to know what to do. It is always advisable to speak to your veterinarian, who may ask you to bring your cat into the practice for a check-up.
If the head or mouthparts remain after removing the tick, do not panic. You have killed the tick and removed its body, preventing a serious risk of disease transmission. But any residual parts can still lead to infection at the attachment site.
Find out what you need to do to get rid of stubborn ticks once and for all.
Causes of demodicosis
As mentioned above, the main reason for the development of this disease is the active reproduction of the iron mite. There are several possible reasons that can lead to increased activity of these opportunistic microorganisms. These are internal and external factors. The first category includes:
- A significant drop in immune defense and exhaustion of the body caused by poor nutrition, autoimmune pathologies, previous diseases, constant stress, etc.;
- Viral and microbial diseases that occur in chronic forms (hepatitis, tuberculosis, etc.);
- Helminthiases. The vital activity of helminths contributes to the weakening of the immune system;
- Malignant neoplasms. With many types of oncology, the body becomes exhausted, making it more difficult for it to cope with infections;
- Damage to the gastrointestinal tract. There is a proven relationship between the bacterium Helicobacter pylori and demodicosis;
- Other skin diseases. These are seborrheic dermatitis, rosacea, acne, etc. In the presence of inflammatory processes or integrity disorders on the skin, the risk of pathogenic activation of opportunistic flora increases significantly;
- Hormonal imbalance associated with illness or natural condition (for example, pregnancy or breastfeeding).
Skin demodicosis can also develop as a result of exposure to unfavorable external factors. As a rule, they are combined with internal ones, but in some cases (for example, choosing the wrong skincare products) they can be the main etiology. Among them:
- Temperature effect. This parasite multiplies especially actively in warm conditions;
- Unhealthy Lifestyle. This includes poor nutrition, frequent stress and bad habits;
- Use of low-quality cosmetics for care. This is especially true for cosmetics that do not have quality certificates and do not meet legal requirements;
- Poor environmental conditions. High levels of environmental pollution lead to a weakening of the barrier function of the skin.
If the tick's proboscis remains in the wound
Many people wonder what to do if the entire tick could not be removed. It depends on the size of the remaining part. Removing the head is quite simple if you use special methods. But the proboscis - a small thin appendage with which the tick sucks blood - is almost impossible to remove if it is the only thing left in the skin.
To avoid complications, after detecting a proboscis in the skin, you should immediately go to the doctor. Under no circumstances should you try to widen the wound, pick at it, comb it, or cut out a piece of fabric along with the proboscis. All this can lead to both bacterial infection and the spread of the viral pathogen from the remaining part of the parasite.
The best option, if the proboscis has not gone too deep and is located almost perpendicular to the skin, is to use a needle. This instrument must be made of stainless material, otherwise there is a risk of blood poisoning. The needle should be heated - this will remove pathogenic microorganisms. It is also advisable to treat it with alcohol. After this, the instrument is slowly inserted under the skin. They need to pry up the proboscis and carefully pull it out, if possible without widening the bite wound.
The proboscis often remains in the human body, but he does not notice it because the particle is too small. If you are sure that the proboscis is stuck in the skin, but you cannot see it, you can use a dampened piece of cloth. By thoroughly rubbing the wound with it (but without scratching), you can cause blood to drain from the affected area. The skin will lighten slightly and the foreign object will be easier to spot. If the proboscis is close enough to the epidermis, it can be removed with a needle. Otherwise, you urgently need to go to the first aid station.
If the proboscis cannot be removed, it is important to treat the wound with a soap solution before visiting the doctor, then dry it and apply iodine.
Comparison table: pros and cons of different protection methods
When choosing, take into account the effectiveness of the devices, as well as ease of use and comfort during operation. A comparison of the main methods for removing the pest is presented in table form.
| Name | Advantages | Flaws |
| Twister (TickTwister) | Efficient, easy to use | Experience required when performing the procedure |
| Lasso handle | Unusual design solution, ease of use, reliable fixation of the parasite | There is a risk of injury if you squeeze the tick too hard with a loop. In addition, it is not convenient to unscrew the parasite |
| Syringe | They note the low costs of purchasing it. In addition, the syringe acts faster, but there is a risk of getting a significant dose of parasite saliva under the skin | Doesn't always help remove ticks |
| Tweezers | Effective in removing ticks | There is a risk of damaging the parasite |
| Thread | Available method, easy to implement | Effective in 50% of cases, as it can damage the tick |
| ProTrick plate | Compact size, you can always carry it with you on a keychain | The tool is not easy to use - the pliers are not fixed securely |
| Pharmacy clip | Reliably holds ticks | There is a risk of damage to the parasite if you apply a little more effort |
What to do with a tick?
Experts advise taking the caught tick to a laboratory, where it will be tested for carrier infections. It is clear that this is not necessary, but it is advisable:
- firstly, it will help to establish the epizootic situation in a specific area;
- secondly, the owner will know what to do with his four-legged friend if the tick suddenly turns out to be infectious.
Before shipping, the insect is placed in a container with a tightly screwed lid, which will not allow it to escape.
If there is no desire or opportunity to take the parasite anywhere for research, then it is destroyed by burning! There is no need to release the prisoner so that he does not attach himself to someone else.
Diagnostics
Demodicosis on the face and skin is diagnosed by a dermatologist. If the disease is secondary and has developed against the background of the underlying disease, then doctors of other specialties (gastroenterologist, gynecologist, trichologist, endocrinologist, etc.) may be involved for diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. For diagnosis, first of all, visual inspection is used. The doctor evaluates the condition of the skin, eyes and affected areas of the body. In addition, eye biomicroscopy and laboratory examination methods are practiced. The most informative of them are:
- Slit lamp biomicroscopy of the eye is a non-invasive examination aimed at looking for active inflammation. This is an absolutely painless manipulation that does not require special preparation;
- Eyelash test - involves taking freshly removed eyelashes (4 from each eyelid) for further examination under a microscope. Using this method, it is possible to determine the number of parasites (the presence of more than 1 mite on 2-4 eyelashes is pathogenic). This is also a painless procedure, but before it is carried out it is necessary to abandon decorative and skincare cosmetics for several days;
- Biopsy. This is the most informative diagnostic method, but the most traumatic. Diagnosis is carried out under local anesthesia using a tubular knife or scalpel. The taken biomaterial is fixed in a formaldehyde solution for a day and treated with dyes. This makes it possible to fully visualize the gland and adjacent tissues with the pathogenic mite.
Prevention
The risk group includes cats (cats, kittens) walking freely on the street or in a summer cottage. You can protect them with the help of products that you can buy at the pharmacy or prepare yourself:
Sprays are the safest method of protection, but their effect is limited to a short period of time.
Drops: Products in liquid form are dripped onto the coat. They are absorbed into the skin and the protective effect can last for several months. But the composition of such drops is very toxic.
A collar is an excellent helper in protecting your pet. But you should only wear it when walking outside, as long-term contact with the skin can cause allergies.
Despite all the above measures, only constant attentive attitude towards your pet will save you from many unpleasant consequences.
Ticks are active in forests, parks, and meadows throughout the warm season. Owners of four-legged friends should know how to remove a tick from a cat and be able to get this parasite painlessly.
Pets kept indoors are also at risk. A person can bring ticks from the street on clothes and bags. Most often, parasites patiently lie in wait for their prey in the grass and thickets of bushes.
Application procedure
Aversect K&S is administered subcutaneously to animals in the nape, back or lumbar region; IM - into the gluteus medius muscle, quadriceps muscle, triceps brachii muscle at a dose of 0.2 ml of the active substance (aversectin C1) per 1 kg of animal weight, which corresponds to:
- for dogs of medium and large sizes
- 0.4 ml of 0.5% solution of Aversect K&S per 10 kg of animal weight; - for dogs weighing less than 10 kg and cats
- 0.1 ml of 0.2% Aversect K&S solution per 1 kg of animal weight.
For nematodes and entomoses
the drug is used once, for
sarcoptoidosis
- twice, for
demodicosis
- repeatedly until the animal recovers with an interval of 7-10 days.
The clinical recovery of the animal is confirmed by two negative results of acarological examinations of scrapings.
No specific effects of the drug upon its first use were identified.
If the next dose of Aversect K&S is missed, its use is resumed in the same dosage and according to the same regimen.
Treatment of animals with acarosis is recommended to be carried out comprehensively with the use of immunomodulatory antifungal and antimicrobial drugs.
Treatment
Treatment of demodicosis caused by subcutaneous mites is a long and difficult process. Its complexity is that often this disease develops against the background of a decrease in the body’s defenses and has accompanying skin problems. Therapy tactics include suppressing the parasite, treating underlying diseases and increasing immunity.
The most commonly used local therapy is lotions and special ointments. In more severe cases, the doctor prescribes a course of antibiotics in combination with external therapy. Sometimes plasmapheresis procedures are recommended. In special cases, even surgical intervention is possible.
An important point in the course of treatment is diet. It is necessary to exclude hot, spicy and salty foods, foods rich in carbohydrates and fats from the diet. Those who are being treated for subcutaneous mite infestation are recommended to consume large amounts of fruits, vegetables, microelements, fiber, and dairy products. During treatment, you should not use face masks, especially those containing honey. You need to limit your exposure to the sun. You should also wait until better times to visit the bathhouse and sauna.
Diseases of cats caused by subcutaneous mites
Notoedrosis (pruritic scabies) – Notoedrosis is a chronic invasive disease of cats, clinically accompanied by dermatitis in the scalp, itching, scratching and hair loss.
Etiology. The causative agent of Notoedrosis in cats is the sarcoptic mite Notoedrosis cati. Its morphology is somewhat similar to mites of the genus Sarcoptes. The body of sexually mature ticks is round in shape and dirty gray in color. It has a body length of 0.14-0.45 mm. The proboscis is horseshoe-shaped, the anus is located on the dorsal side, and in females there is also a copulatory opening. The legs of the tick are short, thick, and cone-shaped. Male ticks have bell-shaped suckers on conical rods (ambulacras) on the 4th pair of legs. In females, the 3rd and 4th pair of legs do not have bell-shaped suckers. Itches parasitize and multiply in passages that they gnaw in the deep parts of the stratum corneum of the skin, directly bordering the malpighian layer.
Developmental biology, epizootological data, pathogenesis, clinical picture, diagnosis, differential diagnosis, treatment and prevention are described in our article - Notoedrosis (pruritic scabies) in cats.
Feline demodicosis is a chronic parasitic skin disease in cats caused by the microscopic worm-like mite Demodex cati.
Etiology. The causative agent of demodicosis, being itself an endoparasite, is localized in the hair follicles and sebaceous glands. It is half a millimeter long and has a transparent body with poorly defined boundaries between the cephalothorax and abdomen. It has short legs with hooks at the ends. The oral apparatus is equipped with a gnawing type proboscis. When a cat is infected with demodicosis, the parasite first penetrates the skin. At the site where the tick gnaws through the skin, it leaves a pronounced concentric spot. Having penetrated the skin, mites begin to feed on skin cells, and the mites multiply intensively. For more information about demodicosis in cats, see our article – Demodicosis in cats.
Otodectosis or ear scabies is a chronic invasive disease of cats caused by parasitic otodectosis mites on the inner surface of the ears and in the external auditory canal.
For more information about the disease, see our article – Otodectosis in cats.
Conducting a tick inspection
Inspections of cats visiting the street during the warm season are carried out frequently - ideally every day. Although the parasite can attach itself to an absolutely domestic pet by getting into the house with the owner’s shoes or outerwear.
Examine the entire surface of the body from head to tail. Particular attention is paid to areas with delicate skin: neck, armpits and popliteal cavities, ears, muzzle and chin.
Video instructions on how to remove a tick from a cat:
Thank you for subscribing, check your inbox: you should receive an email asking you to confirm your subscription
A tick bite poses a danger not only to humans, but also to domestic cats. Parasites lie in wait not only in the forest. They can be found anywhere where tall grass grows: in a park, in a country house, and even in the city.
If you find a tick on a cat, you should remove it as soon as possible. It is better to go to the veterinarian, but this is not always possible. You can remove a tick from a cat at home, there is nothing complicated about it, just read the instructions and follow them step by step. The method of removing ticks from people and pets is not much different. The article describes the appearance of a tick to make it easier for you to distinguish it, and also provides advice on preventing the development of dangerous diseases in cats.
Special instructions and personal preventive measures
In order to prevent re-infestation by fleas, the animal's bedding is replaced or treated with an insecticidal agent in accordance with the instructions for use.
Aversect K&S should not be used in conjunction with avermectin-containing and other antiparasitic drugs for treating animals.
Personal prevention measures
When carrying out therapeutic and preventive measures using Aversect K&S, you should follow the rules of personal hygiene and safety precautions provided for when working with medications.
In case of accidental contact of the drug with the skin or mucous membranes, it must be washed off with a stream of running water, if ingested, give several glasses of warm water to drink, and if necessary, seek help from a medical facility (have the container label or instructions for use with you). There are no antidotes.
The use of empty drug bottles for household purposes is prohibited.
No special precautions are required when disposing of an unused or expired drug.
Symptoms of a tick bite
Symptoms of a tick bite in a cat may not appear immediately, but only after 2-3 weeks. Therefore, after a tick has been removed from a cat, cat owners should monitor its well-being for a given period. What should alert you:
- Refusal of the cat from the offered food, emaciation.
- Increased body temperature.
- The cat becomes lethargic and apathetic.
- Diarrhea (diarrhea in cats) and vomiting (vomiting in cats) appears, which causes dehydration in the cat.
- Shortness of breath, cough (cough in a cat).
- Anemia (anemia in cats).
- Blood in the urine (blood in the urine of a cat).
- Yellowness of visible mucous membranes (jaundice).
How to properly remove a tick from a cat
To properly remove a tick from a cat, use special tweezers. It is sold at any veterinary store. Take the tool, part the pet's fur, press the grip firmly against the skin and pry up the tick. Gently rotate the tool clockwise or counterclockwise. After you remove the parasite, treat the bite site with an antiseptic.
If you don’t have special tweezers at hand, take regular ones and place them horizontally. Important! Do not pull the tick upward. This way you can tear off the body of the parasite, but the head will remain under the skin and can cause suppuration. Did you get the tick? Treat the bite area.
You can also get rid of ticks with special insectoacaricidal drops, for example BlochNet max. The drug is dripped onto the bloodsucker and the site of its suction. After 20 minutes, the tick should fall off on its own.
What NOT to do if your cat has a tick's head stuck in it
There are various well-known home methods for removing ticks that do not require the use of a hook and are not recommended even if parts of the tick remain on your cat.
- Do not try to remove it yourself . If you think you can remove the tick's head or mouthparts yourself after a few tries with tweezers, stop now. This can make the situation worse and increase the risk of skin infection.
- Do not use petroleum jelly or nail polish remover . The idea that applying Vaseline or nail polish to a tick will help remove it is wrong. This will simply irritate your pet's skin further.
- Never burn a tick . Keep open flames away from your pet. Trying to attack the head of a tick embedded in the skin with a flame will not work. This will only result in you burning your poor cat.
© shutterstock
What then is possible?
To begin with, we should say what is needed - a dietary regimen during and after treatment. What about cosmetic procedures? Some of them are a real salvation in the fight against demodicosis. They help restore infected areas of the skin:
- cryotherapy - cold exposure, causing a sharp spasm of blood vessels followed by persistent dilation; result - peripheral blood supply is enhanced, skin nutrition is improved, metabolic processes are accelerated, the immune system is activated, and the skin's resistance to stress increases;
- mesotherapy - carried out during the period of remission, this is an injection procedure, the essence of which is the delivery of restorative substances contained in the preparations / cocktails to the tissues;
- plasma therapy - carried out during the period of remission, this is the introduction of purified and platelet-rich blood plasma of the patient into the affected areas of the skin; As a result, skin immunity is stimulated, and regeneration processes are launched at the cellular level.
Each of the procedures described above is prescribed in a course; to achieve a sustainable effect, on average, 5–6 procedures are required, which are carried out every 7 days.